End of support notice: On October 7th, 2026, AWS will discontinue support for AWS IoT Greengrass Version 1. After October 7th, 2026, you will no longer be able to access the AWS IoT Greengrass V1 resources. For more information, please visit Migrate from AWS IoT Greengrass Version 1.
Deploy AWS IoT Greengrass groups to an AWS IoT Greengrass core
Use AWS IoT Greengrass groups to organize entities in your edge environment. You also use groups to control how the entities in the group interact with each other and with the AWS Cloud. For example, only the Lambda functions in the group are deployed for running locally, and only the devices in the group can communicate using the local MQTT server.
A group must include a core, which is an AWS IoT device that runs the AWS IoT Greengrass Core software. The core acts as an edge gateway and provides AWS IoT Core capabilities in the edge environment. Depending on your business need, you can also add the following entities to a group:
-
Client devices. Represented as things in the AWS IoT registry. These devices must run FreeRTOS or use the AWS IoT Device SDK or AWS IoT Greengrass Discovery API to get connection information for the core. Only client devices that are members of the group can connect to the core.
Lambda functions. User-defined serverless applications that run code on the core. Lambda functions are authored in AWS Lambda and referenced from a Greengrass group. For more information, see Run Lambda functions on the AWS IoT Greengrass core.
Connectors. Predefined serverless applications that run code on the core. Connectors can provide built-in integration with local infrastructure, device protocols, AWS, and other cloud services. For more information, see Integrate with services and protocols using Greengrass connectors.
Subscriptions. Defines the publishers, subscribers, and MQTT topics (or subjects) that are authorized for MQTT communication.
Resources. References to local devices and volumes, machine learning models, and secrets, used for access control by Greengrass Lambda functions and connectors.
Logs. Logging configurations for AWS IoT Greengrass system components and Lambda functions. For more information, see Monitoring with AWS IoT Greengrass logs.
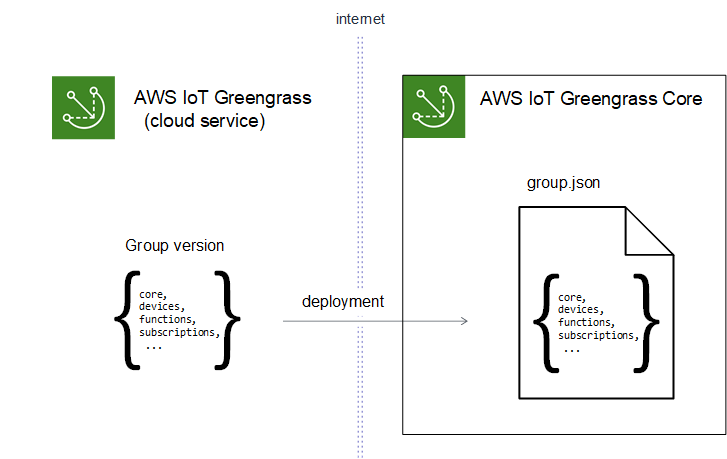
You manage your Greengrass group in the AWS Cloud and then deploy it to a core. The deployment copies the group configuration
to the group.json file on the core device. This file is located in greengrass-root/ggc/deployments/group
Note
During a deployment, the Greengrass daemon process on the core device stops and then restarts.
Deploying groups from the AWS IoT console
You can deploy a group and manage its deployments from the group's configuration page in the AWS IoT console.
Note
To open this page in the console, choose Greengrass devices , then Groups (V1), and then under Greengrass groups, choose your group.
- To deploy the current version of the group
-
-
From the group configuration page, choose Deploy.
-
- To view the deployment history of the group
-
A group's deployment history includes the date and time, group version, and status of each deployment attempt.
-
From the group configuration page, choose the Deployments tab.
-
To see more information about a deployment, including error messages, choose Deployments from the AWS IoT console, under Greengrass devices.
-
- To redeploy a group deployment
-
You might want to redeploy a deployment if the current deployment fails or revert to a different group version.
-
From the AWS IoT console, choose Greengrass devices, and then choose Groups (V1).
-
Choose the Deployments tab.
-
Choose the deployment you want to redeploy and choose Redeploy.
-
- To reset group deployments
-
You might want to reset group deployments to move or delete a group or to remove deployment information. For more information, see Reset deployments.
-
From the AWS IoT console, choose Greengrass devices, and then choose Groups (V1).
-
Choose the Deployments tab.
-
Choose the deployment you want to reset and choose Reset deployments.
