Implement SaaS tenant isolation for Amazon S3 by using an AWS Lambda token vending machine
Tabby Ward, Thomas Davis, and Sravan Periyathambi, Amazon Web Services
Summary
Multitenant SaaS applications must implement systems to ensure that tenant isolation is maintained. When you store tenant data on the same AWS resource—such as when multiple tenants store data in the same Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket—you must ensure that cross-tenant access cannot occur. Token vending machines (TVMs) are one way to provide tenant data isolation. These machines provide a mechanism for obtaining tokens while abstracting the complexity of how these tokens are generated. Developers can use a TVM without having detailed knowledge of how it produces tokens.
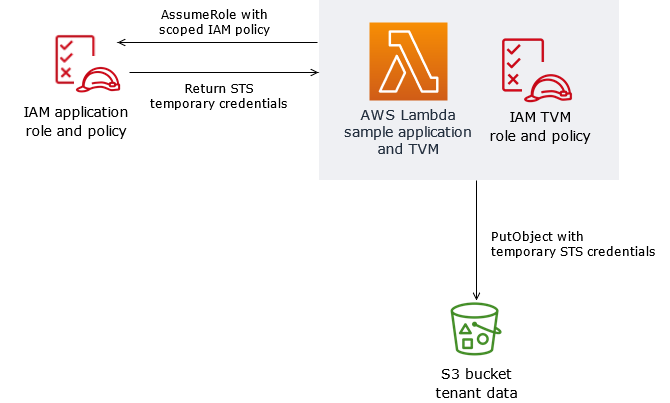
This pattern implements a TVM by using AWS Lambda. The TVM generates a token that consists of temporary security token service (STS) credentials that limit access to a single SaaS tenant's data in an S3 bucket.
TVMs, and the code that’s provided with this pattern, are typically used with claims that are derived from JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) to associate requests for AWS resources with a tenant-scoped AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policy. You can use the code in this pattern as a basis to implement a SaaS application that generates scoped, temporary STS credentials based on the claims provided in a JWT token.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
Limitations
This code runs in Java and doesn’t currently support other programming languages.
The sample application doesn’t include AWS cross-Region or disaster recovery (DR) support.
This pattern demonstrates how a Lambda TVM for a SaaS application can provide scoped tenant access. This pattern is not intended to be used in production environments without additional security testing as a part of your specific application or use case.
Architecture
Target technology stack
Target architecture
AWS services
Code
The source code for this pattern is available as an attachment and includes the following files:
s3UploadSample.jar provides the source code for a Lambda function that uploads a JSON document to an S3 bucket.
tvm-layer.zip provides a reusable Java library that supplies a token (STS temporary credentials) for the Lambda function to access the S3 bucket and upload the JSON document.
token-vending-machine-sample-app.zip provides the source code used to create these artifacts and compilation instructions.
To use these files, follow the instructions in the next section.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|
Determine variable values. | The implementation of this pattern includes several variable names that must be used consistently. Determine the values that should be used for each variable, and provide that value when requested in subsequent steps. <AWS Account ID> ─ The 12-digit account ID that is associated with the AWS account you are implementing this pattern in. For information about how to find your AWS account ID, see Using an alias for your AWS account ID in the IAM documentation.
<AWS Region> ─ The AWS Region that you are implementing this pattern in. For more information on AWS Regions, see Regions and Availability Zones on the AWS website.
<sample-tenant-name> ─ The name of a tenant to use in the application. We recommend that you use only alphanumeric characters in this value for simplicity, but you can use any valid name for an S3 object key.
<sample-tvm-role-name> ─ The name of the IAM role attached to the Lambda function that runs the TVM and sample application. The role name is a string that consists of uppercase and lowercase alphanumeric characters with no spaces. You can also include any of the following characters: underscore (_), plus sign (+), equal sign (=), comma (,), period (.), at sign (@), and hyphen (-). The role name must be unique within the account.
<sample-app-role-name> ─ The name of the IAM role that is assumed by the Lambda function when it generates scoped, temporary STS credentials. The role name is a string that consists of uppercase and lowercase alphanumeric characters with no spaces. You can also include any of the following characters: underscore (_), plus sign (+), equal sign (=), comma (,), period (.), at sign (@), and hyphen (-). The role name must be unique within the account.
<sample-app-function-name> ─ The name of the Lambda function. This is a string that’s up to 64 characters in length.
