Analyzing Aurora performance anomalies with Amazon DevOps Guru for Amazon RDS
Amazon DevOps Guru is a fully managed operations service that helps developers and operators improve the performance and availability of their applications. DevOps Guru offloads the tasks associated with identifying operational issues so that you can quickly implement recommendations to improve your application. For more information, see What is Amazon DevOps Guru? in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
DevOps Guru detects, analyzes, and makes recommendations for existing operational issues for all Amazon RDS DB engines. DevOps Guru for RDS extends this capability by applying machine learning to Performance Insights metrics for Amazon Aurora databases. These monitoring features allow DevOps Guru for RDS to detect and diagnose performance bottlenecks and recommend specific corrective actions. DevOps Guru for RDS can also detect problematic conditions in your Aurora databases before they occur.
You can now view these recommendations in RDS console. For more information, see Recommendations from Amazon Aurora.
Important
Amazon DevOps Guru isn't available for Aurora Serverless DB clusters.
The following video is an overview of DevOps Guru for RDS.
For a deep dive on this subject, see Amazon DevOps Guru for RDS under the hood.
Benefits of DevOps Guru for RDS
If you're responsible for an Amazon Aurora database, you might not know that an event or regression that is affecting that database is occurring. When you learn about the issue, you might not know why it's occurring or what to do about it. Rather than turning to a database administrator (DBA) for help or relying on third-party tools, you can follow recommendations from DevOps Guru for RDS.
You gain the following advantages from the detailed analysis of DevOps Guru for RDS:
- Fast diagnosis
-
DevOps Guru for RDS continuously monitors and analyzes database telemetry. Performance Insights, Enhanced Monitoring, and Amazon CloudWatch collect telemetry data for your database cluster. DevOps Guru for RDS uses statistical and machine learning techniques to mine this data and detect anomalies. To learn more about telemetry data, see Monitoring DB load with Performance Insights on Amazon Aurora and Monitoring OS metrics with Enhanced Monitoring in the Amazon Aurora User Guide .
- Fast resolution
-
Each anomaly identifies the performance issue and suggests avenues of investigation or corrective actions. For example, DevOps Guru for RDS might recommend that you investigate specific wait events. Or it might recommend that you tune your application pool settings to limit the number of database connections. Based on these recommendations, you can resolve performance issues more quickly than by troubleshooting manually.
- Proactive insights
-
DevOps Guru for RDS uses metrics from your resources to detect potentially problematic behavior before it becomes a bigger problem. For example, it can detect when your database is using an increasing number of on-disk temporary tables, which could start to impact performance. DevOps Guru then provides recommendations to help you address issues before they become bigger problems.
- Deep knowledge of Amazon engineers and machine learning
-
To detect performance issues and help you resolve bottlenecks, DevOps Guru for RDS relies on machine learning (ML) and advanced mathematical formulas. Amazon database engineers contributed to the development of the DevOps Guru for RDS findings, which encapsulate many years of managing hundreds of thousands of databases. By drawing on this collective knowledge, DevOps Guru for RDS can teach you best practices.
How DevOps Guru for RDS works
DevOps Guru for RDS collects data about your Aurora
databases from Amazon RDS Performance Insights. The most important metric is
DBLoad. DevOps Guru for RDS consumes the Performance Insights metrics, analyzes them with machine learning,
and publishes insights to the dashboard.
An insight is a collection of related anomalies that were detected by DevOps Guru.
In DevOps Guru for RDS, an anomaly is a pattern that deviates from what is considered normal performance for your Amazon Aurora database.
Proactive insights
A proactive insight lets you know about problematic behavior before it occurs. It contains anomalies with recommendations and related metrics to help you address issues in your Amazon Aurora databases before become bigger problems. These insights are published in the DevOps Guru dashboard.
