Setting up Kerberos for Oracle DB instances
Use AWS Directory Service for Microsoft Active Directory, also called AWS Managed Microsoft AD, to set up Kerberos authentication for an Oracle DB instance. To set up Kerberos authentication, complete the following steps:
Note
During the setup, RDS creates an Oracle database user named
managed_service_user@example.com with the CREATE SESSION privilege,
where example.com is your domain name. This user corresponds to the user that Directory Service creates inside
your Managed Active Directory. Periodically, RDS uses the credentials provided by the Directory Service to log in to your Oracle database.
Afterwards, RDS immediately destroys the ticket cache.
Step 1: Create a directory using the AWS Managed Microsoft AD
Directory Service creates a fully managed Active Directory in the AWS Cloud. When you create an AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory, Directory Service creates two domain controllers and Domain Name System (DNS) servers on your behalf. The directory servers are created in different subnets in a VPC. This redundancy helps make sure that your directory remains accessible even if a failure occurs.
When you create an AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory, Directory Service performs the following tasks on your behalf:
-
Sets up an Active Directory within the VPC.
-
Creates a directory administrator account with the user name Admin and the specified password. You use this account to manage your directory.
Note
Be sure to save this password. Directory Service doesn't store it. You can reset it, but you can't retrieve it.
-
Creates a security group for the directory controllers.
When you launch an AWS Managed Microsoft AD, AWS creates an Organizational Unit (OU) that contains all of your directory's objects. This OU has the NetBIOS name that you typed when you created your directory and is located in the domain root. The domain root is owned and managed by AWS.
The Admin account that was created with your AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory has permissions for the most common administrative activities for your OU:
-
Create, update, or delete users
-
Add resources to your domain such as file or print servers, and then assign permissions for those resources to users in your OU
-
Create additional OUs and containers
-
Delegate authority
-
Restore deleted objects from the Active Directory Recycle Bin
-
Run AD and DNS Windows PowerShell modules on the Active Directory Web Service
The Admin account also has rights to perform the following domain-wide activities:
-
Manage DNS configurations (add, remove, or update records, zones, and forwarders)
-
View DNS event logs
-
View security event logs
To create the directory, use the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, or the Directory Service API. Make sure to open the relevant outbound ports on the directory security group so that the directory can communicate with the Oracle DB instance.
To create a directory with AWS Managed Microsoft AD
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Directory Service console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/directoryservicev2/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Directories and choose Set up Directory.
-
Choose AWS Managed Microsoft AD. AWS Managed Microsoft AD is the only option that you can currently use with Amazon RDS.
-
Enter the following information:
- Directory DNS name
-
The fully qualified name for the directory, such as
corp.example.com. - Directory NetBIOS name
-
The short name for the directory, such as
CORP. - Directory description
-
(Optional) A description for the directory.
- Admin password
-
The password for the directory administrator. The directory creation process creates an administrator account with the user name Admin and this password.
The directory administrator password and can't include the word "admin." The password is case-sensitive and must be 8–64 characters in length. It must also contain at least one character from three of the following four categories:
-
Lowercase letters (a–z)
-
Uppercase letters (A–Z)
-
Numbers (0–9)
-
Non-alphanumeric characters (~!@#$%^&*_-+=`|\(){}[]:;"'<>,.?/)
-
- Confirm password
-
The administrator password retyped.
-
Choose Next.
-
Enter the following information in the Networking section and then choose Next:
- VPC
-
The VPC for the directory. Create the Oracle DB instance in this same VPC.
- Subnets
-
Subnets for the directory servers. The two subnets must be in different Availability Zones.
-
Review the directory information and make any necessary changes. When the information is correct, choose Create directory.
