Migrate an ELK Stack to Elastic Cloud on AWS
Battulga Purevragchaa and Antony Prasad Thevaraj, Amazon Web Services
uday reddy, None
Summary
Elastic
When you move from self-managed Elasticsearch to Elastic Cloud, the Elasticsearch service takes care of the following:
Provisioning and managing the underlying infrastructure
Creating and managing Elasticsearch clusters
Scaling clusters up and down
Upgrades, patching, and taking snapshots
This gives you more time to focus on solving other challenges.
This pattern defines how to migrate on-premises Elasticsearch 7.13 to Elasticsearch on Elastic Cloud on Amazon Web Services (AWS). Other versions might require slight modifications to the processes described in thie pattern. For more information, contact your Elastic representative.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
An active AWS account
with access to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) for snapshots A secure, sufficiently high-bandwidth private link for copying snapshot data files to Amazon S3
Elastic Snapshot policies
to ensure that data ingestion is archived regularly, either to a sufficiently large local data store or to remote storage (Amazon S3)
You must understand how large your snapshots and the lifecyle policies
Roles and skills
The migration process also requires the roles and expertise described in the following table.
Role | Expertise | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
App support | Familiarity with Elastic Cloud and Elastic on premises | All Elastic related tasks |
Systems administrator or DBA | In-depth knowledge of the on-premises Elastic environment and its configuration | The ability to provision storage, install and use the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), and identify all data sources feeding Elastic on premises |
Network administrator | Knowledge of on-premises to AWS network connectivity, security, and performance | Establishment of network links from on premises to Amazon S3, with an understanding of connectivity bandwidth |
Limitations
Elasticsearch on Elastic Cloud is available only in supported AWS Regions (September 2021)
.
Product versions
Elasticsearch 7.13
Architecture
Source technology stack
On-premises Elasticsearch 7.13 or later:
Cluster snapshots
Index snapshots
Beats
configuration
Source technology architecture
The following diagram shows a typical on-premises architecture with different ingestion methods, node types, and Kibana. The different node types reflect the Elasticsearch cluster, authentication, and visualization roles.

Ingestion from Beats to Logstash
Ingestion from Beats to Apache Kafka messaging queue
Ingestion from Filebeat to Logstash
Ingestion from Apache Kafka messaging queue to Logstash
Ingestion from Logstash to an Elasticsearch cluster
Elasticsearch cluster
Authentication and notification node
Kibana and blob nodes
Target technology stack
Elastic Cloud is deployed to your software as a service (SaaS) account in multiple AWS Regions with cross-cluster replication.
Cluster snapshots
Index snapshots
Beats configurations
Elastic Cloud
Network Load Balancer
Amazon Route 53
Amazon S3
Target architecture

The managed Elastic Cloud infrastructure is:
Highly available, being present in multiple Availability Zones
and multiple AWS Regions. Region failure tolerant because data (indexes and snapshots) is replicated using Elastic Cloud cross-cluster replication (CCR)
Archival, because snapshots are archived in Amazon S3
Network partition tolerant through a combination of Network Load Balancers
and Route 53 Data ingestion originating from (but not limited to) Elastic APM
, Beats , Logstash
High-level migration steps
Elastic has developed its own prescriptive methodology for migrating on-premises Elastic Cluster to Elastic Cloud. The Elastic methodology is directly aligned and complementary to the AWS migration guidance and best practices, including Well-Architected Framework
Assess
Mobilize
Migrate and modernize
Elastic follows similar migration phases with complementary terminology:
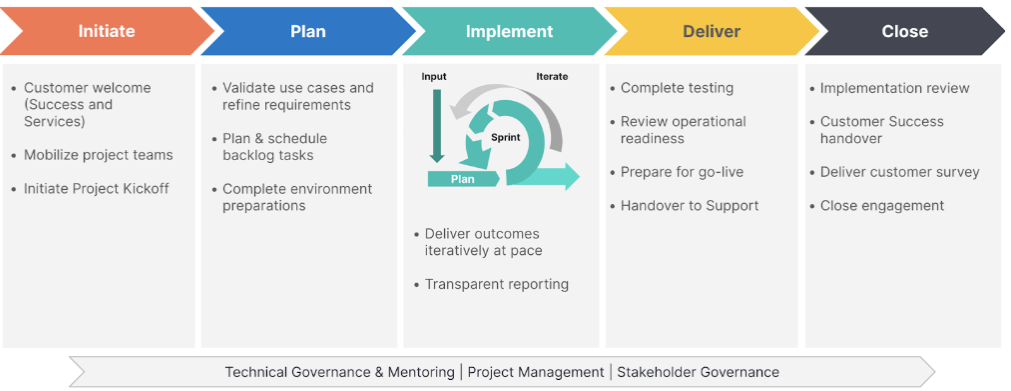
Initiate
Plan
Implement
Deliver
Close
Elastic uses the Elastic Implementation Methodology to facilitate the delivery of project outcomes. This is inclusive by design to ensure that the Elastic, consulting teams, and customer teams work together with clarity to jointly deliver intended outcomes.
The Elastic methodology combines traditional waterfall phasing with Scrum within the implementation phase. Configurations of technical requirements are delivered iteratively in a collaborative manner while minimizing risk.
Tools
AWS services
Amazon Route 53 – Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) web service. You can use Route 53 to perform three main functions in any combination: domain registration, DNS routing, and health checking.