For example, DevOps Guru might detect that your Aurora PostgreSQL database is creating many on-disk temporary tables. If not addressed, this trend might lead to performance issues. Each proactive insight includes recommendations for corrective behavior and links to relevant topics in either Tuning Aurora MySQL with Amazon DevOps Guru proactive insights or Tuning Aurora PostgreSQL with Amazon DevOps Guru proactive insights. For more information, see Working with insights in DevOps Guru in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
Reactive insights
A reactive insight identifies anomalous behavior as it occurs. If DevOps Guru for RDS finds performance issues in your Amazon Aurora DB instances, it publishes a reactive insight in the DevOps Guru dashboard. For more information, see Working with insights in DevOps Guru in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
Causal anomalies
A causal anomaly is a top-level anomaly within a reactive insight. Database load (DB load) is the causal anomaly for DevOps Guru for RDS.
An anomaly measures performance impact by assigning a severity level of High, Medium, or Low. To learn more, see Key concepts for DevOps Guru for RDS in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
If DevOps Guru detects a current anomaly on your DB instance, you're alerted in the Databases page of the RDS console. The console also alerts you to anomalies that occurred in the past 24 hours. To go to the anomaly page from the RDS console, choose the link in the alert message. The RDS console also alerts you in the page for your Amazon Aurora DB cluster .
Contextual anomalies
A contextual anomaly is a finding within Database load (DB load) that is related to a reactive insight. Each contextual anomaly describes a specific Amazon Aurora performance issue that requires investigation. For example, DevOps Guru for RDS might recommend that you consider increasing CPU capacity or investigate wait events that are contributing to DB load.
Important
We recommend that you test any changes on a test instance before modifying a production instance. In this way, you understand the impact of the change.
To learn more, see Analyzing anomalies in Amazon RDS in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
Setting up DevOps Guru for RDS
To allow DevOps Guru for Amazon RDS to publish insights for an Amazon Aurora database, complete the following tasks.
Topics
Configuring IAM access policies for DevOps Guru for RDS
To view alerts from DevOps Guru in the RDS console, your AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) user or role must have either of the following policies:
-
The AWS managed policy
AmazonDevOpsGuruConsoleFullAccess -
The AWS managed policy
AmazonDevOpsGuruConsoleReadOnlyAccessand either of the following policies:-
The AWS managed policy
AmazonRDSFullAccess -
A customer managed policy that includes
pi:GetResourceMetricsandpi:DescribeDimensionKeys
-
For more information, see Configuring access policies for Performance Insights.
Turning on Performance Insights for your Aurora DB instances
DevOps Guru for RDS relies on Performance Insights for its data. Without Performance Insights, DevOps Guru publishes anomalies, but doesn't include the detailed analysis and recommendations.
When you create an Aurora DB cluster or modify a cluster instance, you can turn on Performance Insights. For more information, see Turning Performance Insights on and off for Aurora.
Turning on DevOps Guru and specifying resource coverage
You can turn on DevOps Guru to have it monitor your Amazon Aurora databases in either of the following ways.
Topics
Turning on DevOps Guru in the RDS console
You can take multiple paths in the Amazon RDS console to turn on DevOps Guru.
Topics
Turning on DevOps Guru when you create an Aurora database
The creation workflow includes a setting that turns on DevOps Guru coverage for your database. This setting is turned on by default when you choose the Production template.
To turn on DevOps Guru when you create an Aurora database
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
Follow the steps in Creating a DB cluster, up to but not including the step where you choose monitoring settings.
