Die vorliegende Übersetzung wurde maschinell erstellt. Im Falle eines Konflikts oder eines Widerspruchs zwischen dieser übersetzten Fassung und der englischen Fassung (einschließlich infolge von Verzögerungen bei der Übersetzung) ist die englische Fassung maßgeblich.
Implementieren Sie KI-gestützte Kubernetes-Diagnose und -Fehlerbehebung mit der Integration von K8SGPT und Amazon Bedrock
Ishwar Chauthaiwale, Muskan., und Prafful Gupta, Amazon Web Services
Übersicht
Dieses Muster zeigt, wie KI-gestützte Kubernetes-Diagnose und -Fehlerbehebung implementiert werden können, indem K8SGPT in das auf Amazon Bedrock verfügbare Anthropic Claude v2-Modell integriert wird. Die Lösung bietet mithilfe einer sicheren Bastion-Host-Architektur Analysen in natürlicher Sprache und Schritte zur Behebung von Problemen mit Kubernetes-Clustern. Durch die Kombination von K8SGPT Kubernetes-Expertise mit den erweiterten Sprachfunktionen von Amazon Bedrock können DevOps Teams Clusterprobleme schnell identifizieren und lösen. Mit diesen Funktionen ist es möglich, die mittlere Zeit bis zur Problemlösung (MTTR) um bis zu 50 Prozent zu reduzieren.
Dieses cloudnative Muster nutzt Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) für das Kubernetes-Management. Das Muster implementiert bewährte Sicherheitsmethoden durch geeignete AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM-) Rollen und Netzwerkisolierung. Diese Lösung ist besonders wertvoll für Unternehmen, die ihren Kubernetes-Betrieb rationalisieren und ihre Fähigkeiten zur Fehlerbehebung mit KI-Unterstützung verbessern möchten.
Voraussetzungen und Einschränkungen
Voraussetzungen
Ein Aktiv AWS-Konto mit den entsprechenden Berechtigungen
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) installiert und konfiguriert
Ein Amazon EKS-Cluster
Zugriff auf das Modell Anthropic Claude 2 auf Amazon Bedrock
Ein Bastion-Host mit den erforderlichen Sicherheitsgruppeneinstellungen
Einschränkungen
Die K8sGPT-Analyse ist durch die Größe des Kontextfensters des Claude v2-Modells begrenzt.
Amazon Bedrock API-Tariflimits gelten auf der Grundlage Ihrer Kontokontingente.
Einige AWS-Services sind nicht in allen AWS-Regionen verfügbar. Informationen zur Verfügbarkeit in den einzelnen Regionen finden Sie unter AWS Dienste nach Regionen
. Informationen zu bestimmten Endpunkten finden Sie unter Dienstendpunkte und Kontingente. Wählen Sie dort den Link für den Dienst aus.
Produktversionen
Amazon EKS Version 1.31 oder höher
Modell Claude 2 auf Amazon Bedrock
Architektur
Das folgende Diagramm zeigt die Architektur für KI-gestützte Kubernetes-Diagnosen unter Verwendung von K8SGPT, das in Amazon Bedrock integriert ist. AWS Cloud
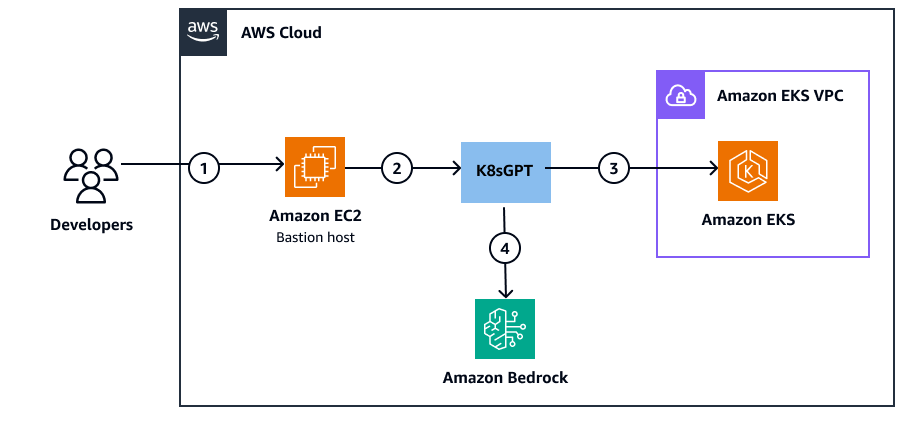
Die Architektur zeigt den folgenden Workflow:
Entwickler greifen über eine sichere Verbindung zum Bastion-Host auf die Umgebung zu. Diese EC2 Amazon-Instance dient als sicherer Einstiegspunkt und enthält die Installation der K8SGPT-Befehlszeilenschnittstelle (CLI) und die erforderlichen Konfigurationen.
