Migrating data from an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance to an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster using an Aurora read replica
You can use an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance as the basis for a new Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster by using an Aurora read replica for the migration process. The Aurora read replica option is available only for migrating within the same AWS Region and account, and it's available only if the Region offers a compatible version of Aurora PostgreSQL for your RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance. By compatible, we mean that the Aurora PostgreSQL version is the same as the RDS for PostgreSQL version, or that it is a higher minor version in the same major version family.
For example, to use this technique to migrate an RDS for PostgreSQL 11.14 DB instance, the Region must offer Aurora PostgreSQL version 11.14 or a higher minor version in the PostgreSQL version 11 family.
Topics
Overview of migrating data by using an Aurora read replica
Migrating from an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance to an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster is a multistep procedure. First, you create an Aurora read replica of your source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance. That starts a replication process from your RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance to a special-purpose DB cluster known as a Replica cluster. The Replica cluster consists solely of an Aurora read replica (a reader instance).
Note
It can take several hours per terabyte of data for the migration to complete.
Promoting an Aurora PostgreSQL Replica
After you create an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, follow these steps to promote the Aurora Replica:
-
Stop all database write workload on the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance.
-
Get the current
WAL LSNfrom the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance:SELECT pg_current_wal_lsn();pg_current_wal_lsn -------------------- 0/F0000318 (1 row) -
On the Aurora PostgreSQL Replica cluster, check that the replayed LSN is greater than the LSN from step 2:
SELECT pg_last_wal_replay_lsn();pg_last_wal_replay_lsn ------------------------ 0/F0000400 (1 row)Alternatively, you can use the following query on the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance:
SELECT restart_lsn FROM pg_replication_slots; -
Promote the Aurora PostgreSQL Replica cluster.
When the replication stops, the replica cluster is promoted to a standalone Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, and the reader is promoted to writer instance for the cluster. At this point, you can add instances to the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster to size it according to your use case. If you no longer need the original RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance, you can delete it.
You can't create an Aurora read replica if your RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance already has an Aurora read replica or if it has a cross-Region read replica.
Preparing to migrate data by using an Aurora read replica
Note
When preparing to migrate data to Aurora PostgreSQL, it's important to identify and handle unlogged tables appropriately. For more information, see Handling unlogged tables during migration.
During the migration process using Aurora read replica, updates made to the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance are asynchronously replicated to the Aurora read replica of the Replica cluster. The process uses PostgreSQL's native streaming replication functionality which stores write-ahead logs (WAL) segments on the source instance. Before starting this migration process, make sure that your instance has sufficient storage capacity by checking values for the metrics listed in the table.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The available storage space. Units: Bytes |
|
|
The size of the lag for WAL data in the replica that is lagging the most. Units: Megabytes |
|
|
The amount of time in seconds that an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster lags behind the source RDS DB instance. |
|
|
The disk space used by the transaction logs. Units: Megabytes |
For more information about monitoring your RDS instance, see Monitoring in the Amazon RDS User Guide.
Creating an Aurora read replica
You can create an Aurora read replica for an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance by using the AWS Management Console or the AWS CLI. The option to create an Aurora read replica using the AWS Management Console is available only if the AWS Region offers a compatible Aurora PostgreSQL version. That is, it's available only if there's an Aurora PostgreSQL version that is the same as the RDS for PostgreSQL version or a higher minor version in the same major version family.
To create an Aurora read replica from a source PostgreSQL DB instance
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
-
Choose the RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance that you want to use as the source for your Aurora read replica. For Actions, choose Create Aurora read replica. If this choice doesn't display, it means that a compatible Aurora PostgreSQL version isn't available in the Region.
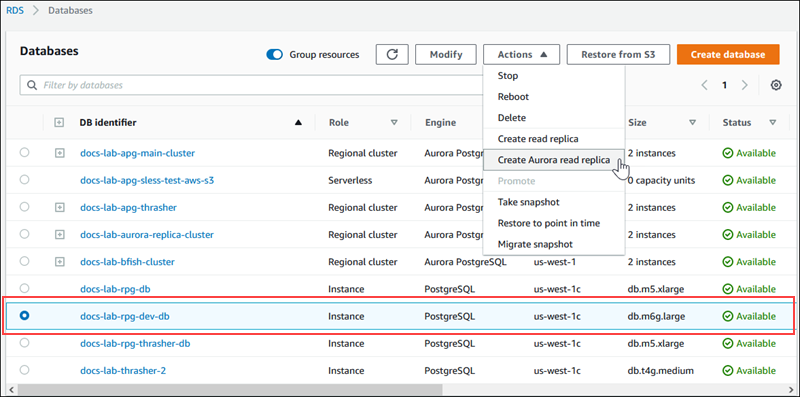
-
On the Create Aurora read replica settings page, you configure the properties for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster as shown in the following table. The Replica DB cluster is created from a snapshot of the source DB instance using the same 'master' user name and password as the source, so you can't change these at this time.