-
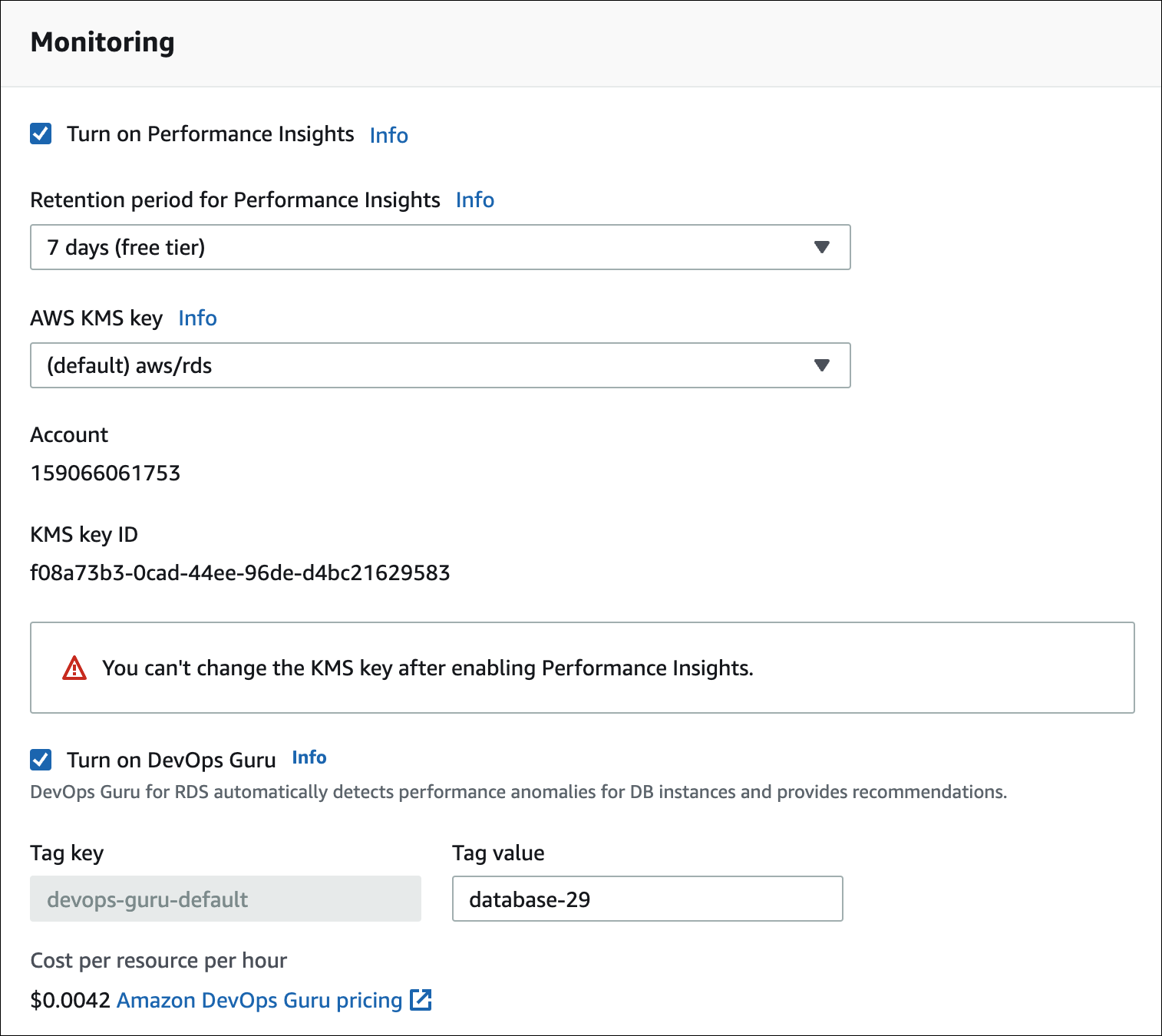
In Monitoring, choose Turn on Performance Insights. For DevOps Guru for RDS to provide detailed analysis of performance anomalies, Performance Insights must be turned on.
-
Choose Turn on DevOps Guru.
-
Create a tag for your database so that DevOps Guru can monitor it. Do the following:
-
In the text field for Tag key, enter a name that begins with
Devops-Guru-. -
In the text field for Tag value, enter any value. For example, if you enter
rds-database-1for the name of your Aurora database, you can also enterrds-database-1as the tag value.
