Using Elastic Beanstalk saved configurations
You can save your environment's configuration as an object in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) that can be applied to other environments during environment creation, or applied to a running environment. Saved configurations are YAML formatted templates that define an environment's platform version, tier, configuration option settings, and tags.
You can apply tags to a saved configuration when you create it, and edit tags of existing saved configurations. The tags applied to a saved configuration aren't related to the tags specified in a saved configuration using the Tags: key. The latter
are applied to an environment when you apply the saved configuration to the environment. For details, see Tagging saved configurations.
Note
You can create and apply saved configurations to your Elastic Beanstalk environments using several methods. These include the Elastic Beanstalk console, the EB CLI, and the AWS CLI.
See the following topics for examples of alternate methods for creating and applying saved configurations:
Create a saved configuration from the current state of your environment in the Elastic Beanstalk management console.
To save an environment's configuration
Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
, and in the Regions list, select your AWS Region. -
In the navigation pane, choose Environments, and then choose the name of your environment from the list.
Note
If you have many environments, use the search bar to filter the environment list.
-
Choose Actions, and then choose Save configuration.
-
Use the on-screen form to name the saved configuration. Optionally, provide a brief description, and add tag keys and values.
-
Choose Save.
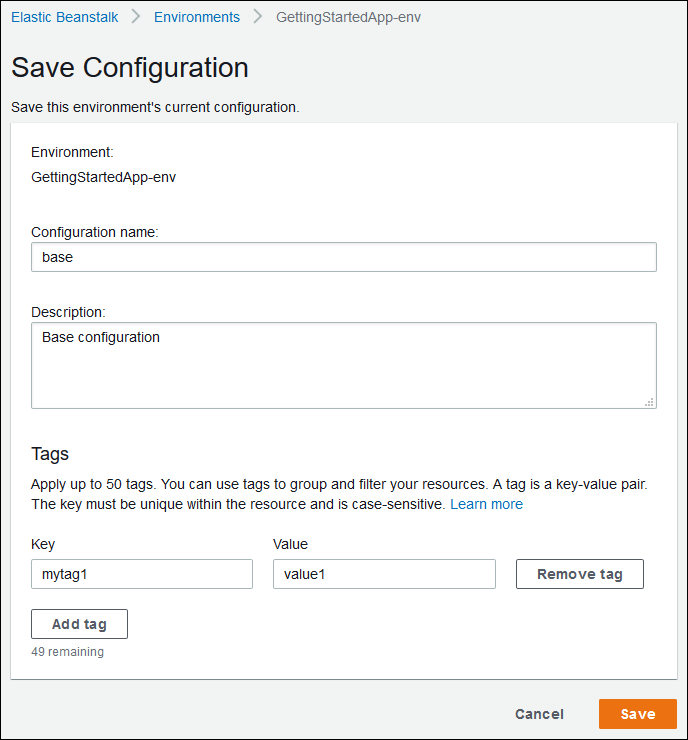
The saved configuration includes any settings that you have applied to the environment with the console or any other client that uses the Elastic Beanstalk API. You can then apply the saved configuration to your environment at a later date to restore it to its previous state, or apply it to a new environment during environment creation.
You can download a configuration using the EB CLI eb config command, as shown in the following example.
NAME is the name of your saved configuration.
eb config getNAME
To apply a saved configuration during environment creation (Elastic Beanstalk console)
Open the Elastic Beanstalk console
, and in the Regions list, select your AWS Region. -
In the navigation pane, choose Applications, and then choose your application's name from the list.
Note
If you have many applications, use the search bar to filter the application list.
In the navigation pane, find your application's name and choose Saved configurations.
-
Select the saved configuration you want to apply, and then choose Launch environment.
-
Proceed through the wizard to create your environment.
Saved configurations don't include settings applied with configuration files in your application's source code. If the same setting is applied in both a configuration file and saved configuration, the setting in the saved configuration takes precedence. Likewise, options specified in the Elastic Beanstalk console override options in saved configurations. For more information, see Precedence.
Saved configurations are stored in the Elastic Beanstalk S3 bucket in a folder named after your application. For example, configurations for an application named
my-app in the us-west-2 region for account number 123456789012 can be found at
s3://elasticbeanstalk-us-west-2-123456789012/resources/templates/my-app/.
View the contents of a saved configuration by opening it in a text editor. The following example configuration shows the configuration of a web server environment launched with the Elastic Beanstalk management console.
EnvironmentConfigurationMetadata:
Description: Saved configuration from a multicontainer Docker environment created with the Elastic Beanstalk Management Console
DateCreated: '1520633151000'
DateModified: '1520633151000'
Platform:
PlatformArn: arn:aws:elasticbeanstalk:us-east-2::platform/Java 8 running on 64bit Amazon Linux/2.5.0
OptionSettings:
aws:elasticbeanstalk:command:
BatchSize: '30'
BatchSizeType: Percentage
aws:elasticbeanstalk:sns:topics:
Notification Endpoint: me@example.com
aws:elb:policies:
ConnectionDrainingEnabled: true
ConnectionDrainingTimeout: '20'
aws:elb:loadbalancer:
CrossZone: true
aws:elasticbeanstalk:environment:
ServiceRole: aws-elasticbeanstalk-service-role
aws:elasticbeanstalk:application:
Application Healthcheck URL: /
aws:elasticbeanstalk:healthreporting:system:
SystemType: enhanced
aws:autoscaling:launchconfiguration:
IamInstanceProfile: aws-elasticbeanstalk-ec2-role
InstanceType: t2.micro
EC2KeyName: workstation-uswest2
aws:autoscaling:updatepolicy:rollingupdate:
RollingUpdateType: Health
RollingUpdateEnabled: true
EnvironmentTier:
Type: Standard
Name: WebServer
AWSConfigurationTemplateVersion: 1.1.0.0
Tags:
Cost Center: WebApp DevYou can modify the contents of a saved configuration and save it in the same location in Amazon S3. Any properly formatted saved configuration stored in the right location can be applied to an environment by using the Elastic Beanstalk management console.
The following keys are supported.
-
AWSConfigurationTemplateVersion (required) – The configuration template version (1.1.0.0).
AWSConfigurationTemplateVersion: 1.1.0.0 -
Platform – The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the environment's platform version. You can specify the platform by ARN or solution stack name.
Platform: PlatformArn:arn:aws:elasticbeanstalk:us-east-2::platform/Java 8 running on 64bit Amazon Linux/2.5.0 -
SolutionStack – The full name of the solution stack used to create the environment.
SolutionStack:64bit Amazon Linux 2017.03 v2.5.0 running Java 8 -
OptionSettings – Configuration option settings to apply to the environment. For example, the following entry sets the instance type to t2.micro.
OptionSettings: aws:autoscaling:launchconfiguration: InstanceType: t2.micro -
Tags – Up to 47 tags to apply to resources created within the environment.
Tags: Cost Center: WebApp Dev -
EnvironmentTier – The type of environment to create. For a web server environment, you can exclude this section (web server is the default). For a worker environment, use the following.
EnvironmentTier: Name: Worker Type: SQS/HTTP
Note
You can create and apply saved configurations to your Elastic Beanstalk environments using several methods. These include the Elastic Beanstalk console, the EB CLI, and the AWS CLI.
See the following topics for examples of alternate methods for creating and applying saved configurations: