翻訳は機械翻訳により提供されています。提供された翻訳内容と英語版の間で齟齬、不一致または矛盾がある場合、英語版が優先します。
MQTT
MQTT
AWS IoT Core は、MQTT プロトコルと MQTT over WSS プロトコルを使用し、クライアント ID で識別されるデバイス接続をサポートします。AWS IoT デバイス SDKsは両方のプロトコルをサポートしており、デバイスを AWS IoT Coreに接続するための推奨される方法です。 AWS IoT Device SDKs、デバイスとクライアントが サービスに接続してアクセス AWS IoT するために必要な機能をサポートしています。Device SDKs、 AWS IoT サービスが必要とする認証プロトコルと、MQTT プロトコルと MQTT over WSS プロトコルが必要とする接続 ID 要件をサポートします。 AWS Device SDK AWS IoT を使用して に接続する方法と、サポートされている言語 AWS IoT の の例へのリンクについては、「」を参照してくださいAWS IoT Device SDKs を使用した MQTT との接続。 SDKs MQTT メッセージの認証メソッドとポートマッピングの詳細については、プロトコル、ポートマッピング、認証 を参照してください。
Device AWS IoT SDKs を使用して に接続することをお勧めしますが AWS IoT、必須ではありません。ただし、 AWS IoT Device SDKs を使用しない場合は、必要な接続と通信のセキュリティを提供する必要があります。クライアントは、接続リクエストで Server Name Indication (SNI) TLS extension
クライアントが接続されると、API を使用して MQTT クライアント接続をモニタリングおよび管理できます。詳細については、「MQTT 接続の管理」を参照してください。
このトピックの内容
AWS IoT Device SDKs を使用した MQTT との接続
このセクションでは、 AWS IoT Device SDKsと、デバイスの接続方法を示すサンプルプログラムのソースコードへのリンクを示します AWS IoT。ここでリンクされているサンプルアプリは、MQTT プロトコルと MQTT over WSS AWS IoT を使用して に接続する方法を示しています。
注記
AWS IoT Device SDKsは MQTT 5 クライアントをリリースしました。
MQTT Quality of Service (QoS) オプション
AWS IoT および AWS IoT Device SDKs、MQTT Quality of Service (QoS) レベル0と 12、サポート AWS IoT していません。MQTT プロトコルのみが QoS 機能をサポートします。HTTPS は、クエリ文字列パラメータ ?qos=qos を渡すことによって QoS をサポートし、ここで、値は 0 または 1 にすることができます。
この表は、各 QoS レベルが、メッセージブローカーに発行されたメッセージ、およびメッセージブローカーによって発行されたメッセージにどのように影響するかを示しています。
|
次の QoS レベルを使用..。 |
メッセージは..。 |
コメント |
|---|---|---|
|
QoS レベル 0 |
送信回数 0 回以上 |
このレベルは、信頼できる通信リンクを介して送信されるメッセージや、見逃しても問題がないメッセージに使用する必要があります。 |
|
QoS レベル 1 |
少なくとも 1 回送信され、 |
送信者が正常に配信されたことを示す |
MQTT 永続的セッション
永続セッションは、クライアントによって承認されていない、Quality of Service (QoS) が 1 のクライアントのサブスクリプションとメッセージを保存します。コネクテッドデバイスが永続セッションに再接続すると、セッションが再開され、そのサブスクリプションが復元され、再接続前に受信され、クライアントによって確認されていないサブスクライブされたメッセージがクライアントに送信されます。
保存されたメッセージの処理は、CloudWatch メトリクスと CloudWatch Logs に記録されます。CloudWatch と CloudWatch Logs に書き込まれるエントリについては、「メッセージブローカーのメトリクス」および「キューに保存されたログエントリ」を参照してください。
永続セッションの作成
MQTT 3 で、永続セッションを作成するには、CONNECT メッセージを送信して、cleanSession フラグを 0 に設定します。CONNECT メッセージを送信したクライアントのセッションが存在しない場合は、新しい永続セッションが作成されます。クライアントのセッションが既に存在する場合は、クライアントは既存のセッションを再開します。クリーンセッションを作成するには、CONNECT メッセージを送信して cleanSession フラグを 1 に設定します。クライアントが切断してもブローカーはセッション状態を保存しません。
MQTT 5 では、Clean Start フラグと Session Expiry Interval を設定することで永続セッションを処理します。クリーンスタートは、接続セッションの開始と前のセッションの終了を制御します。Clean