For more information about tags, see "Use tags to identify resources in your DevOps Guru applications" in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
-
-
Complete the remaining steps in Creating a DB cluster.
Turning on DevOps Guru from the notification banner
If your resources aren't covered by DevOps Guru, Amazon RDS notifies you with a banner in the following locations:
-
The Monitoring tab of a DB cluster instance
-
The Performance Insights dashboard

To turn on DevOps Guru for your Aurora database
-
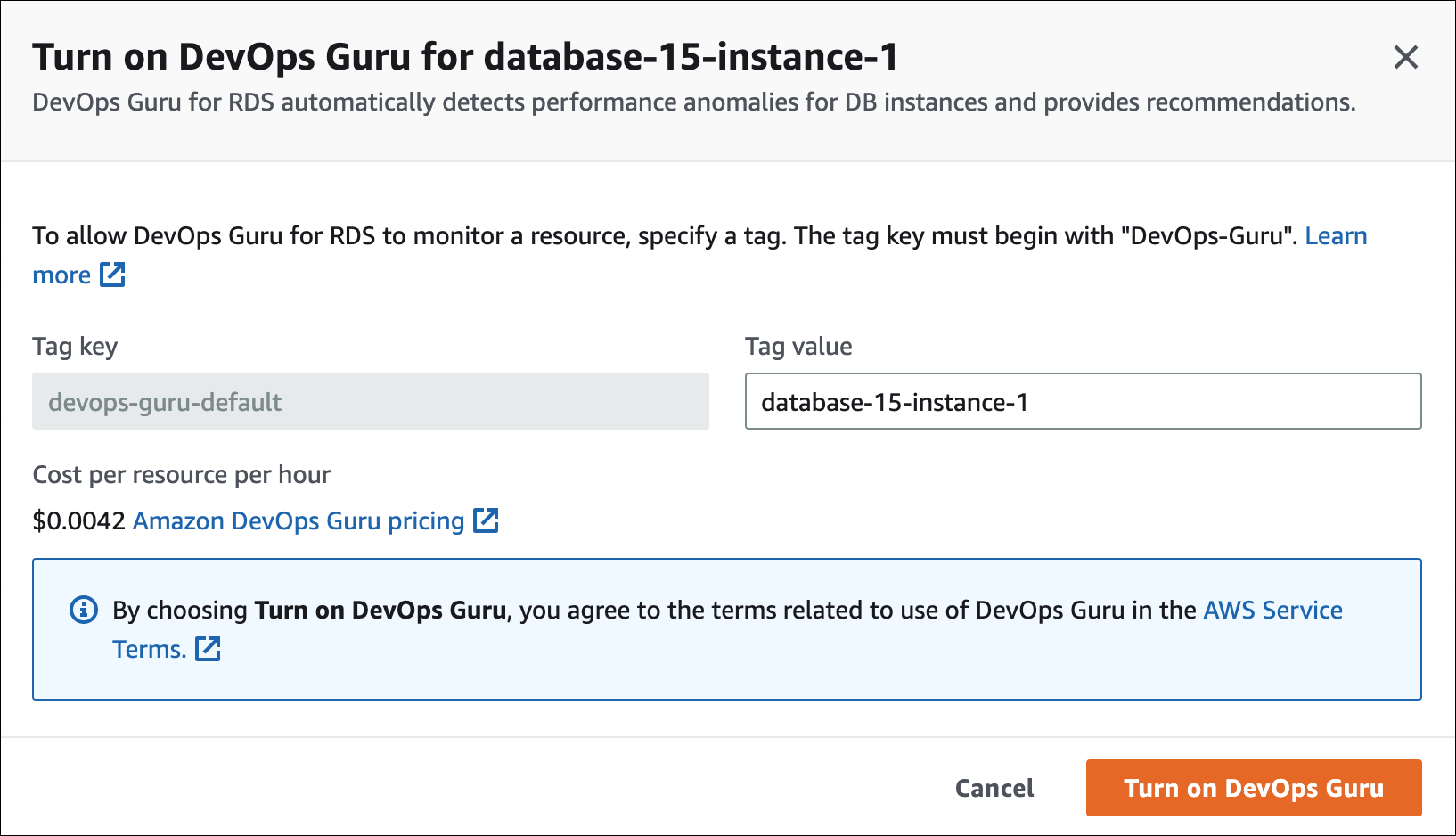
In the banner, choose Turn on DevOps Guru for RDS.
