Deploy a React-based single-page application to Amazon S3 and CloudFront
Jean-Baptiste Guillois, Amazon Web Services
Summary
A single-page application (SPA) is a website or web application that dynamically updates the contents of a displayed webpage by using JavaScript APIs. This approach enhances the user experience and performance of a website because it updates only new data instead of reloading the entire webpage from the server.
This pattern provides a step-by-step approach to coding and hosting an SPA that’s written in React on Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and Amazon CloudFront. The SPA in this pattern uses a REST API that’s configured in Amazon API Gateway and exposed through an Amazon CloudFront distribution to simplify cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) management.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
An active AWS account.
Node.js and
npm, installed and configured. For more information, see the Downloadssection of the Node.js documentation. Yarn, installed and configured. For more information, see the Yarn documentation
. Git, installed and configured. For more information, see the Git documentation
.
Architecture
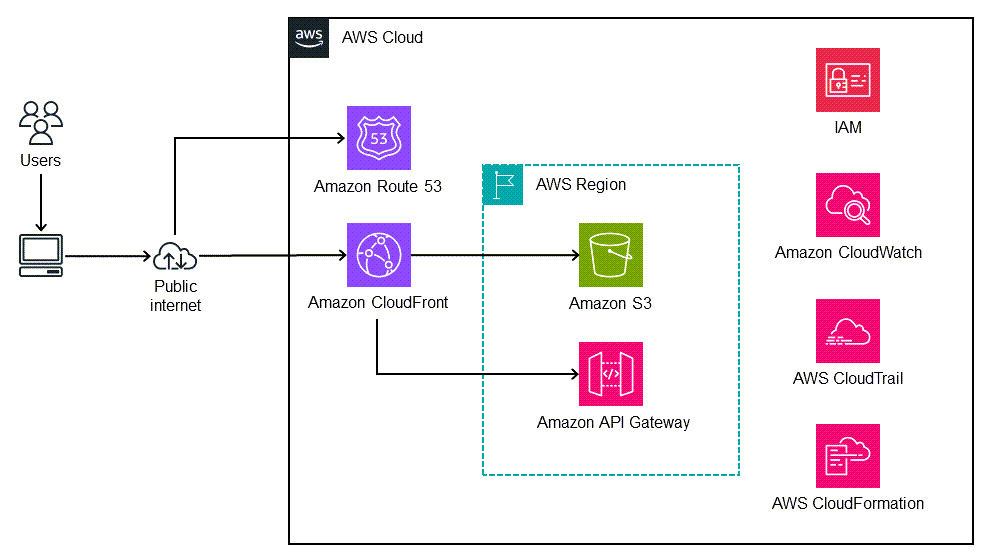
This architecture is automatically deployed by using AWS CloudFormation (infrastructure as code). It uses Regional services such as Amazon S3 to store the static assets and Amazon CloudFront with Amazon API Gateway to expose Regional API (REST) endpoints. The application logs are collected by using Amazon CloudWatch. All AWS API calls are audited in AWS CloudTrail. All security configuration (for example, identities and permissions) is managed in AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). Static content is delivered through the Amazon CloudFront content delivery network (CDN), and DNS queries are handled by Amazon Route 53.
Tools
AWS services
Amazon API Gateway helps you create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure REST, HTTP, and WebSocket APIs at any scale.
AWS CloudFormation helps you set up AWS resources, provision them quickly and consistently, and manage them throughout their lifecycle across AWS accounts and Regions.
Amazon CloudFront speeds up distribution of your web content by delivering it through a worldwide network of data centers, which lowers latency and improves performance.
AWS CloudTrail helps you audit the governance, compliance, and operational risk of your AWS account.
Amazon CloudWatch helps you monitor the metrics of your AWS resources and the applications you run on AWS in real time.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) helps you securely manage access to your AWS resources by controlling who is authenticated and authorized to use them.
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable DNS web service.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is a cloud-based object storage service that helps you store, protect, and retrieve any amount of data.
Code
This pattern's sample application code is available in the GitHub React-based CORS single-page application
Best practices
By using Amazon S3 object storage, you can store your application’s static assets in a secure, highly resilient, performant, and cost-effective way. There is no need to use a dedicated container or an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance for this task.
By using the Amazon CloudFront content delivery network, you can reduce the latency your users might experience when they access your application. You can also attach a web application firewall (AWS WAF) to protect your assets from malicious attacks.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Clone the repository. | Run the following command to clone the sample application's repository:
| App developer, AWS DevOps |
Locally deploy the application. |
| App developer, AWS DevOps |
Locally access the application. | Open a browser window and enter the | App developer, AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Deploy the AWS CloudFormation template. |
| App developer, AWS DevOps |
Customize your application source files. |
| App developer |
Build the application package. | In your project directory, run the | App developer |
Deploy the application package. |
| App developer, AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Access and test the application. | Open a browser window, and then paste the CloudFront distribution domain (the | App developer, AWS DevOps |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Delete the S3 bucket contents. |
| AWS DevOps, App developer |
Delete the AWS CloudFormation stack. |
| AWS DevOps, App developer |
Related resources
To deploy and host your web application, you can also use AWS Amplify Hosting, which provides a Git-based workflow for hosting full-stack, serverless web apps with continuous deployment. Amplify Hosting is part of AWS Amplify, which provides a set of purpose-built tools and features that enable frontend web and mobile developers to quickly and easily build full-stack applications on AWS.
Additional information
To handle invalid URLs requested by the user that might generate 403 errors, a custom error page that’s configured in the CloudFront distribution catches 403 errors and redirects them to the application entry point (index.html).
To simplify the management of CORS, the REST API is exposed through a CloudFront distribution.