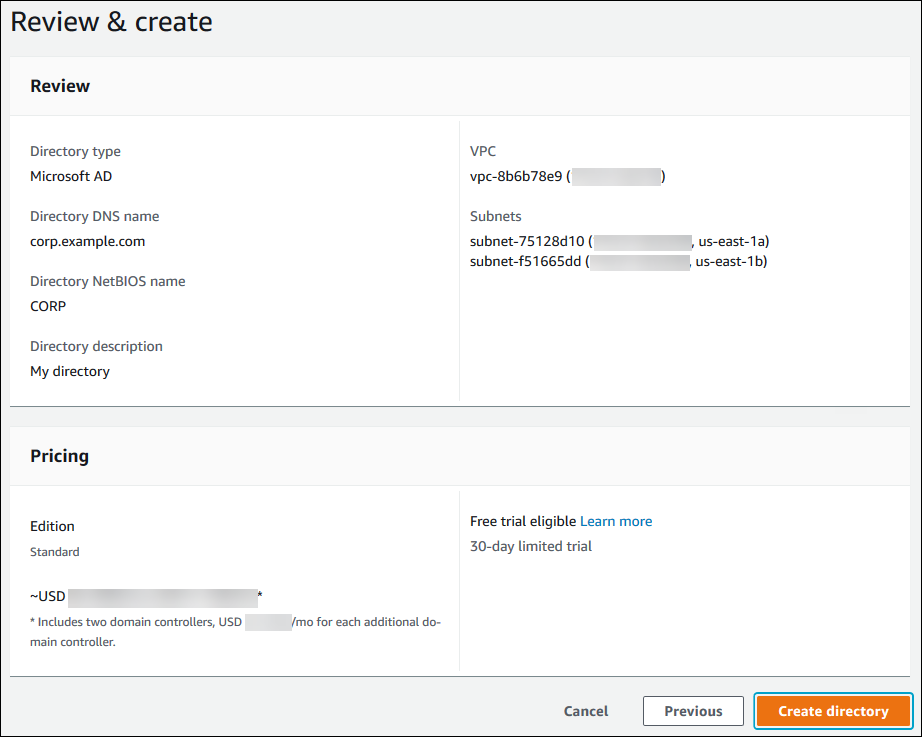
It takes several minutes for the directory to be created. When it has been successfully created, the Status value changes to Active.
To see information about your directory, choose the directory name in the directory listing. Note the Directory ID value because you need this value when you create or modify your Oracle DB instance.

Step 2: Create a trust
If you plan to use AWS Managed Microsoft AD only, move on to Step 3: Configure IAM permissions for Amazon RDS.
To enable Kerberos authentication using your self-managed Active Directory, you must create a forest trust relationship between your self-managed Active Directory and the AWS Managed Microsoft AD created in the previous step. The trust can be one-way, where the AWS Managed Microsoft AD trusts the self-managed Active Directory. The trust can also be two-way, where both Active Directories trust each other. For more information about setting up forest trusts using Directory Service, see When to create a trust relationship in the Directory Service Administration Guide.
Step 3: Configure IAM permissions for Amazon RDS
To call Directory Service for you, Amazon RDS requires an IAM role that uses the managed IAM policy AmazonRDSDirectoryServiceAccess. This role
allows Amazon RDS to make calls to the Directory Service.
Note
For the role to allow access, the AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) endpoint must be activated in the correct AWS Region for your AWS account. AWS STS endpoints are active by default in all AWS Regions, and you can use them without any further actions. For more information, see Activating and deactivating AWS STS in an AWS Region in the IAM User Guide.
Creating an IAM role
When you create a DB instance using the AWS Management Console, and the console user has the iam:CreateRole permission, the console
creates rds-directoryservice-kerberos-access-role automatically. Otherwise, you must create the IAM role manually. When
you create an IAM role manually, choose Directory Service, and attach the AWS managed policy
AmazonRDSDirectoryServiceAccess to it.
For more information about creating IAM roles for a service, see Creating a role to delegate permissions to an AWS service in the IAM User Guide.
Note
The IAM role used for Windows Authentication for RDS for Microsoft SQL Server can't be used for RDS for Oracle.
Creating an IAM trust policy manually
Optionally, you can create resource policies with the required permissions instead of using the managed IAM policy
AmazonRDSDirectoryServiceAccess. Specify both directoryservice.rds.amazonaws.com and
rds.amazonaws.com as principals.
To limit the permissions that Amazon RDS gives another service for a specific resource, we recommend using the aws:SourceArn and aws:SourceAccount global condition context keys in resource policies. The most effective way to protect
against the confused deputy problem is to use the aws:SourceArn global condition context key with the full ARN of an
Amazon RDS resource. For more information, see Preventing cross-service confused deputy problems.
The following example shows how you can use the aws:SourceArn and aws:SourceAccount global condition
context keys in Amazon RDS to prevent the confused deputy problem.
For opt-in Regions, you must also include a service principal for that Region
in the form of directoryservice.rds..
For example, in the Africa (Cape Town) Region, use the following trust policy:region_name.amazonaws.com
The role must also have the following IAM policy.
