Migrate an on-premises MySQL database to Amazon RDS for MySQL
Lorenzo Mota, Amazon Web Services
Summary
This pattern provides guidance for migrating an on-premises MySQL database to Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for MySQL. The pattern discusses the use of AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) or native MySQL tools such as mysqldump for a full database migration. This pattern is primarily for DBAs and solution architects. It can be used in small or large projects as a testing procedure (we recommend at least one testing cycle) or as a final migration procedure.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
An active AWS account
A MySQL source database in an on-premises data center
Limitations
Database size limit: 64 TB
Product versions
MySQL versions 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 8.0. For the latest list of supported versions, see MySQL on Amazon RDS in the AWS documentation. If you're using AWS DMS, see also Using a MySQL-Compatible Database as a Target for AWS DMS for MySQL versions currently supported by AWS DMS.
Architecture
Source technology stack
An on-premises MySQL database
Target technology stack
An Amazon RDS DB instance running MySQL
Target architecture
The following diagram shows the target Amazon RDS for MySQL implementation after migration.

AWS data migration architecture
Using AWS DMS:
The following diagram shows the data migration architecture when you use AWS DMS to send full and incremental changes until cutover. The network connection from on premises to AWS depends on your requirements and is out of scope for this pattern.

Using native MySQL tools:
The following diagram shows the data migration architecture when you use native MySQL tools. The export dump files are copied to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and imported into the Amazon RDS for MySQL database in AWS before the cutover. The network connection from on premises to AWS depends on your requirements and is out of scope for this pattern.
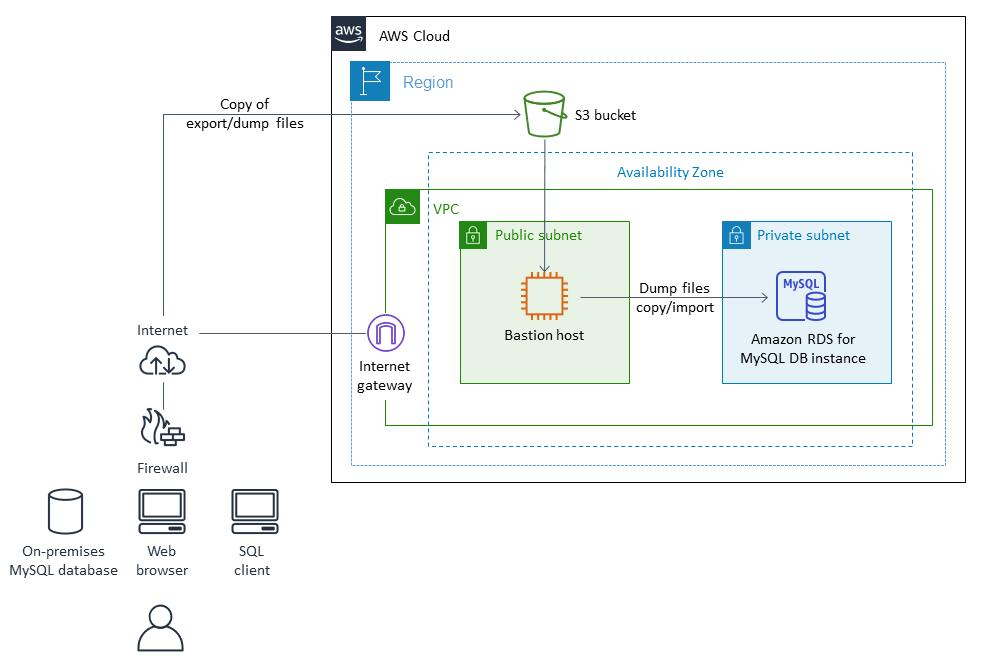
Notes:
Depending on downtime requirements and the size of the database, using AWS DMS or a change data capture (CDC) tool minimizes cutover time. AWS DMS can help reduce cutover time to the new target to a minimum (typically minutes). An offline strategy with mysqldump can suffice if the size of the database and network latency allow for a short window. (We recommend testing to get an approximate time.)
Usually a CDC strategy such as AWS DMS requires more monitoring and complexity than offline options.
Tools
AWS services: AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) helps you migrate data stores to the AWS Cloud or between combinations of cloud and on-premises setups. For information about MySQL source and target databases supported by AWS DMS, see Migrating MySQL-Compatible Databases to AWS. If your source database isn't supported by AWS DMS, you must choose another method to migrate your data.
Native MySQL tools: mysqldump
Third-party tools: Percona XtraBackup
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Validate database versions. | Validate the source and target database versions. | DBA |
Identify hardware requirements. | Identify the hardware requirements for the target server. | DBA, Systems administrator |
Identify storage requirements. | Identify storage requirements (such as storage type and capacity) for the target database. | DBA, Systems administrator |
Choose the instance type. | Choose the target instance type based on capacity, storage features, and networking features. | DBA, Systems administrator |
Identify network access requirements. | Identify the security requirements for network access for the source and target databases. | DBA, Systems administrator |
Identify unsupported objects. | Identify unsupported objects (if any) and determine the migration effort. | DBA |
Identify dependencies. | Identify any dependencies on remote databases. | DBA |
Determine the application migration strategy. | Determine the strategy for migrating client applications. | DBA, App owner, Systems administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Create a virtual private cloud (VPC). | Configure route tables, internet gateway, NAT gateways, and subnets. For more information, see VPCs and Amazon RDS in the Amazon RDS documentation. | Systems administrator |
Create security groups. | Configure ports and CIDR ranges or specific IPs depending on your requirements. The default port for MySQL is 3306. For more information, see Controlling access with security groups in the Amazon RDS documentation. | Systems administrator |
Configure and start an Amazon RDS for MySQL DB instance. | For instructions, see Creating an Amazon RDS DB instance in the Amazon RDS documentation. Check for supported versions. | Systems administrator |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Use native MySQL tools or third-party tools to migrate database objects and data. | For instructions, see the documentation for MySQL tools such as mysqldump For more information about options, see the blog post Migration options for MySQL to Amazon RDS for MySQL or Amazon Aurora MySQL | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Migrate data with AWS DMS. | For instructions, see the AWS DMS documentation. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Fix object count discrepancies. | Collect object counts from the source database and new target database. Fix discrepancies in the target database. | DBA |
Check dependencies. | Check whether dependencies (links) to and from other databases are valid and work as expected. | DBA |
Perform tests. | If this is a testing cycle, perform query testing, gather metrics, and fix issues. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Switch to the target database. | Switch client applications to the new infrastructure. | DBA, App owner, Systems administrator |
Provide testing support. | Provide support for functional application testing. | DBA |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Shut down resources. | Shut down the temporary AWS resources you created for the migration. | DBA, Systems administrator |
Validate project documents. | Review and validate the project documents. | DBA, App owner, Systems administrator |
Gather metrics. | Gather metrics such as time to migrate, percentage of manual versus automated effort, cost savings, and so on. | DBA, App owner, Systems administrator |
Close out the project. | Close out the project and provide feedback. | DBA, App owner, Systems administrator |
Decommission the source database. | When all migration and cutover tasks are complete, decommission the on-premises database. | DBA, Systems administrator |
Related resources
References
Tutorials