Start = 1 を設定すると、新しいセッションが作成され、以前のセッションが存在する場合は終了します。Clean Start = 0 を設定すると、接続セッションは以前のセッションが存在する場合はそれを再開します。セッションの有効期限間隔は、接続セッションの終了を制御します。セッション有効期限間隔は、セッションが切断後も持続する時間を秒単位 (4 バイト整数) で指定します。Session Expiry interval = 0 に設定すると、セッションは切断時にすぐに終了します。セッションの有効期限が CONNECT メッセージで指定されていない場合、デフォルトは 0 です。
| プロパティ値 | 説明 |
|---|---|
Clean Start= 1 |
新しいセッションを作成し、以前のセッションが存在する場合は終了します。 |
Clean Start= 0 |
以前のセッションが存在する場合、セッションを再開します。 |
Session Expiry Interval> 0 |
セッションを保持する。 |
Session Expiry interval= 0 |
セッションを保持しない。 |
MQTT 5 では、Clean Start = 1 と Session
Expiry Interval = 0 を設定すると、これは MQTT 3 のクリーンセッションと同等になります。Clean Start=0 と Session Expiry Interval > 0 を設定すると、これは MQTT 3 の永続セッションと同等になります。
注記
複数の MQTT バージョン (MQTT 3 と MQTT 5) の永続セッションはサポートされていません。MQTT 3 永続セッションを MQTT 5 セッションとして再開することはできません。その逆も同様です。
永続セッション中の操作
クライアントは、connection acknowledged (CONNACK) メッセージの sessionPresent 属性を調べて、永続的セッションが存在するかどうかを確認します。sessionPresent が 1 の場合、永続セッションが存在し、クライアントの保存済みメッセージは、クライアントが CONNACK を受信した後にクライアントに配信されます。これについては、「永続セッションへの再接続後のメッセージトラフィック」を参照してください。sessionPresent が 1 の場合、クライアントは再サブスクライブする必要はありません。ただし、sessionPresent が 0 である場合は、永続的セッションが存在しないため、クライアントはそのトピックフィルターに再度サブスクライブする必要があります。
クライアントは永続セッションに参加した後も、各オペレーションにフラグを追加することなく、メッセージの発行とトピックフィルターのサブスクライブを行うことができます。
永続セッションへの再接続後のメッセージトラフィック
永続的セッションは、クライアントと MQTT メッセージブローカーの間の継続的な接続を表します。クライアントが永続的セッションを使用してメッセージブローカーに接続すると、クライアントが接続中に作成するすべてのサブスクリプションがメッセージブローカーによって保存されます。クライアントの接続が切断されると、クライアントがサブスクライブしているトピックにパブリッシュされた未確認の QoS 1 メッセージと新しい QoS 1 メッセージが保存されます。メッセージはアカウントの制限に従って保存されます。制限を超えるメッセージは削除されます。永続的なメッセージの制限の詳細については、「AWS IoT Core のエンドポイントとクォータ」を参照してください。クライアントが永続的セッションに再接続すると、すべてのサブスクリプションが回復され、保存されているすべてのメッセージがクライアントに送信されます。その際の最大レートは 1 秒あたり 10 メッセージです。MQTT 5 では、クライアントがオフラインのときにメッセージ有効期限が設定されたアウトバウンド QoS 1 が期限切れになった場合、接続が再開された後、クライアントは期限切れメッセージを受信しません。
再接続後、保存されたメッセージは、Publish
requests per second per connection 制限に達するまで、現在のメッセージトラフィックとともに、1 秒あたり 10 個の保存されたメッセージに制限されたレートでクライアントに送信されます。保存されたメッセージの配信レートは制限されているため、再接続後にセッションに 10 個を超える保存されたメッセージがある場合、すべての保存されたメッセージを配信するには数秒かかります。
共有サブスクライバーの場合、グループの少なくとも 1 人のサブスクライバーが永続セッションを使用し、QoS 1 メッセージを受信するオンラインのサブスクライバーがいない場合、メッセージはキューに入れられます。メッセージのキュー解除は、最大速度 (グループ内のアクティブなサブスクライバーごとに 1 秒あたり 20 件のメッセージ) で行われます。詳細については、「共有サブスクリプションのメッセージキュー機能」を参照してください。
永続セッションの終了
永続セッションは、次の方法で終了できます。
-
永続セッションの有効期限が経過した。永続セッションの有効期限タイマーは、クライアントの切断または接続のタイムアウトによってクライアントが切断されたことをメッセージブローカーが検出すると開始されます。
-
クライアントが
cleanSessionフラグを1に設定するCONNECTメッセージを送信した。 -