-
Deploying groups with the AWS IoT Greengrass API
The AWS IoT Greengrass API provides the following actions to deploy AWS IoT Greengrass groups and manage group deployments. You can call these actions from the AWS CLI, AWS IoT Greengrass API, or AWS SDK.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
Creates a You might want to redeploy a deployment if the current deployment fails. Or you might want to redeploy to revert to a different group version. |
|
|
Returns the status of a deployment: You can configure Amazon EventBridge events to receive deployment notifications. For more information, see Get deployment notifications. |
|
Returns the deployment history for the group. |
|
|
Resets the deployments for the group. You might want to reset group deployments to move or delete a group or to remove deployment information. For more information, see Reset deployments. |
Note
For information about bulk deployment operations, see Create bulk deployments for groups.
Getting the group ID
The group ID is commonly used in API actions. You can use
the ListGroups action to find the ID of the target group from your list of groups.
For example, in the AWS CLI, use the list-groups command.
aws greengrass list-groups
You can also include the query option to filter results. For example:
To get the most recently created group:
aws greengrass list-groups --query "reverse(sort_by(Groups, &CreationTimestamp))[0]"-
To get a group by name:
aws greengrass list-groups --query "Groups[?Name=='MyGroup']"Group names are not required to be unique, so multiple groups might be returned.
The following is an example list-groups response. The information for each group includes the ID of the group (in the Id property)
and the ID of the most recent group version (in the LatestVersion property).
To get other version IDs for a group, use the group ID with ListGroupVersions.
Note
You can also find these values in the AWS IoT console. The group ID is displayed on the group's Settings page. Group version IDs are displayed on the group's Deployments tab.
{ "Groups": [ { "LatestVersionArn": "arn:aws:us-west-2:123456789012:/greengrass/groups/00dedaaa-ac16-484d-ad77-c3eedEXAMPLE/versions/4cbc3f07-fc5e-48c4-a50e-7d356EXAMPLE", "Name": "MyFirstGroup", "LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2019-11-11T05:47:31.435Z", "LatestVersion": "4cbc3f07-fc5e-48c4-a50e-7d356EXAMPLE", "CreationTimestamp": "2019-11-11T05:47:31.435Z", "Id": "00dedaaa-ac16-484d-ad77-c3eedEXAMPLE", "Arn": "arn:aws:us-west-2:123456789012:/greengrass/groups/00dedaaa-ac16-484d-ad77-c3eedEXAMPLE" }, { "LatestVersionArn": "arn:aws:us-west-2:123456789012:/greengrass/groups/036ceaf9-9319-4716-ba2a-237f9EXAMPLE/versions/8fe9e8ec-64d1-4647-b0b0-01dc8EXAMPLE", "Name": "GreenhouseSensors", "LastUpdatedTimestamp": "2020-01-07T19:58:36.774Z", "LatestVersion": "8fe9e8ec-64d1-4647-b0b0-01dc8EXAMPLE", "CreationTimestamp": "2020-01-07T19:58:36.774Z", "Id": "036ceaf9-9319-4716-ba2a-237f9EXAMPLE", "Arn": "arn:aws:us-west-2:123456789012:/greengrass/groups/036ceaf9-9319-4716-ba2a-237f9EXAMPLE" }, ... ] }
If you don't specify an AWS Region, AWS CLI commands use the default Region from your profile.
To return groups in a different Region, include the region option. For example:
aws greengrass list-groups --region us-east-1
Overview of the AWS IoT Greengrass group object model
When programming with the AWS IoT Greengrass API, it's helpful to understand the Greengrass group object model.
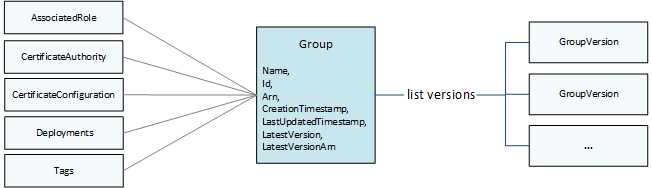
Groups
In the AWS IoT Greengrass API, the top-level Group object consists of metadata and a list of
GroupVersion objects. GroupVersion objects are associated with a
Group by ID.
Group versions
GroupVersion objects define group membership. Each GroupVersion references a
CoreDefinitionVersion and other component versions by ARN.
These references determine which entities to include in the group.