Der mit bestimmten IAM-Rollen konfigurierte Bastion-Host stellt sichere Verbindungen sowohl zum Amazon EKS-Cluster als auch zu den Amazon Bedrock-Endpunkten her. K8SGPT ist auf dem Bastion-Host installiert und konfiguriert, um die Kubernetes-Clusteranalyse durchzuführen.
Amazon EKS verwaltet die Kubernetes-Steuerebene und die Worker-Knoten und stellt die Zielumgebung für die K8SGPT-Analyse bereit. Der Service läuft über mehrere Availability Zones innerhalb einer Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), was zu hoher Verfügbarkeit und Ausfallsicherheit beiträgt. Amazon EKS stellt Betriebsdaten über die Kubernetes-API bereit und ermöglicht so eine umfassende Clusteranalyse.
K8sgpt sendet Analysedaten an Amazon Bedrock, das das Claude v2 Foundation Model (FM) für die Verarbeitung natürlicher Sprache bereitstellt. Der Service verarbeitet die K8SGPT-Analyse, um für Menschen lesbare Erklärungen zu generieren, und bietet detaillierte Lösungsvorschläge auf der Grundlage der identifizierten Probleme. Amazon Bedrock arbeitet als serverloser KI-Service mit hoher Verfügbarkeit und Skalierbarkeit.
Anmerkung
Während dieses Workflows steuert IAM den Zugriff zwischen Komponenten über Rollen und Richtlinien und verwaltet die Authentifizierung für die Interaktionen mit dem Bastion-Host, Amazon EKS und Amazon Bedrock. IAM implementiert das Prinzip der geringsten Rechte und ermöglicht eine sichere dienstübergreifende Kommunikation in der gesamten Architektur.
Automatisierung und Skalierung
K8sGPT-Operationen können mithilfe verschiedener AND-Tools automatisiert und auf mehrere Amazon EKS-Cluster skaliert werden. AWS-Services Diese Lösung unterstützt die Integration von Continuous Integration und Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) mithilfe von Jenkins
Tools
AWS-Services
AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) ist ein Open-Source-Tool, mit dem Sie AWS-Services über Befehle in Ihrer Befehlszeilen-Shell interagieren können.
Mit Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) können Sie Kubernetes ausführen, AWS ohne dass Sie Ihre eigene Kubernetes-Steuerebene oder Knoten installieren oder verwalten müssen.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) hilft Ihnen dabei, den Zugriff auf Ihre AWS Ressourcen sicher zu verwalten, indem kontrolliert wird, wer authentifiziert und autorisiert ist, diese zu verwenden.