Option Description DB instance class
Choose a DB instance class that meets the processing and memory requirements primary instance in the DB cluster. For more information, see Amazon Aurora DB instance classes.
Multi-AZ deployment
Not available during the migration
DB instance identifier
Enter the name that you want to give to the DB instance. This identifier is used in the endpoint address for the primary instance of the new DB cluster.
The DB instance identifier has the following constraints:
-
It must contain 1–63 alphanumeric characters or hyphens.
-
Its first character must be a letter.
-
It can't end with a hyphen or contain two consecutive hyphens.
-
It must be unique for all DB instances for each AWS account, for each AWS Region.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Choose the VPC to host the DB cluster. Choose Create new VPC to have Amazon RDS create a VPC for you. For more information, see DB cluster prerequisites.
DB subnet group
Choose the DB subnet group to use for the DB cluster. Choose Create new DB Subnet Group to have Amazon RDS create a DB subnet group for you. For more information, see DB cluster prerequisites.
Public accessibility
Choose Yes to give the DB cluster a public IP address; otherwise, choose No. The instances in your DB cluster can be a mix of both public and private DB instances. For more information about hiding instances from public access, see Hiding a DB cluster in a VPC from the internet.
Availability zone
Determine if you want to specify a particular Availability Zone. For more information about Availability Zones, see Regions and Availability Zones.
VPC security groups
Choose one or more VPC security groups to secure network access to the DB cluster. Choose Create new VPC security group to have Amazon RDS create a VPC security group for you. For more information, see DB cluster prerequisites.
Database port
Specify the port for applications and utilities to use to access the database. Aurora PostgreSQL DB clusters default to the default PostgreSQL port, 5432. Firewalls at some companies block connections to this port. If your company firewall blocks the default port, choose another port for the new DB cluster.
DB parameter group
Choose a DB parameter group for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster. Aurora has a default DB parameter group you can use, or you can create your own DB parameter group. For more information about DB parameter groups, see Parameter groups for Amazon Aurora.
DB cluster parameter group
Choose a DB cluster parameter group for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster. Aurora has a default DB cluster parameter group you can use, or you can create your own DB cluster parameter group. For more information about DB cluster parameter groups, see Parameter groups for Amazon Aurora.
Encryption
Choose Enable encryption for your new Aurora DB cluster to be encrypted at rest. If you choose Enable encryption, also choose a KMS key as the AWS KMS key value.
Priority
Choose a failover priority for the DB cluster. If you don't choose a value, the default is tier-1. This priority determines the order in which Aurora Replicas are promoted when recovering from a primary instance failure. For more information, see Fault tolerance for an Aurora DB cluster.
Backup retention period
Choose the length of time, 1–35 days, for Aurora to retain backup copies of the database. Backup copies can be used for point-in-time restores (PITR) of your database down to the second.
Enhanced monitoring
Choose Enable enhanced monitoring to enable gathering metrics in real time for the operating system that your DB cluster runs on. For more information, see Monitoring OS metrics with Enhanced Monitoring.
Monitoring Role
Only available if you chose Enable enhanced monitoring. The AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role to use for Enhanced Monitoring. For more information, see Setting up and enabling Enhanced Monitoring.
Granularity
Only available if you chose Enable enhanced monitoring. Set the interval, in seconds, between when metrics are collected for your DB cluster.
Auto minor version upgrade
Choose Yes to enable your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster to receive minor PostgreSQL DB engine version upgrades automatically when they become available.
The Auto minor version upgrade option only applies to upgrades to PostgreSQL minor engine versions for your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster. It doesn't apply to regular patches applied to maintain system stability.
Maintenance window
Choose the weekly time range during which system maintenance can occur.
-
-
Choose Create read replica.