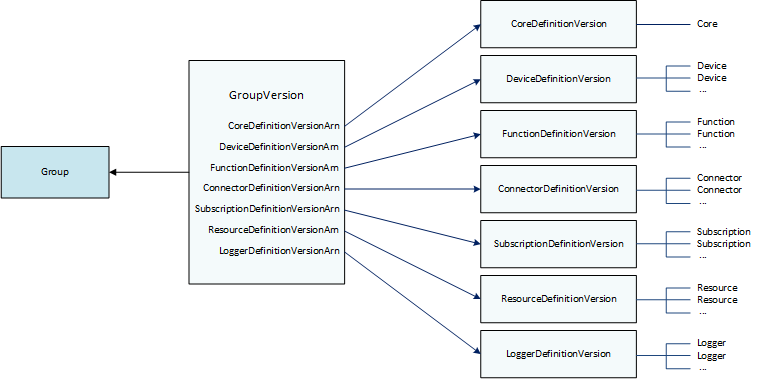
For example, to include three Lambda functions, one device, and two subscriptions in the group,
the GroupVersion references:
The
CoreDefinitionVersionthat contains the required core.The
FunctionDefinitionVersionthat contains the three functions.The
DeviceDefinitionVersionthat contains the client device.The
SubscriptionDefinitionVersionthat contains the two subscriptions.
The GroupVersion deployed to a core device determines the entities that are available
in the local environment and how they can interact.
Group components
Components that you add to groups have a three-level hierarchy:
A Definition that references a list of DefinitionVersion objects of a given type. For example, a
DeviceDefinitionreferences a list ofDeviceDefinitionVersionobjects.A DefinitionVersion that contains a set of entities of a given type. For example, a
DeviceDefinitionVersioncontains a list ofDeviceobjects.Individual entities that define their properties and behavior. For example, a
Devicedefines the ARN of the corresponding client device in the AWS IoT registry, the ARN of its device certificate, and whether its local shadow syncs automatically with the cloud.You can add the following types of entities to a group:
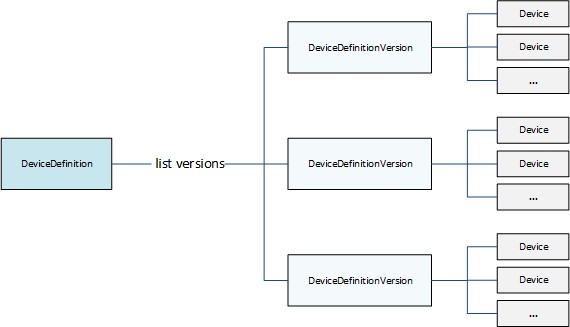
The following example DeviceDefinition references three DeviceDefinitionVersion objects
that each contain multiple Device objects. Only one DeviceDefinitionVersion at a time is used in a group.
Updating groups
In the AWS IoT Greengrass API, you use versions to update a group's configuration. Versions are immutable, so to add, remove, or change group components, you must create DefinitionVersion objects that contain new or updated entities.
You can associate new DefinitionVersions objects with new or
existing Definition objects. For example,
you can use the CreateFunctionDefinition action to create a FunctionDefinition
that includes the FunctionDefinitionVersion as an initial version,
or you can use the CreateFunctionDefinitionVersion action and reference an existing
FunctionDefinition.
After you create your group components, you create a GroupVersion that contains
all DefinitionVersion objects that you want to include in the group.
Then, you deploy the GroupVersion.
To deploy a GroupVersion, it must reference a CoreDefinitionVersion
that contains exactly one Core. All referenced entities must be members
of the group. Also, a Greengrass service role
must be associated with your AWS account in the AWS Region where you are deploying the GroupVersion.
Note
The Update actions in the API are used to change the name of a Group or
component Definition object.
Updating entities that reference AWS resources
Greengrass Lambda functions and secret resources define Greengrass-specific properties and also reference corresponding AWS resources. To update these entities, you might make changes to the corresponding AWS resource instead of your Greengrass objects. For example, Lambda functions reference a function in AWS Lambda and also define lifecycle and other properties that are specific to the Greengrass group.
To update Lambda function code or packaged dependencies, make your changes in AWS Lambda. During the next group deployment, these changes are retrieved from AWS Lambda and copied to your local environment.
To update Greengrass-specific properties, you create a
FunctionDefinitionVersionthat contains the updatedFunctionproperties.
Note
Greengrass Lambda functions can reference a Lambda function by alias ARN or version ARN. If you reference the alias ARN
(recommended), you don't need to update your FunctionDefinitionVersion (or
SubscriptionDefinitionVersion) when you publish a new function version in AWS Lambda.
For more information, see Reference Lambda functions by alias or version.
See also
-
AWS IoT Greengrass commands in the AWS CLI Command Reference