クライアントを手動で切断し、
DeleteConnectionAPI を使用してセッションをクリアします。詳細については、「MQTT 接続の管理」を参照してください。
MQTT 3 では、永続セッションの有効期限のデフォルト値は 1 時間で、これはアカウント内のすべてのセッションに適用されます。
MQTT 5 では、CONNECT パケットと DISCONNECT パケットのセッション有効期限間隔をセッションごとに設定できます。
DISCONNECT パケットのセッション有効期限間隔について:
-
現在のセッションのセッション有効期限間隔が 0 の場合、DISCONNECT パケットのセッション有効期限間隔を 0 より大きい値に設定することはできません。
-
現在のセッションのセッション有効期限間隔が 0 より大きく、DISCONNECT パケットのセッション有効期限間隔を 0 に設定した場合、セッションは DISCONNECT で終了します。
-
そうしないと、DISCONNECT パケットのセッション有効期限間隔が現在のセッションのセッション有効期限間隔を更新します。
注記
セッションの終了時にクライアントに送信されるのを待機している保存済みメッセージは破棄されます。ただし、送信できなかった場合でも、標準のメッセージングレートで請求されます。メッセージの料金の詳細については、「AWS IoT Core
の料金
永続セッションの有効期限が切れた後の再接続
有効期限が切れる前にクライアントが永続セッションに再接続しない場合、セッションは終了し、保存されたメッセージは破棄されます。セッションの有効期限が切れた後に cleanSession フラグを使用してクライアントが 0 に再接続すると、サービスは新しい永続的セッションを作成します。前のセッションのサブスクリプションまたはメッセージは、前のセッションの有効期限が切れたときに破棄されたため、このセッションでは使用できません。
永続セッションのメッセージ料金
メッセージブローカーがクライアントまたはオフラインの永続セッションにメッセージを送信 AWS アカウント すると、メッセージは に課金されます。永続セッションを持つオフラインデバイスが再接続してセッションを再開すると、保存されたメッセージがデバイスに配信され、アカウントに再び課金されます。メッセージの料金の詳細については、「AWS IoT Core の料金 - メッセージング
標準の制限引き上げプロセスを使用すると、デフォルトの永続セッションの有効期間を 1 時間引き上げることができます。セッションの有効期限を延長すると、メッセージ料金が増加する可能性があることに注意してください。これは、時間を延長するとオフラインデバイスに保存されるメッセージが増える可能性があり、標準のメッセージング料金でこれらの追加のメッセージが課金され、アカウントに請求されるためです。セッションの有効期限は概算であり、セッションはアカウントの制限よりも最長で 30 分長く持続する可能性があります。ただし、セッションはアカウントの制限より短くなることはありません。セッションの制限の詳細については、「AWS Service Quotas」を参照してください。
保持された MQTT メッセージ
AWS IoT Core は、MQTT プロトコルで説明されている RETAINフラグをサポートします。クライアントが発行する MQTT メッセージに RETAINフラグを設定すると、 はメッセージ AWS IoT Core を保存します。その後、新しいサブスクライバーに送信し、GetRetainedMessage オペレーションを呼び出して取得し、AWS IoT コンソール
保持された MQTT メッセージの使用例
-
初期設定メッセージとしての使用
保持されたMQTTメッセージは、クライアントがトピックにサブスクライブした後、クライアントに送信されます。トピックをサブスクライブするすべてのクライアントが、サブスクライブ後すぐに保持された MQTT メッセージを受信できるようにする場合は、設定された
RETAINフラッグで設定されたメッセージを発行することができます。サブスクライブしているクライアントはまた、新しい設定メッセージが発行されるたびに、その設定に対する更新が受信できます。 -
最新のメッセージとして
デバイスは、 AWS IoT Core が現在の状態メッセージを保存するように、それらに
RETAINフラッグを設定することができます。アプリケーションは、接続または再接続するときに、このトピックをサブスクライブし、保持されているメッセージのトピックをサブスクライブした直後に、最後に報告された状態を取得できます。こうすることで、現在の状態を確認するために、デバイスからの次のメッセージを待つ必要がなくなります。
このセクションの内容:
での MQTT 保持メッセージの一般的なタスク AWS IoT Core
AWS IoT Core は、 RETAINフラグが設定された MQTT メッセージを保存します。これらの保持されたメッセージは、通常の MQTT メッセージとしてトピックにサブスクライブしたすべてのクライアントに送信されると同時に、トピックへの新しいサブスクライバーに送信するために保存されます。
保持されたMQTTメッセージは、クライアントがメッセージにアクセスすることを許可するために特定のポリシーアクションが必要です。保持されるメッセージポリシーの使用例については、保持されたメッセージポリシーの例を参照してください。