<sample-app-bucket-name> ─ The name of an S3 bucket that must be accessed with permissions that are scoped to a specific tenant. S3 bucket names:
Must be between 3 and 63 characters long. Must consist of only lowercase letters, numbers, periods (.), and hyphens (-). Must begin and end with a letter or number. Must not be formatted as an IP address (for example, 192.168.5.4). Must be unique within a partition. A partition is a grouping of Regions. AWS currently has three partitions: aws for Standard Regions, aws-cn for China Regions, and aws-us-gov for AWS GovCloud (US) Regions.
| Cloud administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|
Create an S3 bucket for the sample application. | Use the following AWS CLI command to create an S3 bucket. Provide the <sample-app-bucket-name> value in the code snippet: aws s3api create-bucket --bucket <sample-app-bucket-name>
The Lambda sample application uploads JSON files to this bucket. | Cloud administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|
Create a TVM role. | Use one of the following AWS CLI commands to create an IAM role. Provide the <sample-tvm-role-name> value in the command. For macOS or Linux shells: aws iam create-role \
--role-name <sample-tvm-role-name> \
--assume-role-policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole"
],
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"lambda.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:SourceAccount": "<AWS Account ID>"
}
}
}
]
}'
For the Windows command line: aws iam create-role ^
--role-name <sample-tvm-role-name> ^
--assume-role-policy-document "{\"Version\": \"2012-10-17\", \"Statement\": [{\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Action\": [\"sts:AssumeRole\"], \"Principal\": {\"Service\": [\"lambda.amazonaws.com\"]}, \"Condition\": {\"StringEquals\": {\"aws:SourceAccount\": \"<AWS Account ID>\"}}}]}"
The Lambda sample application assumes this role when the application is invoked. The capability to assume the application role with a scoped policy gives the code broader permissions to access the S3 bucket. | Cloud administrator |
Create an inline TVM role policy. | Use one of the following AWS CLI commands to create an IAM policy. Provide the <sample-tvm-role-name>, <AWS Account ID>, and <sample-app-role-name> values in the command. For macOS or Linux shells: aws iam put-role-policy \
--role-name <sample-tvm-role-name> \
--policy-name assume-app-role \
--policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-app-role-name>"
}
]}'
For the Windows command line: aws iam put-role-policy ^
--role-name <sample-tvm-role-name> ^
--policy-name assume-app-role ^
--policy-document "{\"Version\": \"2012-10-17\", \"Statement\": [{\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\", \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-app-role-name>\"}]}"
This policy is attached to the TVM role. It gives the code the capability to assume the application role, which has broader permissions to access the S3 bucket. | Cloud administrator |
Attach the managed Lambda policy. | Use the following AWS CLI command to attach the AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole IAM policy. Provide the <sample-tvm-role-name> value in the command: aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name <sample-tvm-role-name> \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
For the Windows command line: aws iam attach-role-policy ^
--role-name <sample-tvm-role-name> ^
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
This managed policy is attached to the TVM role to permit Lambda to send logs to Amazon CloudWatch. | Cloud administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|
Create the application role. | Use one of the following AWS CLI commands to create an IAM role. Provide the <sample-app-role-name>, <AWS Account ID>, and <sample-tvm-role-name> values in the command. For macOS or Linux shells: aws iam create-role \
--role-name <sample-app-role-name> \
--assume-role-policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect":
"Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-tvm-role-name>"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]}'
For the Windows command line: aws iam create-role ^
--role-name <sample-app-role-name> ^
--assume-role-policy-document "{\"Version\": \"2012-10-17\", \"Statement\": [{\"Effect\": \"Allow\",\"Principal\": {\"AWS\": \"arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-tvm-role-name>\"},\"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\"}]}"
The Lambda sample application assumes this role with a scoped policy to get tenant-based access to an S3 bucket. | Cloud administrator |
Create an inline application role policy. | Use one of the following AWS CLI mmands to create an IAM policy. Provide the <sample-app-role-name> and <sample-app-bucket-name> values in the command. For macOS or Linux shells: aws iam put-role-policy \
--role-name <sample-app-role-name> \
--policy-name s3-bucket-access \
--policy-document '{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:DeleteObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<sample-app-bucket-name>/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["s3:ListBucket"],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<sample-app-bucket-name>"
}
]}'
For the Windows command line: aws iam put-role-policy ^
--role-name <sample-app-role-name> ^
--policy-name s3-bucket-access ^
--policy-document "{\"Version\": \"2012-10-17\", \"Statement\": [{\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Action\": [\"s3:PutObject\", \"s3:GetObject\", \"s3:DeleteObject\"], \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:s3:::<sample-app-bucket-name>/*\"}, {\"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Action\": [\"s3:ListBucket\"], \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:s3:::<sample-app-bucket-name>\"}]}"
This policy is attached to the application role. It provides broad access to objects in the S3 bucket. When the sample application assumes the role, these permissions are scoped to a specific tenant with the TVM's dynamically generated policy. | Cloud administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|