To create an Aurora read replica from a source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance by using the AWS CLI, you first use the create-db-cluster CLI command to create an empty Aurora DB cluster. Once the DB cluster exists, you then use the create-db-instance command to create the primary instance for your DB cluster. The primary instance is the first instance that's created in an Aurora DB cluster. In this case, it's created initially as an Aurora read replica of your RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance. When the process concludes, your RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance has effectively been migrated to an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster.
You don't need to specify the main user account (typically, postgres), its password,
or the database name. The Aurora read replica obtains these automatically from
the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance that you identify when you invoke the AWS CLI commands.
You do need to specify the engine version to use for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster and the DB instance. The version you specify should match the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance. If the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance is encrypted, you need to also specify encryption for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster primary instance. Migrating an encrypted instance to an unencrypted Aurora DB cluster isn't supported.
The following examples create an Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster named my-new-aurora-cluster
that's going to use an unencrypted RDS DB source instance. You first create the Aurora PostgreSQL
DB cluster by calling the create-db-cluster CLI command. The example shows how to use
the optional --storage-encrypted parameter to specify that the DB cluster should
be encrypted. Because the source DB isn't encrypted, the --kms-key-id is used to specify the key to use.
For more information about required and optional parameters, see the list following the example.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-cluster \ --db-cluster-identifiermy-new-aurora-cluster\ --db-subnet-group-namemy-db-subnet--vpc-security-group-idssg-11111111--engine aurora-postgresql \ --engine-versionsame-as-your-rds-instance-version\ --replication-source-identifier arn:aws:rds:aws-region:111122223333:db/rpg-source-db\ --storage-encrypted \ --kms-key-id arn:aws:kms:aws-region:111122223333:key/11111111-2222-3333-444444444444
For Windows:
aws rds create-db-cluster ^ --db-cluster-identifiermy-new-aurora-cluster^ --db-subnet-group-namemy-db-subnet^ --vpc-security-group-idssg-11111111^ --engine aurora-postgresql ^ --engine-versionsame-as-your-rds-instance-version^ --replication-source-identifier arn:aws:rds:aws-region:111122223333:db/rpg-source-db^ --storage-encrypted ^ --kms-key-id arn:aws:kms:aws-region:111122223333:key/11111111-2222-3333-444444444444
In the following list you can find more information about some of the options shown in the example. Unless otherwise specified, these parameters are required.
-
--db-cluster-identifier– You need to give your new Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster a name. -
--db-subnet-group-name– Create your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster in the same DB subnet as the source DB instance. -
--vpc-security-group-ids– Specify the security group for your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster. -
--engine-version– Specify the version to use for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster. This should be the same as or a higher minor version than the version used by your source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance. -
--replication-source-identifier– Identify your RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance using its Amazon Resource Name (ARN). For more information about Amazon RDS ARNs, see Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) in the AWS General Reference. of your DB cluster. -
--storage-encrypted– Optional. Use only when needed to specify encryption as follows:Use this parameter when the source DB instance has encrypted storage. The call to
create-db-clusterfails if you don't use this parameter with a source DB instance that has encrypted storage. If you want to use a different key for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster than the key used by the source DB instance, you need to also specify the--kms-key-id.Use if the source DB instance's storage is unencrypted but you want the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster to use encryption. If so, you also need to identify the encryption key to use with the
--kms-key-idparameter.
-
--kms-key-id– Optional. When used, you can specify the key to use for storage encryption (--storage-encrypted) by using the key's ARN, ID, alias ARN, or its alias name. This parameter is needed only for the following situations:-
To choose a different key for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster than that used by the source DB instance.
To create an encrypted cluster from an unencrypted source. In this case, you need to specify the key that Aurora PostgreSQL should use for encryption.
-
After creating the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, you then create the primary instance
by using the create-db-instance
CLI command, as shown in the following:
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-instance \ --db-cluster-identifiermy-new-aurora-cluster\ --db-instance-classdb.x2g.16xlarge\ --db-instance-identifierrpg-for-migration\ --engine aurora-postgresql
For Windows:
aws rds create-db-instance ^ --db-cluster-identifiermy-new-aurora-cluster^ --db-instance-classdb.x2g.16xlarge^ --db-instance-identifierrpg-for-migration^ --engine aurora-postgresql
In the following list, you can find more information about some of the options shown in the example.
-
--db-cluster-identifier– Specify the name of the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster that you created with thecreate-db-instancecommand in the previous steps. -
--db-instance-class– The name of the DB instance class to use for your primary instance, such asdb.r4.xlarge,db.t4g.medium,db.x2g.16xlarge, and so on. For a list of available DB instance classes, see DB instance class types. -
--db-instance-identifier– Specify the name to give your primary instance. -
--engine aurora-postgresql– Specifyaurora-postgresqlfor the engine.