このセクションでは、保持されたメッセージに関連する一般的な操作について説明します。
-
保持されたメッセージの作成
クライアントは、MQTT メッセージを発行するときにメッセージを保持するかどうかを決定します。クライアントは、デバイス SDK を使用してメッセージを発行するときに、
RETAINフラッグを設定できます。アプリケーションおよびサービスは、Publishアクションを使用して MQTT メッセージを発行するときに、RETAINフラッグを設定することができます。メッセージは、トピック名ごとに 1 つのみ保持されます。トピックに対して発行されたRETAIN フラッグが付いた新しいメッセージは、以前にトピックに送信されたあらゆる既存の保持メッセージを置き換えます。
注記
RETAINフラッグが設定された状態で予約済みトピックに対して発行することはできません。 -
保持されたメッセージのトピックのサブスクライブ
クライアントは、他の MQTT メッセージトピックと同様に、保持されるメッセージトピックをサブスクライブします。保持メッセージのトピックをサブスクライブすることによって受信される保持メッセージには、
RETAINフラグが設定されています。保持されたメッセージは、クライアントが 0 バイトのメッセージペイロードを持つ保持されたメッセージを保持されたメッセージトピックに発行 AWS IoT Core すると、 から削除されます。保持されているメッセージのトピックをサブスクライブしたクライアントも、0 バイトのメッセージを受信する事になります。
保持されたメッセージのトピックが含まれるワイルドカードトピックフィルターにサブスクライブすると、クライアントは保持されたメッセージのトピックに発行された後続のメッセージを受信できるようになりますが、トピックはサブスクライブ時に保持されたメッセージを配信しません。
注記
サブスクライブ時に保持されたメッセージを受信するには、サブスクリプションリクエストのトピックフィルターが、保持されたメッセージのトピックと完全に一致する必要があります。
保持されたメッセージのトピックへのサブスクライブ時に受信する保持されたメッセージには、
RETAINフラグが設定されています。サブスクライブしているクライアントが、サブスクライブ後に受信するメッセージに、このフラッグは設定されません。 -
保持されたメッセージの取得
保持されたメッセージが、保持されたメッセージが含まれたトピックにサブスクライブするときに、クライアントに自動配信されます。クライアントがサブスクライブ時に保持されたメッセージを受信するには、保持されたメッセージの正確なトピック名にサブスクライブする必要があります。保持されたメッセージのトピックが含まれるワイルドカードトピックフィルターにサブスクライブすると、クライアントは保持されたメッセージのトピックに発行された後続のメッセージを受信できるようになりますが、トピックはサブスクライブ時に保持されたメッセージを配信しません。
サービスとアプリは、
ListRetainedMessagesおよびGetRetainedMessageを呼び出す事によって、保持されているメッセージを一覧表示および取得する事ができます。クライアントは、
RETAINフラグを設定しなくても、保持されているメッセージのトピックにメッセージを発行できます。これは、保持されたメッセージが、トピックをサブスクライブすることで受信したメッセージと一致しないなど、予期しない結果を発生させる可能性があります。MQTT 5 では、保持メッセージにメッセージ有効期限が設定されていて保持メッセージの有効期限が切れると、そのトピックをサブスクライブする新規サブスクライバーは、サブスクリプションが成功しても保持メッセージを受信しません。
-
保持されたメッセージのトピックの一覧表示
保持されたメッセージは、
ListRetainedMessagesを呼び出す事で、リスト化する事ができ、保持されたメッセージはAWS IoT consoleに表示する事ができます。 -
保持されたメッセージの詳細情報の取得
GetRetainedMessageを呼び出す事で、保持されたメッセージの詳細を取得する事ができ、それらは、AWS IoT consoleに表示する事ができます。 -
Will メッセージの保持
デバイス接続時に作成されるMQTTウィルメッセージ
は Connect Flag bitsフィールドにWill Retainフラッグを設定する事で保持する事ができます。 -
保持されたメッセージの削除
デバイス、アプリケーション、およびサービスは、
RETAINフラグが設定されたメッセージと、削除するメッセージのトピック名に空の (0 バイト) メッセージペイロードを発行することで、保持されたメッセージを削除することができます。このようなメッセージは、保持されたメッセージを削除し AWS IoT Core、トピックへのサブスクリプションを持つクライアントに送信されますが、 によって保持されません AWS IoT Core。保持されたメッセージは、AWS IoT コンソール
で保持されたメッセージにアクセスすることによって、インタラクティブに削除することもできます。AWS IoT コンソール を使用して削除される保持されたメッセージも、保持されたメッセージのトピックにサブスクライブしているクライアントに対して 0 バイトメッセージを送信します。 保持されたメッセージの削除後に、それらを復元することはできません。クライアントは、削除されたメッセージの代わりに新しい保持されたメッセージを発行する必要があります。