Step 4: Create and configure users
You can create users with the Active Directory Users and Computers tool, which is one of the Active Directory Domain Services and Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services tools. In this case, users are individual people or entities that have access to your directory.
To create users in an Directory Service directory, you must be connected to a Windows-based Amazon EC2 instance that is a member of the Directory Service directory. At the same time, you must be logged in as a user that has privileges to create users. For more information about creating users in your Microsoft Active Directory, see Manage users and groups in AWS Managed Microsoft AD in the Directory Service Administration Guide.
Step 5: Enable cross-VPC traffic between the directory and the DB instance
If you plan to locate the directory and the DB instance in the same VPC, skip this step and move on to Step 6: Create or modify an Oracle DB instance.
If you plan to locate the directory and the DB instance in different AWS accounts or VPCs, configure cross-VPC traffic using VPC peering or AWS Transit Gateway. The following procedure enables traffic between VPCs using VPC peering. Follow the instructions in What is VPC peering? in the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Peering Guide.
To enable cross-VPC traffic using VPC peering
-
Set up appropriate VPC routing rules to ensure that network traffic can flow both ways.
-
Ensure that the DB instance's security group can receive inbound traffic from the directory's security group. For more information, see Best practices for AWS Managed Microsoft AD in the Directory Service Administration Guide.
-
Ensure that there is no network access control list (ACL) rule to block traffic.
If a different AWS account owns the directory, you must share the directory.
To share the directory between AWS accounts
-
Start sharing the directory with the AWS account that the DB instance will be created in by following the instructions in Tutorial: Sharing your AWS Managed Microsoft AD directory for seamless EC2 Domain-join in the Directory Service Administration Guide.
-
Sign in to the Directory Service console using the account for the DB instance, and ensure that the domain has the
SHAREDstatus before proceeding. -
While signed into the Directory Service console using the account for the DB instance, note the Directory ID value. You use this directory ID to join the DB instance to the domain.
Step 6: Create or modify an Oracle DB instance
Create or modify an Oracle DB instance for use with your directory. You can use the console, CLI, or RDS API to associate a DB instance with a directory. You can do this in one of the following ways:
-
Create a new Oracle DB instance using the console, the create-db-instance CLI command, or the CreateDBInstance RDS API operation.
For instructions, see Creating an Amazon RDS DB instance.
-
Modify an existing Oracle DB instance using the console, the modify-db-instance CLI command, or the ModifyDBInstance RDS API operation.
For instructions, see Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance.
-
Restore an Oracle DB instance from a DB snapshot using the console, the restore-db-instance-from-db-snapshot CLI command, or the RestoreDBInstanceFromDBSnapshot RDS API operation.
For instructions, see Restoring to a DB instance.
-
Restore an Oracle DB instance to a point-in-time using the console, the restore-db-instance-to-point-in-time CLI command, or the RestoreDBInstanceToPointInTime RDS API operation.
For instructions, see Restoring a DB instance to a specified time for Amazon RDS.
Kerberos authentication is only supported for Oracle DB instances in a VPC. The DB instance can be in the same VPC as the directory, or in a different VPC. When you create or modify the DB instance, do the following:
-
Provide the domain identifier (
d-*identifier) that was generated when you created your directory. -
Provide the name of the IAM role that you created.
-
Ensure that the DB instance security group can receive inbound traffic from the directory security group and send outbound traffic to the directory.
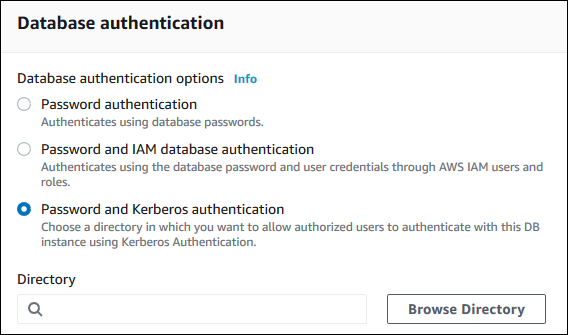
When you use the console to create a DB instance, choose Password and Kerberos authentication in the Database authentication section. Choose Browse Directory and then select the directory, or choose Create a new directory.
