What is AWS Managed Services?
Welcome to AWS Managed Services (AMS), infrastructure operations management for Amazon Web Services (AWS). AMS is an enterprise service that provides ongoing management of your AWS infrastructure.
This user guide is intended for IT and application developer professionals. A basic understanding of IT functionality, networking, and application deployment terms and practices is assumed.
AMS implements best practices and maintains your infrastructure to reduce your operational overhead and risk. AMS provides full-lifecycle services to provision, run, and support your infrastructure, and automates common activities such as change requests, monitoring, patch management, security, and backup services. AMS enforces your corporate and security infrastructure policies, and enables you to develop solutions and applications using your preferred development approach.
To better understand AMS architecture, see
these diagrams
Topics
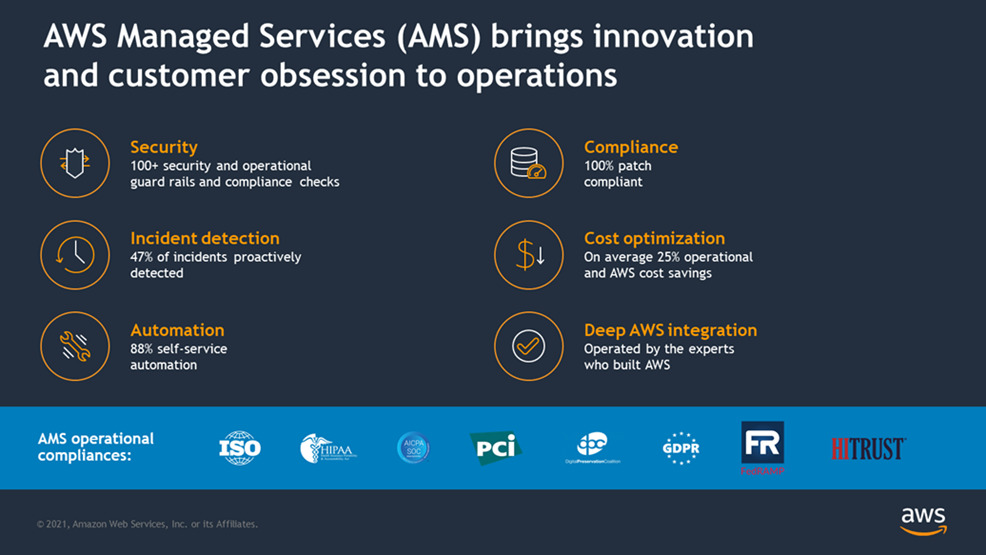
Note
New AWS Regions are added frequently. For the most recent AMS-supported AWS Regions, and the most recent AMS-supported operating systems, see Supported configurations.
To learn more about AWS Regions, see Managing AWS Regions.
AMS seeks to continuously improve our services based on your feedback. We use several mechanisms to enable your self-service, to automate repetitive tasks, and to implement new AWS services and features as they are released. You can submit an AMS service request at any time to suggest new features or feature improvements.
AMS business hours are 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year.
AMS follows a set of practices for IT service management (ITSM) that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of your business.
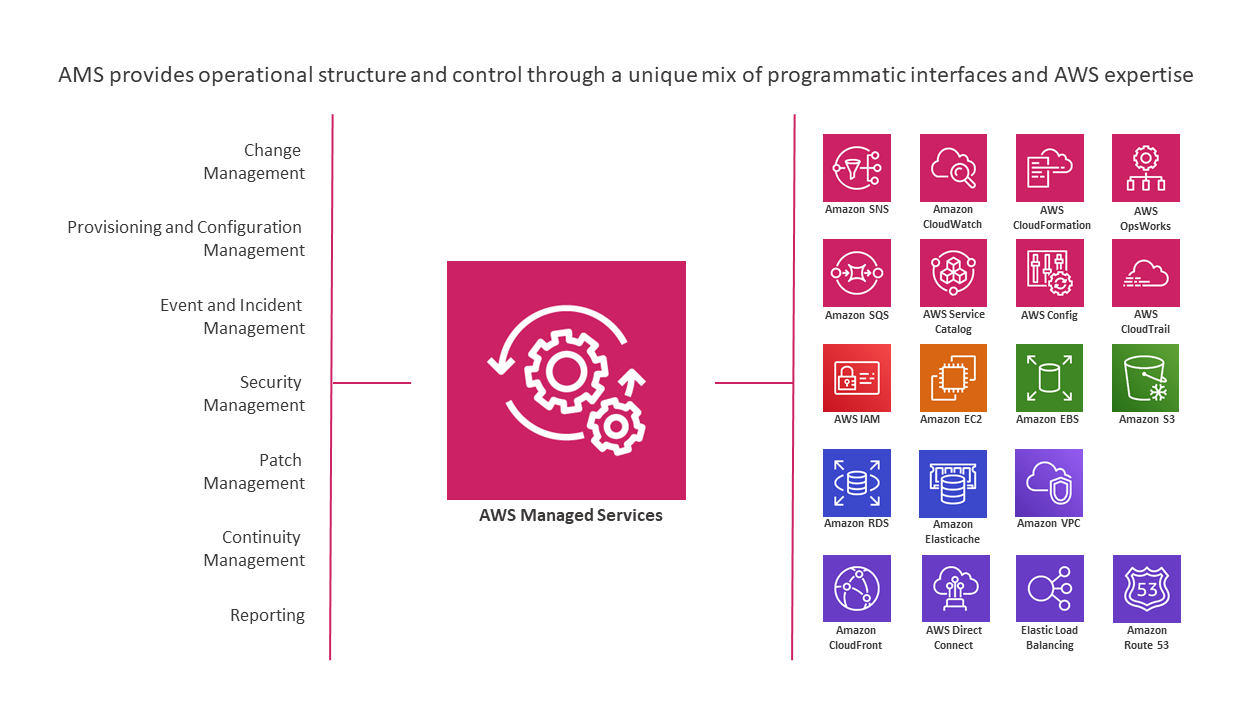
About this AMS user guide
This user guide is intended for AMS Advanced customers with either a multi-account or single-account landing zone. For more details about the AMS landing zone offerings, see the AMS Key Terms; also see Multi-Account Landing Zone architecture and Single-Account Landing Zone architecture.