-
保持されたメッセージのデバッグとトラブルシューティング
AWS IoT console
は、保持されたメッセージのトラブルシューティングに役立つツールをいくつか提供します。 -
保持されたメッセージ
のページ AWS IoT コンソールの保持されたメッセージのページは、現在の地域で、アカウントによって保存された保持されたメッセージのページ分けされたリストを提供します。このページからは、以下を実行できます。
-
メッセージペイロード、QoS、受信時間など、保持されたメッセージそれぞれの詳細を確認してください。
-
保持されたメッセージの内容を更新する。
-
保持されたメッセージを削除する。
-
-
MQTT テストクライアント
AWS IoT コンソールのMQTT テストクライアントページは、MQTT トピックにサブスクライブおよび発行する事ができます。公開オプションは、どのようにデバイスが動作するかをシミュレートするために発行するメッセージにRETAIN フラグを設定してくれます。MQTT テストクライアントを使用して、クライアント接続インターフェイスを介して管理する接続されたクライアントからのメッセージをモニタリングすることもできます。クライアント接続の管理の詳細については、「MQTT 接続の管理」を参照してください。
一部の予期しない結果は、保持されたメッセージの実装方法に関するこれらの側面の結果である可能性があります AWS IoT Core。
-
保持されるメッセージの制限
アカウントが保持されたメッセージの最大数を保存すると、 は、保持されたメッセージの一部が削除され、保持されたメッセージ数が制限を下回るまで、RETAIN セットと 0 バイトを超えるペイロードで発行されたメッセージに対してスロットリングされたレスポンス AWS IoT Core を返します。
-
保持されたメッセージの配信順序
保持されたメッセージとサブスクライブされたメッセージの配信順序は保証されていません。
-
請求と保持メッセージ
AWS IoT
コンソールを使用して、または Publish を呼び出して、クライアントからの RETAIN フラグが設定されたメッセージを発行すると、「AWS IoT Core 料金 - メッセージング
クライアント、 AWS IoT コンソール、または を呼び出して保持されたメッセージを取得すると、通常の API GetRetainedMessage 使用料に加えてメッセージング料金が発生します。追加料金については、AWS IoT Core
料金表-メッセージング
予期せずデバイス接続が切断された際、発行されるMQTTウィルメッセージ
メッセージコストの詳細については、AWS IoT Core の料金 – メッセージング
保持されたMQTTメッセージと永続MQTTセッションの比較
保持メッセージと永続セッションは、MQTT の標準機能であり、オフライン中に発行されたメッセージをデバイスが受信できるようにします。保持されたメッセージは、永続的なセッションから発行する事ができます。このセクションでは、これらの機能の主な側面と、これらがどのように連携するかについて説明します。
|
保持されたメッセージ |
永続セッション |
|
|---|---|---|
|
主な特徴 |
保持されたメッセージは、接続後に、デバイスを設定または大規模なグループにデバイスを通知するために使用することができます。 保持されたメッセージは、デバイスが再接続した後で、トピックに発行された最後のメッセージのみを受信するようにしたい場合にも使用できます。 |
永続セッションは、接続が断続的で、いくつかの重要なメッセージを受信しない可能性があるデバイスに役立ちます。 デバイスは、永続セッションで接続して、オフライン中に送信されたメッセージを受信できます。 |
|
例 |
保持メッセージを使用すると、デバイスがオンラインになったときに、デバイスの環境に関する設定情報が提供できます。初期設定には、サブスクライブする他のメッセージのトピックのリストや、ローカルタイムゾーン設定方法についての情報を含める事ができます。 |
接続が断続的なセルラーネットワーク経由で接続するデバイスは、デバイスがネットワーク圏外またはセルラー無線をオフにする必要があるときに送信される重要なメッセージを受信し損ねる事がないように、永続セッションを使う事ができます。 |
|
トピックへの初回サブスクライブ時に受信したメッセージ |
保持されたメッセージを持つトピックをサブスクライブすると、最新の保持されたメッセージが受信されます。 |
保持されたメッセージがないトピックをサブスクライブすると、そのトピックに発行されるまでメッセージを受信しません。 |
|
再接続後にサブスクライブされたトピック |
永続セッションを使用しない場合、クライアントは再接続後にトピックをサブスクライブする必要があります。 |
サブスクライブされたトピックは、再接続後に復元されます。 |
|
再接続後に受信したメッセージ |
保持されたメッセージを持つトピックをサブスクライブすると、最新の保持されたメッセージが受信されます。 |
デバイスが切断されている間に QOS = 1 で発行され、QOS = 1 でサブスクライブされたすべてのメッセージは、デバイスの再接続後に送信されます。 |
|
データ/セッションの有効期限 |