-
Enter a tag key name and value. For more information about tags, see "Use tags to identify resources in your DevOps Guru applications" in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
-
Choose Turn on DevOps Guru.
Responding to a permissions error when you turn on DevOps Guru
If you turn on DevOps Guru from the RDS console when you create a database, RDS might display the following banner about missing permissions.

To respond to a permissions error
-
Grant your IAM user or role the user managed role
AmazonDevOpsGuruConsoleFullAccess. For more information, see Configuring IAM access policies for DevOps Guru for RDS. -
Open the RDS console.
-
In the navigation pane, choose Performance Insights.
-
Choose a DB instance in the cluster that you just created.
-
Choose the switch to turn on DevOps Guru for RDS.

-
Choose a tag value. For more information, see "Use tags to identify resources in your DevOps Guru applications" in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.

-
Choose Turn on DevOps Guru.
Adding Aurora resources in the DevOps Guru console
You can specify your DevOps Guru resource coverage on the DevOps Guru console. Follow the step described in Specify your DevOps Guru resource coverage in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide. When you edit your analyzed resources, choose one of the following options:
-
Choose All account resources to analyze all supported resources, including the Aurora databases, in your AWS account and Region.
-
Choose CloudFormation stacks to analyze the Aurora databases that are in stacks you choose. For more information, see Use AWS CloudFormation stacks to identify resources in your DevOps Guru applications in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
-
Choose Tags to analyze the Aurora databases that you have tagged. For more information, see Use tags to identify resources in your DevOps Guru applications in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
For more information, see Enable DevOps Guru in the Amazon DevOps Guru User Guide.
Adding Aurora resources using AWS CloudFormation
You can use tags to add coverage for your Aurora resources to your CloudFormation templates. The following procedure assumes that you have a CloudFormation template both for your Aurora DB instance and DevOps Guru stack.
To specify an Aurora DB instance using a CloudFormation tag
-
In the CloudFormation template for your DB instance, define a tag using a key/value pair.
The following example assigns the value
my-aurora-db-instance1toDevops-guru-cfn-defaultfor an Aurora DB instance.MyAuroraDBInstance1: Type: "AWS::RDS::DBInstance" Properties: DBClusterIdentifier: my-aurora-db-cluster DBInstanceIdentifier: my-aurora-db-instance1 Tags: - Key: Devops-guru-cfn-default Value: devopsguru-my-aurora-db-instance1 -
In the CloudFormation template for your DevOps Guru stack, specify the same tag in your resource collection filter.
The following example configures DevOps Guru to provide coverage for the resource with the tag value
my-aurora-db-instance1.DevOpsGuruResourceCollection: Type: AWS::DevOpsGuru::ResourceCollection Properties: ResourceCollectionFilter: Tags: - AppBoundaryKey: "Devops-guru-cfn-default" TagValues: - "devopsguru-my-aurora-db-instance1"The following example provides coverage for all resources within the application boundary
Devops-guru-cfn-default.DevOpsGuruResourceCollection: Type: AWS::DevOpsGuru::ResourceCollection Properties: ResourceCollectionFilter: Tags: - AppBoundaryKey: "Devops-guru-cfn-default" TagValues: - "*"
For more information, see AWS::DevOpsGuru::ResourceCollection and AWS::RDS::DBInstance in the AWS CloudFormation User Guide.