To create an Aurora read replica from a source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance, first use
the RDS API operation CreateDBCluster to create a new Aurora DB cluster for
the Aurora read replica that gets created from your source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance.
When the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster is available, you then use the CreateDBInstance to create the primary instance for
the Aurora DB cluster.
You don't need to specify the main user account (typically, postgres), its password,
or the database name. The Aurora read replica obtains these automatically from
the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance specified with ReplicationSourceIdentifier.
You do need to specify the engine version to use for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster and the DB instance. The version you specify should match the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance. If the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance is encrypted, you need to also specify encryption for the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster primary instance. Migrating an encrypted instance to an unencrypted Aurora DB cluster isn't supported.
To create the Aurora DB cluster for the Aurora read replica, use the RDS API operation CreateDBCluster with the following parameters:
-
DBClusterIdentifier– The name of the DB cluster to create. -
DBSubnetGroupName– The name of the DB subnet group to associate with this DB cluster. -
Engine=aurora-postgresql– The name of the engine to use. -
ReplicationSourceIdentifier– The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the source PostgreSQL DB instance. For more information about Amazon RDS ARNs, see Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) in the Amazon Web Services General Reference. IfReplicationSourceIdentifieridentifies an encrypted source, Amazon RDS uses your default KMS key unless you specify a different key using theKmsKeyIdoption. -
VpcSecurityGroupIds– The list of Amazon EC2 VPC security groups to associate with this DB cluster. -
StorageEncrypted– Indicates that the DB cluster is encrypted. When you use this parameter without also specifying theReplicationSourceIdentifier, Amazon RDS uses your default KMS key. -
KmsKeyId– The key for an encrypted cluster. When used, you can specify the key to use for storage encryption by using the key's ARN, ID, alias ARN, or its alias name.
For more information, see CreateDBCluster
in the Amazon RDS API Reference.
Once the Aurora DB cluster is available, you can then create a primary instance for it by using the RDS API
operation CreateDBInstance with the following
parameters:
-
DBClusterIdentifier– The name of your DB cluster. -
DBInstanceClass– The name of the DB instance class to use for your primary instance. -
DBInstanceIdentifier– The name of your primary instance. -
Engine=aurora-postgresql– The name of the engine to use.
For more information, see CreateDBInstance
in the Amazon RDS API Reference.
Promoting an Aurora read replica
The migration to Aurora PostgreSQL isn't complete until you promote the Replica cluster, so don't delete the RDS for PostgreSQL source DB instance just yet.
Before promoting the Replica cluster, make sure that the RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance doesn't have any in-process transactions or other activity writing to the database. When the replica lag on the Aurora read replica reaches zero (0), you can promote the Replica cluster. For more information about monitoring replica lag, see Monitoring Aurora PostgreSQL replication and Instance-level metrics for Amazon Aurora.
To promote an Aurora read replica to an Aurora DB cluster
-
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
-
Choose the Replica cluster.

-
For Actions, choose Promote. This may take a few minutes and can cause downtime.
When the process completes, the Aurora Replica cluster is a Regional Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, with a Writer instance containing the data from the RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance.
To promote an Aurora read replica to a stand-alone DB cluster, use the promote-read-replica-db-cluster AWS CLI command.
Example
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds promote-read-replica-db-cluster \ --db-cluster-identifiermyreadreplicacluster
For Windows:
aws rds promote-read-replica-db-cluster ^ --db-cluster-identifiermyreadreplicacluster
To promote an Aurora read replica to a stand-alone DB cluster, use the RDS API operation PromoteReadReplicaDBCluster.
After you promote the Replica cluster, you can confirm that the promotion has completed by checking the event log, as follows.
To confirm that the Aurora Replica cluster was promoted
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Events.
-
On the Events page, find the name of your cluster in the Source list. Each event has a source, type, time, and message. You can see all events that have occurred in your AWS Region for your account. A successful promotion generates the following message.
Promoted Read Replica cluster to a stand-alone database cluster.
After promotion is complete, the source RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance and the Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster are unlinked. You can direct your client applications to the endpoint for the Aurora read replica. For more information on the Aurora endpoints, see Amazon Aurora endpoint connections. At this point, you can safely delete the DB instance.