MQTT 3 では、保持されたメッセージに有効期限はありません。これらは、置き換えられる、または削除されるまで保存されます。MQTT 5 では、保持されたメッセージは、設定したメッセージ有効期限を過ぎると期限切れになります。詳細については、「メッセージの有効期限」を参照してください。 |
永続セッションは、クライアントがタイムアウト期間内に再接続しない場合、期限切れになります。永続セッションの有効期限が切れると、QOS = 1 で発行され、デバイスが切断されている間に QOS = 1 でサブスクライブされたクライアントのサブスクリプションと保存済みメッセージが削除されます。期限切れのメッセージは配信されません。永続的なセッションでのセッションの有効期限の詳細については、「MQTT 永続的セッション」を参照してください。。 |
永続セッションについては、MQTT 永続的セッション を参照してください。
Retreated Messages を使用すると、発行するクライアントは、接続後にメッセージを保持してデバイスに配信するかどうか、デバイスに以前のセッションがあったかどうかを判断します。メッセージを保存する選択はパブリッシャーが行い、保存されたメッセージは、QoS 0 または QoS 1 のサブスクリプションをサブスクライブする現在および将来のすべてのクライアントに配信されます。保持されたメッセージで一度に維持できるのは、特定のトピックに関するメッセージ 1 つだけです。
アカウントが保持されるメッセージを最大数保存している場合、 AWS IoT Core は、保持されたメッセージの一部が削除され、保持されたメッセージの数が上限を下回るまで、RETAIN が設定され、ペイロードが 0 バイトを超える状態で発行されたメッセージに対してスロットルされたレスポンスを返します。
MQTT 保持メッセージと AWS IoT デバイスシャドウ
保持されたメッセージとデバイスシャドウのどちらでもデバイスからのデータが保持されますが、どちらも動作が異なり、達成する目的も異なります。このセクションでは、それらの類似点と相違点について説明します。
|
保持されたメッセージ |
Device Shadow |
|
|---|---|---|
|
メッセージペイロードに事前定義された構造またはスキーマがある |
実装によって定義されている通り。MQTT は、そのメッセージペイロードの構造やスキーマを指定しません。 |
AWS IoT は、特定のデータ構造をサポートしています。 |
|
メッセージペイロードを更新すると、イベントメッセージが生成されます |
保持されたメッセージを発行すると、サブスクライブしているクライアントにメッセージが送信されますが、追加の更新メッセージは生成されません。 |
Device Shadow を更新すると、変更を説明するメッセージを更新します。 |
|
メッセージの更新に番号が付けられる |
保持されたメッセージには、自動的に番号が付けられません。 | デバイスシャドウドキュメントには、自動のバージョン番号とタイムスタンプがあります。 |
|
メッセージペイロードは、モノのリソースにアタッチされます |
保持されたメッセージは モノの リソースに添付されません。 |
デバイスシャドウは モノの リソースにアタッチされます。 |
|
メッセージペイロードの個々の要素の更新 |
メッセージの個々の要素は、メッセージペイロード全体を更新しないと変更できません。 |
デバイスシャドウドキュメントの個々の要素は、デバイスシャドウドキュメント全体を更新しなくても更新できます。 |
|
クライアントは、サブスクリプションすると直ちにメッセージデータを受信します |
クライアントは、保持メッセージを持つトピックをサブスクライブすると、保持メッセージを自動的に受信します。 |
クライアントはデバイスシャドウ更新にサブスクライブできますが、現在のステータスを意図的にリクエストする必要があります。 |
|
インデックス作成と検索可能性 |
保持されたメッセージは、検索用にインデックス化されません。 |
フリートインデックス作成は、検索および集計のためにDevice Shadowデータをインデックス化します |
MQTT の Last Will and Testament (LWT) メッセージ
Last Will and Testament (LWT) は MQTT の機能です。LWT を使用すると、クライアントはブローカーがクライアント定義のトピックに発行し、開始されていない切断が発生したときにそのトピックをサブスクライブしているすべてのクライアントに送信するメッセージを指定できます。クライアントが指定するメッセージは LWT メッセージまたは Will メッセージと呼ばれ、クライアントが定義するトピックは Will トピックと呼ばれます。デバイスがブローカーに接続するときに LWT メッセージを指定できます。これらのメッセージは、接続中に Connect Flag bits フィールドで Will
Retain フラグを設定することで保持できます。例えば、Will Retain フラグが 1 に設定されている場合、Will メッセージはブローカーの関連する Will トピックに保存されます。詳細については、「Will メッセージ
クライアント接続を管理する場合、クライアントを切断するときに LWT メッセージを発行するかどうかを制御できます。詳細については、「MQTT 接続の管理」を参照してください。