Download the compiled source files. | Download the s3UploadSample.jar and tvm-layer.zip files, which are included as attachments. The source code used to create these artifacts and compilation instuctions are provided in token-vending-machine-sample-app.zip. | Cloud administrator |
Create the Lambda layer. | Use the following AWS CLI command to create a Lambda layer, which makes the TVM accessible to Lambda. If you aren’t running this command from the location where you downloaded tvm-layer.zip, provide the correct path to tvm-layer.zip in the --zip-file parameter. aws lambda publish-layer-version \
--layer-name sample-token-vending-machine \
--compatible-runtimes java11 \
--zip-file fileb://tvm-layer.zip
For the Windows command line: aws lambda publish-layer-version ^
--layer-name sample-token-vending-machine ^
--compatible-runtimes java11 ^
--zip-file fileb://tvm-layer.zip
This command creates a Lambda layer that contains the reusable TVM library. | Cloud administrator, App developer |
Create the Lambda function. | Use the following AWS CLI command to create a Lambda function. Provide the <sample-app-function-name>, <AWS Account ID>, <AWS Region>, <sample-tvm-role-name>, <sample-app-bucket-name>, and <sample-app-role-name> values in the command. If you aren’t running this command from the location where you downloaded s3UploadSample.jar, provide the correct path to s3UploadSample.jar in the --zip-file parameter. aws lambda create-function \
--function-name <sample-app-function-name> \
--timeout 30 \
--memory-size 256 \
--runtime java11 \
--role arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-tvm-role-name> \
--handler com.amazon.aws.s3UploadSample.App \
--zip-file fileb://s3UploadSample.jar \
--layers arn:aws:lambda:<AWS Region>:<AWS Account ID>:layer:sample-token-vending-machine:1 \
--environment "Variables={S3_BUCKET=<sample-app-bucket-name>,
ROLE=arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-app-role-name>}"
For the Windows command line: aws lambda create-function ^
--function-name <sample-app-function-name> ^
--timeout 30 ^
--memory-size 256 ^
--runtime java11 ^
--role arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-tvm-role-name> ^
--handler com.amazon.aws.s3UploadSample.App ^
--zip-file fileb://s3UploadSample.jar ^
--layers arn:aws:lambda:<AWS Region>:<AWS Account ID>:layer:sample-token-vending-machine:1 ^
--environment "Variables={S3_BUCKET=<sample-app-bucket-name>,ROLE=arn:aws:iam::<AWS Account ID>:role/<sample-app-role-name>}"
This command creates a Lambda function with the sample application code and the TVM layer attached. It also sets two environment variables: S3_BUCKET and ROLE. The sample application uses these variables to determine the role to assume and the S3 bucket to upload JSON documents to. | Cloud administrator, App developer |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|
Invoke the Lambda sample application. | Use one of the following AWS CLI commands to start the Lambda sample application with its expected payload. Provide the <sample-app-function-name> and <sample-tenant-name> values in the command. For macOS and Linux shells: aws lambda invoke \
--function <sample-app-function-name> \
--invocation-type RequestResponse \
--payload '{"tenant": "<sample-tenant-name>"}' \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out response.json
For the Windows command line: aws lambda invoke ^
--function <sample-app-function-name> ^
--invocation-type RequestResponse ^
--payload "{\"tenant\": \"<sample-tenant-name>\"}" ^
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out response.json
This command calls the Lambda function and returns the result in a response.json document. On many Unix-based systems, you can change response.json to /dev/stdout to output the results directly to your shell without creating another file. Changing the <sample-tenant-name> value in subsequent invocations of this Lambda function alters the location of the JSON document and the permissions the token provides. | Cloud administrator, App developer |
View the S3 bucket to see created objects. | Browse to the S3 bucket ( <sample-app-bucket-name>) that you created earlier. This bucket contains an S3 object prefix with the value of <sample-tenant-name>. Under that prefix, you will find a JSON document named with a UUID. Invoking the sample application multiple times adds more JSON documents. | Cloud administrator |
View the logs for the sample application in CloudWatch Logs. | View the logs that are associated with the Lambda function named <sample-app-function-name> in CloudWatch Logs. For instructions, see Sending Lambda function logs to CloudWatch Logs in the Lambda documentation. You can view the tenant-scoped policy generated by the TVM in these logs. This tenant-scoped policy gives permissions for the sample application to the Amazon S3 PutObject, GetObject, DeleteObject, and ListBucket APIs, but only for the object prefix that’s associated with <sample-tenant-name>. In subsequent invocations of the sample application, if you change <sample-tenant-name>, the TVM updates the scoped policy to correspond to the tenant provided in the invocation payload. This dynamically generated policy shows how tenant-scoped access can be maintained with a TVM in SaaS applications. The TVM functionality is provided in a Lambda layer so that it can be attached to other Lambda functions used by an application without having to replicate the code. For an illustration of the dynamically generated policy, see the Additional information section. | Cloud administrator |
Related resources
Additional information
The following log shows the dynamically generated policy produced by the TVM code in this pattern. In this screenshot, the <sample-app-bucket-name> is DOC-EXAMPLE-BUCKET and the <sample-tenant-name> is test-tenant-1. The STS credentials returned by this scoped policy are unable to perform any actions on objects in the S3 bucket except for objects that are associated with the object key prefix test-tenant-1.
Attachments
To access additional content that is associated with this document, unzip the following file: attachment.zip