Amazon S3 – Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service. You can use Amazon S3 to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time, from anywhere on the web. This pattern uses an S3 bucket and Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration.
Elastic Load Balancing – Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes your incoming traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, in one or more Availability Zones.
Other tools
Beats
– Beats ship data from Logstash or Elasticsearch Elastic Cloud
– Elastic Cloud is a managed service for hosting Elasticsearch. Elasticsearch
– Elasticsearch is a search and analytics engine that uses the Elastic Stack to centrally store your data for search and analytics that scale. This pattern also uses snapshot creation and cross-cluster replication. Logstash
– Logstash is a server-side data processing pipeline that ingests data from multiple sources, transforms it, and then sends it to your data storage.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Identify servers running the on-premises Elastic solution. | Confirm that Elastic migration is supported. | App owner |
Understand the on-premises server configuration. | To understand the server configuration needed to drive workloads successfully on premises, find the server hardware footprint, network configuration, and storage characteristics that are currently in use | App Support |
Gather user and app account information. | Identify the user names and app names that are used by the on-premises Elastic environment. | Systems administrator, App support |
Document Beats and data shipper configuration. | To document the configurations, look at existing data sources and sinks. For more information, see the Elastic documentation | App support |
Determine the velocity and volume of data. | Establish a baseline for how much data the cluster is handling. | Systems administrator, App support |
Document RPO and RTO scenarios. | Document recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO) scenarios in terms of outages and service level agreements (SLAs). | App owner, Systems administrator, App support |
Determine the optimal snapshot lifecycle settings. | Define how often data needs to be secured by using Elastic snapshots during and after the migration. | App owner, Systems administrator, App support |
Define post-migration performance expectations. | Generate metrics on current and expected screen refresh, query runtimes, and user interface behaviors. | Systems administrator, App support |
Document internet access transport, bandwidth, and availability requirements. | Ascertain speed, latency, and resiliency of internet connections for copying snapshots to Amazon S3. | Network administrator |
Document current costs of on-premises runtime for Elastic. | Ensure that the sizing of the AWS targeted environment is designed to be both high performing and cost effective. | DBA, Systems administrator, App support |
Identify the authentication and authorization needs. | The Elastic Stack security features provide built-in realms such as Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), and OpenID Connect (OIDC). | DBA, Systems administrator, App support |
Understand the specific regulatory requirements based on the geographic location. | Ensure that data is exported and encrypted according to your requirements and to any relevant national requirements. | DBA, Systems administrator, App support |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Prepare the staging area on Amazon S3. | To receive snapshots on Amazon S3, create an S3 bucket and a temporary AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role with full access to your newly created bucket. For more information, see Creating a role to delegate permissions to an IAM user. Use the AWS Security Token Service to request temporary security credentials. Keep the access key ID, secret access key, and session token secured. Enable Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration on the bucket. | AWS administrator |
Install AWS CLI and the Amazon S3 plugin on premises. | On each Elasticsearch node, run the following command.
Then reboot the node. | AWS administrator |
Configure Amazon S3 client access. | Add the keys created previously by running the following commands.
| AWS administrator |
Register a snapshot repository for Elastic data | Use the Kibana Dev Tools | AWS administrator |
Configure snapshot policy. | To configure snapshot lifecycle management, on the Kibana Policies tab, choose SLM policy, and define which times, data streams, or indexes should be included, and what names to use. Configure a policy that takes frequent snapshots. Snapshots are incremental and make efficient use of storage. Match your readiness assessment decision. A policy can also specify a retention policy | App support |
Verify that snapshots work. | In Kibana Dev Tools, run the following command.
| AWS administrator, App support, |
Deploy a new cluster on Elastic Cloud. | Log in to Elastic | AWS administrator, App support |
Set up cluster key store access. | The new cluster needs access to the S3 bucket that will store the snapshots. On the Elasticsearch Service Console, choose Security, and enter the access and secret IAM keys that you created earlier. | AWS administrator |
Configure the Elastic Cloud hosted cluster to access Amazon S3. | Set up new cluster access to the previously created snapshot repository in Amazon S3. Using Kibana, do the following:
| AWS administrator, App Support |
Verify the new Amazon S3 repository. | Ensure that you can access your new repository hosted in the Elastic Cloud cluster. | AWS administrator |
Initilaize the Elasticsearch service cluster. | On the Elasticsearch Service Console, initialize the Elasticsearch service cluster from the S3 snapshot. Run the following commands as POST.
| App Support |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Verify that the snapshot restore was successful. | Using Kibana Dev Tools, run the following command.
| App support |
Redploy ingestion services. | Connect the endpoints for Beats and Logstash to the new Elasticsearch service endpoint. | App support |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Validate the cluster environment. | After the on-premises Elastic cluster environment is migrated to AWS, you can connect to it and use your own user acceptance testing (UAT) tools to validate the new environment. | App support |
Clean-up the resources. | After you validate that the cluster migrated successfully, remove the S3 bucket and the IAM role used for the migration. | AWS administrator |
Related resources
Elastic references
Elastic blog posts
How to migrate from self-managed Elasticsearch to Elastic Cloud on AWS
(blog post) Migrating to Elastic Cloud
(blog post)
Elastic documentation
Elastic video and webinar
AWS references
Additional information
If you're planning to migrate complex workloads, engage Elastic Consulting Services