ブローカーは、開始されていない切断が発生するまで Will メッセージを保存します。その場合、ブローカーは Will トピックにサブスクライブしているすべてのクライアントにメッセージを発行して切断を通知します。MQTT DISCONNECT メッセージを使用してクライアントが開始した切断により、クライアントがブローカーから切断した場合、ブローカーは保存されている LWT メッセージを発行しません。それ以外の場合は、すべて LWT メッセージが送信されます。切断処理は非同期であるため、再接続時に LWT メッセージが順番にディスパッチされるとは限りません。接続状態の検出精度を向上させるために、ライフサイクルイベントを使用することをお勧めします。これらのイベントでは、タイムスタンプやバージョン番号などの属性が提供されるため、順不同のイベントを管理することができます。ブローカーが LWT メッセージを送信するときの切断シナリオの完全なリストについては、「接続/切断イベント」を参照してください。
connectAttributes の使用
ConnectAttributes を使用すると、PersistentConnect や LastWill などの IAM ポリシーの接続メッセージで使用する属性を指定できます。ConnectAttributes を使用すると、デフォルトではデバイスに新機能へのアクセスを許可しないポリシーを構築できます。これは、デバイスが侵害された場合に役立ちます。
connectAttributes でサポートされる機能は以下のとおりです。
PersistentConnect-
PersistentConnect機能を使用して、クライアントとブローカー間の接続が中断されたときに、接続中にクライアントが作成したすべてのサブスクリプションを保存します。 LastWill-
LastWill機能を使用して、クライアントが予期せず切断したときにメッセージをLastWillTopicに発行します。
デフォルトでは、ポリシーには非永続的な接続があり、この接続用に渡される属性はありません。永続的な接続が必要な場合は、IAM ポリシーで永続的な接続を指定する必要があります。
クライアント接続を管理するときに、接続されたクライアントの接続属性とセッションの設定を表示することができます。詳細については、「MQTT 接続の管理」を参照してください。
ConnectAttributes 例については、接続ポリシーの例を参照してください。
MQTT 5 がサポートしている機能
AWS IoT Core MQTT 5 のサポートは MQTT v5.0 仕様
AWS IoT Core は、次の MQTT 5 機能をサポートしています。
共有サブスクリプション
AWS IoT Core は、MQTT 3.1.1 と MQTT 5 の両方の共有サブスクリプションをサポートしています。共有サブスクリプションを使用すると、1 つのトピックへのサブスクリプションを複数のクライアントで共有できますが、そのトピックに公開されたメッセージをランダム配信を使って受信できるのは 1 つのクライアントのみです。共有サブスクリプションでは、多数のサブスクライバー間で MQTT メッセージを効果的に負荷分散できます。例えば、同じトピックを発行するデバイスが 1,000 台あり、それらのメッセージを処理するバックエンドアプリケーションが 10 台あるとします。その場合、バックエンドアプリケーションは同じトピックをサブスクライブでき、それぞれが共有トピックにデバイスによって発行されたメッセージをランダムに受信します。これにより、それらのメッセージの負荷を効果的に「共有」できます。共有サブスクリプションでは、耐障害性も向上します。バックエンドアプリケーションの接続が切断されると、ブローカーはグループ内の残りのサブスクライバーに負荷を分散します。すべてのサブスクライバーが切断されると、メッセージはキューに入れられます。
メッセージキュー機能は、メッセージ配信の信頼性を高めるために、MQTT 3.1.1 と MQTT 5 のどちらの接続でも共有サブスクリプションで使用できます。
共有サブスクリプションを使用するには、クライアントは次のように共有サブスクリプションのトピックフィルターをサブスクライブします。
$share/{ShareName}/{TopicFilter}
-
$shareは共有サブスクリプションのトピックフィルターを示すリテラル文字列です。トピックフィルターは$shareで始まる必要があります。 -
{ShareName}はサブスクライバーのグループが使用する共有名を指定する文字列です。共有サブスクリプションのトピックフィルターは、ShareNameを含み、その後に/の文字が続く必要があります。{ShareName}には、/、+、または#などの文字を含めないでください。{ShareName}の最大長は UTF-8 の 128 文字です。 -
{TopicFilter}は、非共有サブスクリプションとして、同じトピックフィルターの構文に従います。{TopicFilter}の最大長は UTF-8 の 256 文字です。 -
$share/{ShareName}/{TopicFilter}に必要な 2 つのスラッシュ (/) は、トピックおよびトピックフィルターのスラッシュの最大数の制限に含まれていません。
同じ {ShareName}/{TopicFilter} を持つサブスクリプションは、同じ共有サブスクリプショングループに属します。共有サブスクリプショングループは複数作成できますが、グループあたりの共有サブスクリプションの制限を超えないようにしてください。詳細については、AWS 全般のリファレンスの「AWS IoT Core エンドポイントとクォータ」を参照してください。