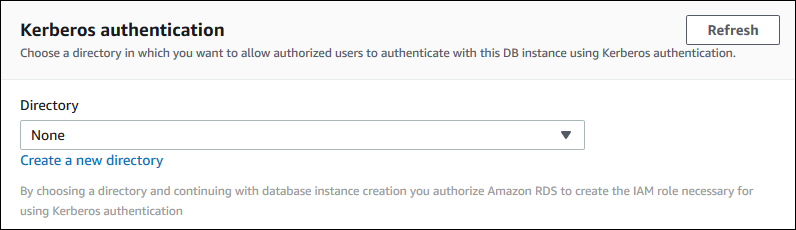
When you use the console to modify or restore a DB instance, choose the directory in the Kerberos authentication section, or choose Create a new directory.
When you use the AWS CLI, the following parameters are required for the DB instance to be able to use the directory that you created:
-
For the
--domainparameter, use the domain identifier ("d-*" identifier) generated when you created the directory. -
For the
--domain-iam-role-nameparameter, use the role you created that uses the managed IAM policyAmazonRDSDirectoryServiceAccess.
For example, the following CLI command modifies a DB instance to use a directory.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds modify-db-instance \ --db-instance-identifiermydbinstance\ --domain d-ID\ --domain-iam-role-namerole-name
For Windows:
aws rds modify-db-instance ^ --db-instance-identifiermydbinstance^ --domain d-ID^ --domain-iam-role-namerole-name
Important
If you modify a DB instance to enable Kerberos authentication, reboot the DB instance after making the change.
Note
MANAGED_SERVICE_USER is a service account whose name is randomly generated by Directory Service for RDS.
During the Kerberos authentication setup, RDS for Oracle creates a user with the same name and assigns it the CREATE
SESSION privilege. The Oracle DB user is identified externally as
MANAGED_SERVICE_USER@EXAMPLE.COM, where EXAMPLE.COM is the name of your
domain. Periodically, RDS uses the credentials provided by the Directory Service to log in to your Oracle database. Afterward, RDS
immediately destroys the ticket cache.
Step 7: Create Kerberos authentication Oracle logins
Use the Amazon RDS master user credentials to connect to the Oracle DB instance as you do any other DB instance. The DB instance is joined to the AWS Managed Microsoft AD domain. Thus, you can provision Oracle logins and users from the Microsoft Active Directory users in your domain. To manage database permissions, you grant and revoke standard Oracle permissions to these logins.
To allow a Microsoft Active Directory user to authenticate with Oracle
-
Connect to the Oracle DB instance using your Amazon RDS master user credentials.
-
Create an externally authenticated user in Oracle database.
In the following example, replace
KRBUSER@CORP.EXAMPLE.COMCREATE USER "KRBUSER@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM" IDENTIFIED EXTERNALLY; GRANT CREATE SESSION TO "KRBUSER@CORP.EXAMPLE.COM";Users (both humans and applications) from your domain can now connect to the Oracle DB instance from a domain joined client machine using Kerberos authentication.
Step 8: Configure an Oracle client
To configure an Oracle client, meet the following requirements:
-
Create a configuration file named krb5.conf (Linux) or krb5.ini (Windows) to point to the domain. Configure the Oracle client to use this configuration file.
-
Verify that traffic can flow between the client host and Directory Service over DNS port 53 over TCP/UDP, Kerberos ports (88 and 464 for managed Directory Service) over TCP, and LDAP port 389 over TCP.
-
Verify that traffic can flow between the client host and the DB instance over the database port.
Following is sample content for AWS Managed Microsoft AD.
[libdefaults] default_realm = EXAMPLE.COM [realms] EXAMPLE.COM = { kdc = example.com admin_server = example.com } [domain_realm] .example.com = CORP.EXAMPLE.COM example.com = CORP.EXAMPLE.COM
Following is sample content for on-premise Microsoft AD. In your krb5.conf or krb5.ini file, replace
on-prem-ad-server-name with the name of your on-premises AD server.
[libdefaults] default_realm = ONPREM.COM [realms] AWSAD.COM = { kdc = awsad.com admin_server = awsad.com } ONPREM.COM = { kdc =on-prem-ad-server-nameadmin_server =on-prem-ad-server-name} [domain_realm] .awsad.com = AWSAD.COM awsad.com= AWSAD.COM .onprem.com = ONPREM.COM onprem.com= ONPREM.COM
Note
After you configure your krb5.ini or krb5.conf file, we recommend that you reboot the server.
The following is sample sqlnet.ora content for a SQL*Plus configuration:
SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES=(KERBEROS5PRE,KERBEROS5) SQLNET.KERBEROS5_CONF=path_to_krb5.conf_file
For an example of a SQL Developer configuration, see Document 1609359.1