Andere Tools
k8SGPT
ist ein KI-gestütztes Open-Source-Tool, das das Kubernetes-Management transformiert. Es fungiert als Experte für Virtual Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) und scannt, diagnostiziert und behebt automatisch Probleme mit Kubernetes-Clustern. Administratoren können mit K8SGPT in natürlicher Sprache interagieren und klare, umsetzbare Einblicke in den Clusterstatus, Pod-Abstürze und Dienstausfälle erhalten. Die integrierten Analysatoren des Tools erkennen eine Vielzahl von Problemen, von falsch konfigurierten Komponenten bis hin zu Ressourcenbeschränkungen, und bieten Erklärungen und Lösungen. easy-to-understand
Bewährte Methoden
Implementieren Sie sichere Zugriffskontrollen, indem Sie AWS Systems Manager Session Manager den Hostzugriff für Bastion verwenden.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass die K8SGPT-Authentifizierung dedizierte IAM-Rollen mit den geringsten Berechtigungen für Amazon Bedrock- und Amazon EKS-Interaktionen verwendet. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der IAM-Dokumentation unter Gewährung der geringsten Rechte und bewährte Methoden zur Sicherheit.
Konfigurieren Sie das Ressourcen-Tagging, aktivieren Sie die CloudWatch Amazon-Protokollierung für Prüfpfade und implementieren Sie die Datenanonymisierung
für vertrauliche Informationen. Sorgen Sie für regelmäßige Backups der K8SGPT-Konfigurationen und richten Sie automatische Scan-Zeitpläne außerhalb der Spitzenzeiten ein, um die Auswirkungen auf den Betrieb zu minimieren.
Epen
| Aufgabe | Beschreibung | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Stellen Sie Amazon Bedrock als KI-Backend-Anbieter für K8SGPT ein. | Verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl, um Amazon Bedrock als KI-Backend-Anbieter
Der Beispielbefehl verwendet für den. Führen Sie den folgenden
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
| AWS DevOps |
| Aufgabe | Beschreibung | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Sehen Sie sich eine Liste der verfügbaren Filter an. | Verwenden Sie den folgenden AWS CLI Befehl, um die Liste aller verfügbaren Filter anzuzeigen:
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
| AWS DevOps |
Scannen Sie einen Pod in einem bestimmten Namespace mithilfe eines Filters. | Dieser Befehl ist nützlich für das gezielte Debuggen bestimmter Pod-Probleme innerhalb eines Kubernetes-Clusters. Dabei werden die KI-Funktionen von Amazon Bedrock verwendet, um die gefundenen Probleme zu analysieren und zu erklären. Verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl, um einen Pod in einem bestimmten Namespace mithilfe eines Filters zu scannen: AWS CLI
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
| AWS DevOps |
Scannen Sie eine Bereitstellung in einem bestimmten Namespace mithilfe eines Filters. | Dieser Befehl ist nützlich, um bereitstellungsspezifische Probleme zu identifizieren und zu beheben, insbesondere wenn der tatsächliche Status nicht dem gewünschten Status entspricht. Verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl, um eine Bereitstellung in einem bestimmten Namespace mithilfe eines Filters zu scannen: AWS CLI
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
| AWS DevOps |
Scannen Sie einen Knoten in einem bestimmten Namespace mithilfe eines Filters. | Verwenden Sie den folgenden AWS CLI Befehl, um einen Knoten in einem bestimmten Namespace mithilfe eines Filters zu scannen:
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
| AWS DevOps |
| Aufgabe | Beschreibung | Erforderliche Fähigkeiten |
|---|---|---|
Erhalten Sie detaillierte Ergebnisse. | Verwenden Sie den folgenden AWS CLI Befehl, um detaillierte Ausgaben zu erhalten:
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
| AWS DevOps |
Überprüfen Sie problematische Pods. | Verwenden Sie den folgenden AWS CLI Befehl, um nach bestimmten problematischen Pods zu suchen:
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
| AWS DevOps |
Erhalten Sie anwendungsspezifische Einblicke. | Dieser Befehl ist besonders nützlich, wenn:
Verwenden Sie den folgenden Befehl, um anwendungsspezifische Einblicke zu erhalten:
Im Folgenden finden Sie ein Beispiel für die erwartete Ausgabe dieses Befehls:
|
Zugehörige Ressourcen
AWS-Blogs
AWS Dokumentation
Sonstige Ressourcen