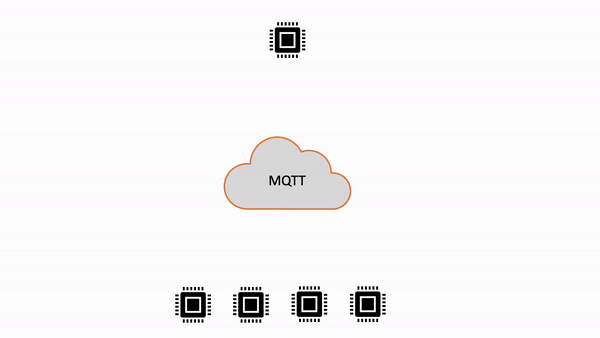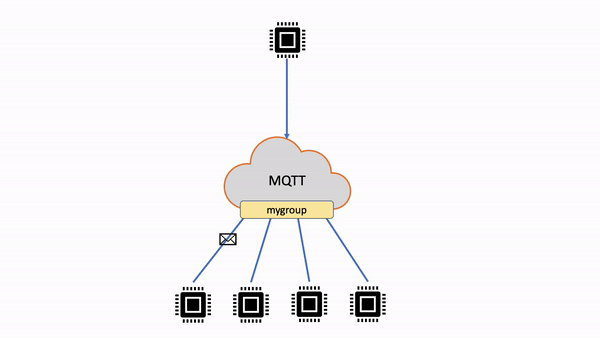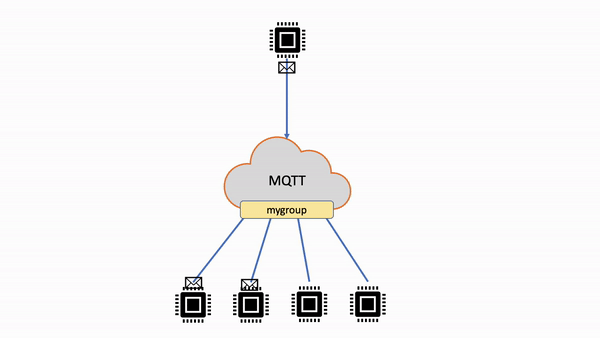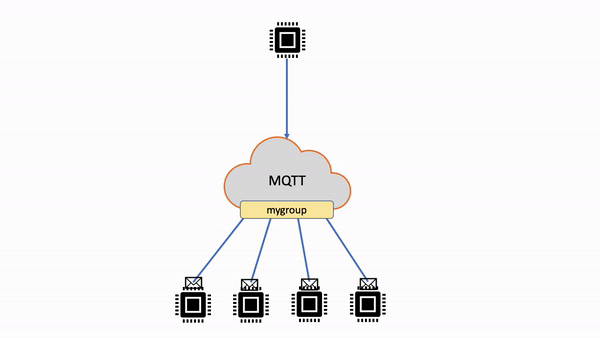
次の表では、非共有サブスクリプションと共有サブスクリプションを比較しています。
| サブスクリプション | 説明 | トピックフィルターの例 |
|---|---|---|
| 非共有サブスクリプション | 各クライアントは、発行されたメッセージを受信するための個別のサブスクリプションを作成します。メッセージがトピックに発行されると、そのトピックのすべてのサブスクライバーがメッセージのコピーを受け取ります。 |
|
| 共有サブスクリプション | 複数のクライアントが 1 つのトピックへのサブスクリプションを共有できますが、そのトピックに公開されたメッセージをランダム配信で受信できるのは 1 つのクライアントのみです。 |
|
| 非共有サブスクリプションのフロー | 共有サブスクリプションのフロー |
|---|---|
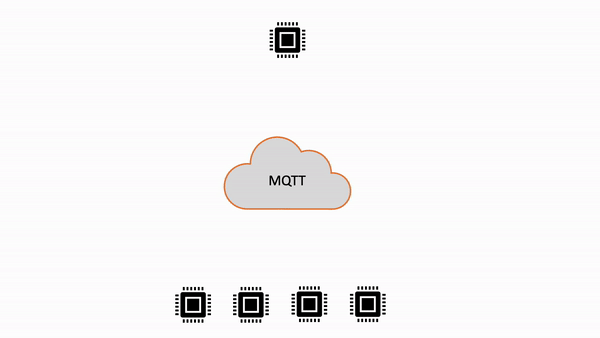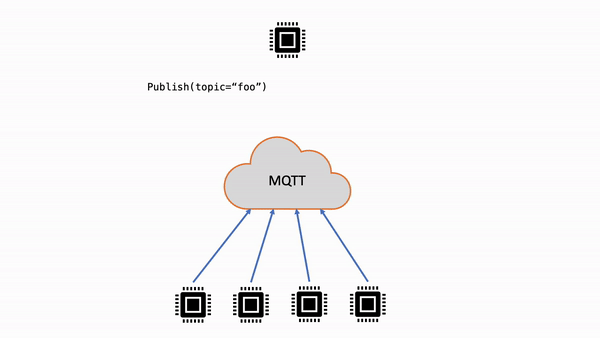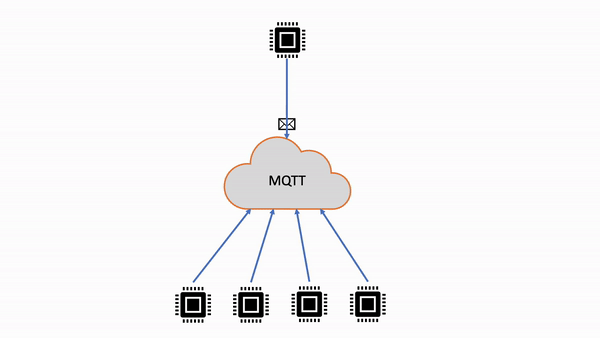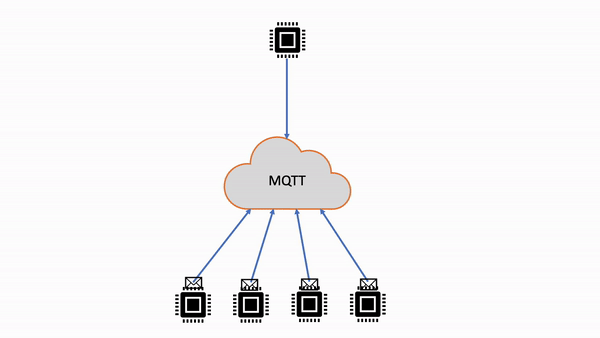
|
|
共有サブスクリプションを使用する際の重要な注意事項
-
共有サブスクライバーグループが永続セッションサブスクライバーで構成されている場合、共有グループ内のすべてのサブスクライバーが切断されると、またはサブスクライバーが接続毎の 1 秒あたりの発行リクエスト数の制限に違反すると、共有サブスクリプショングループに発行された未確認の QoS 1 メッセージと未配信の QoS 1 メッセージがキューに入れられます。詳細については、「共有サブスクリプションのメッセージキュー機能」を参照してください。
-
共有サブスクリプショングループに発行された QoS 0 メッセージは、障害が発生すると削除されます。
-
共有サブスクリプションは、共有サブスクライバーグループの一部としてトピックパターンにサブスクライブしている場合、保持されたメッセージを受信しません。共有サブスクライバーを持つトピックで発行され、
RETAINフラグが設定されているメッセージは、他の発行メッセージと同様に共有サブスクライバーに配信されます。 -
共有サブスクリプションにワイルドカード文字 (# または +) が含まれている場合、1 つのトピックに一致する共有サブスクリプションが複数存在する可能性があります。その場合、メッセージブローカーは発行メッセージをコピーし、一致する共有サブスクリプションごとにランダムなクライアントに送信します。共有サブスクリプションのワイルドカードの動作を、次の図で示しています。
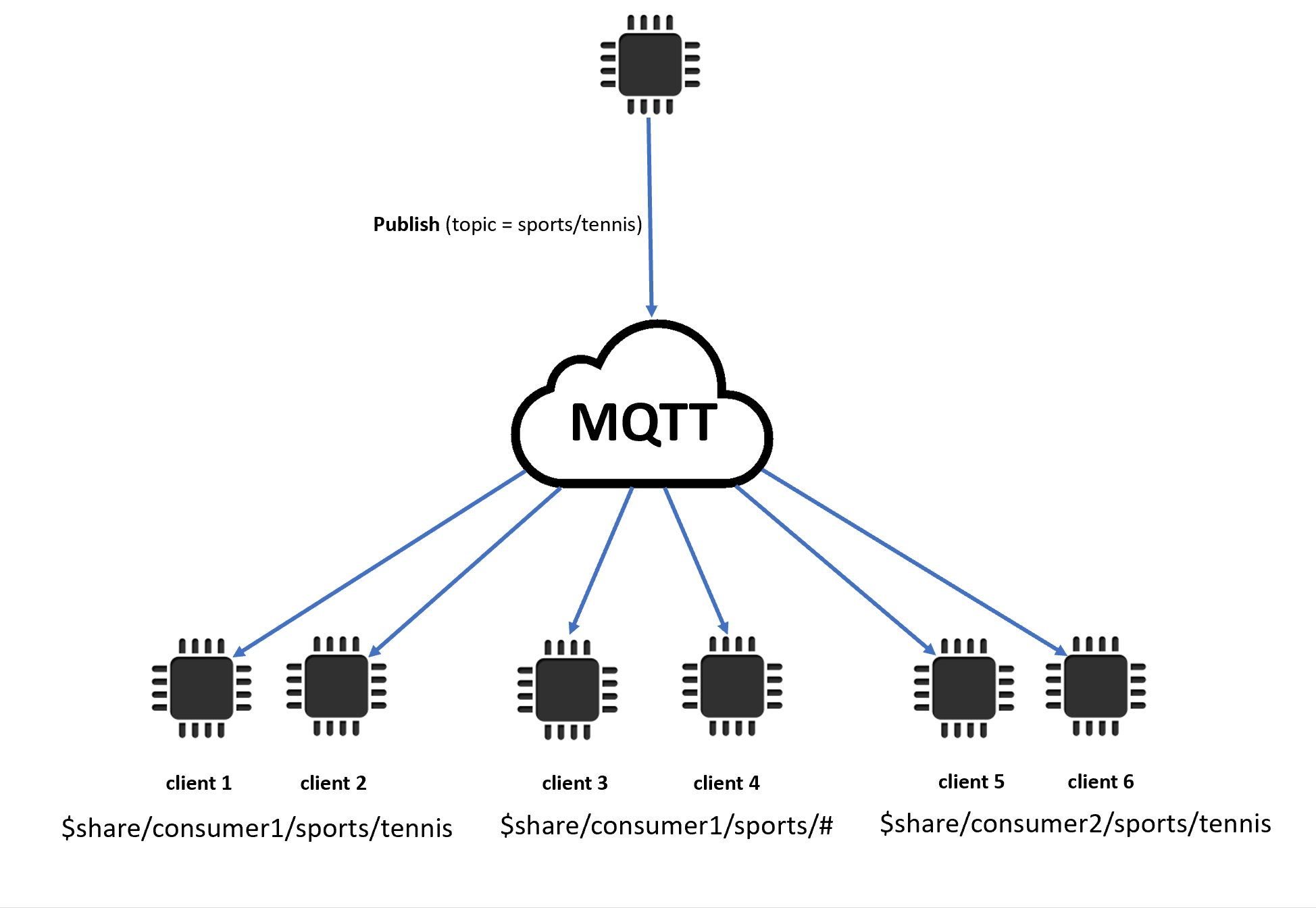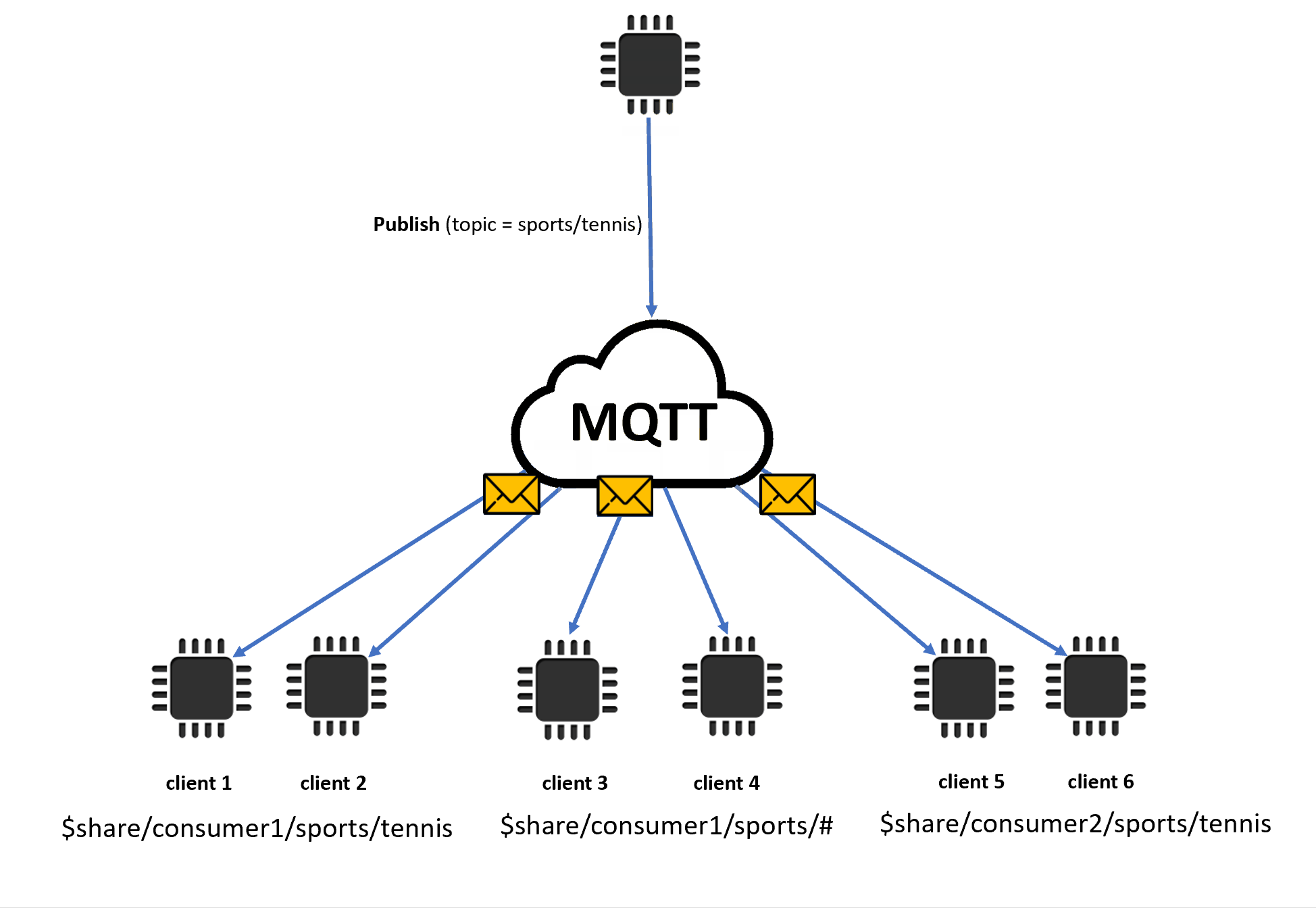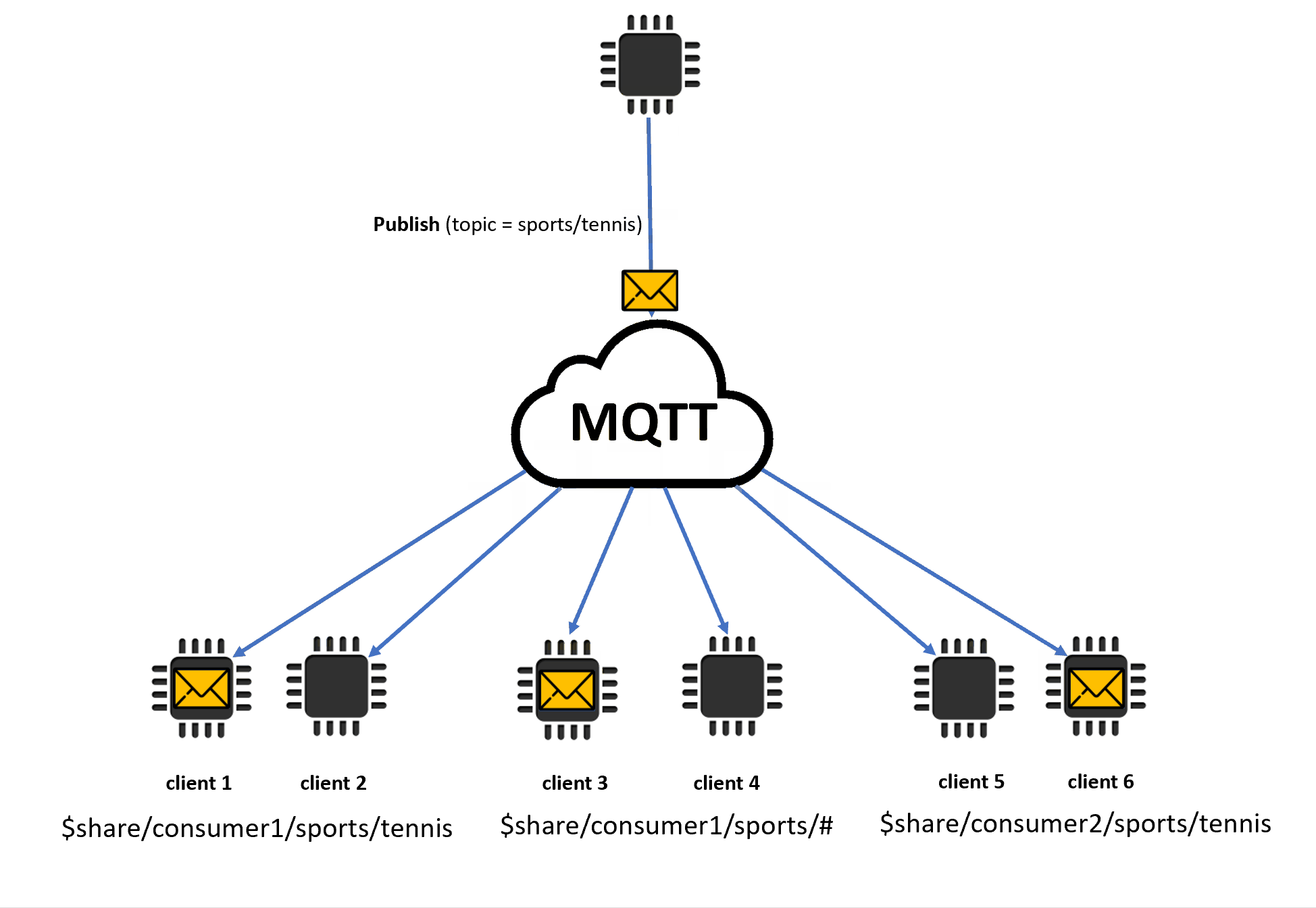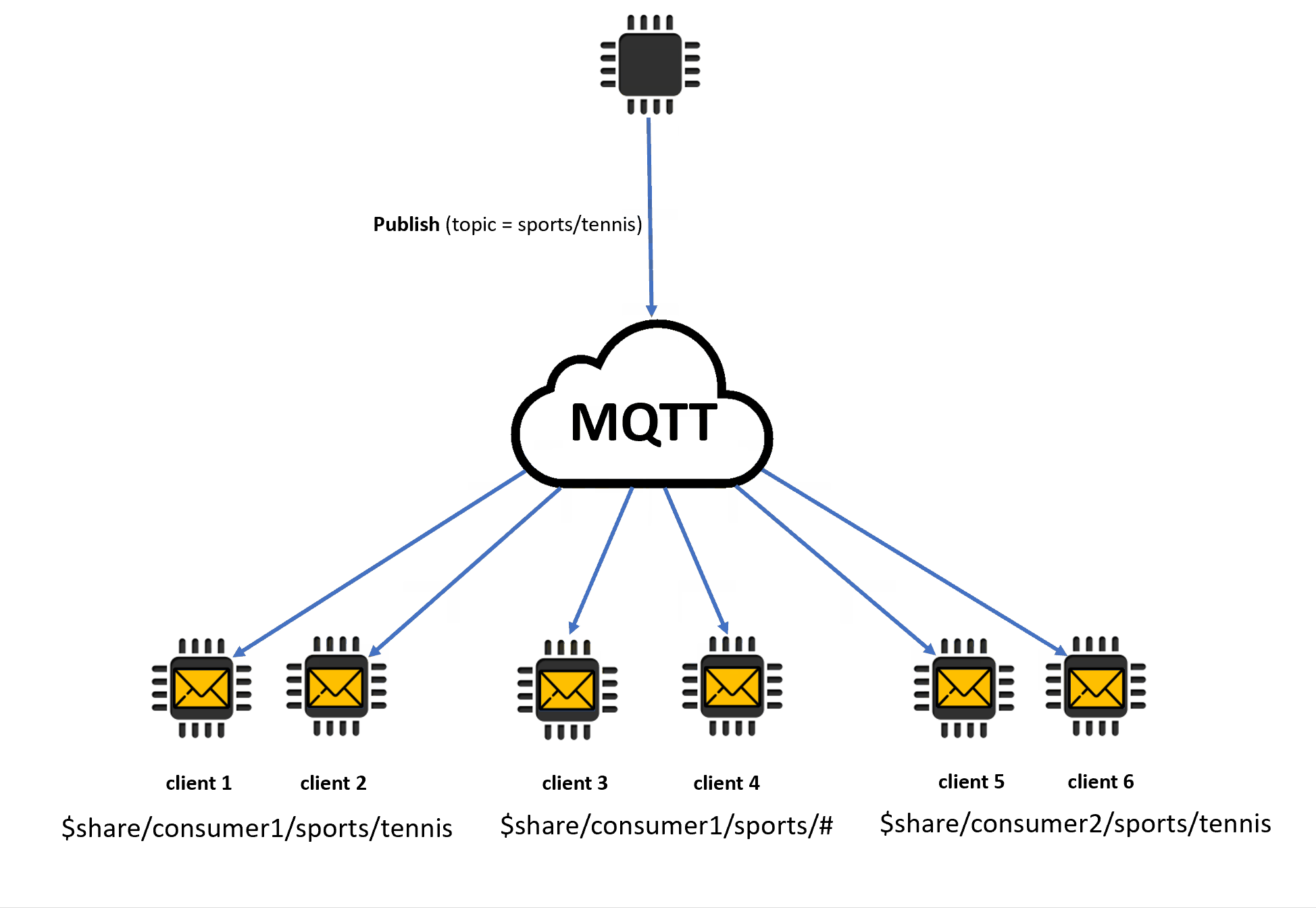
この例では、発行中の MQTT トピック
sports/tennisと一致する共有サブスクリプションが 3 つあります。メッセージブローカーは発行されたメッセージをコピーし、一致する各グループのランダムなクライアントにメッセージを送信します。クライアント 1 とクライアント 2 はサブスクリプション
$share/consumer1/sports/tennisを共有します。クライアント 3 とクライアント 4 はサブスクリプション
$share/consumer1/sports/#を共有します。クライアント 5 とクライアント 6 はサブスクリプション
$share/consumer2/sports/tennisを共有します。
共有サブスクリプションの制限について詳しくは、「AWS 全般のリファレンス」の「AWS IoT Core エンドポイントとクォータ」を参照してください。AWS IoT コンソール
共有サブスクリプションのメッセージキュー機能
メッセージ配信の信頼性を高めるために、共有サブスクリプションには、オンラインサブスクライバーが不在のときにメッセージを保存するメッセージキュー機能が含まれています。共有サブスクリプショングループに永続セッションを持つメンバーが少なくとも 1 つ含まれている場合に、キュー機能はグループに対して有効になります。メッセージを配信する場合、オンラインのメンバーが受信者として選択されます。QoS 1 メッセージは、オンラインでメンバーが見つからなかった場合、またはサブスクライバーが Publish requests per second per connection 制限を超えた場合にキューに入れられます。キューに入れられたメッセージは、既存のメンバーが永続セッションを再開するか、新しいメンバーがグループに参加すると配信されます。キューに入れられたメッセージは、サブスクリプションに従ってサブスクライバーに配信されるその他のメッセージとともに、アクティブなグループサブスクライバーごとに 1 秒あたり最大 20 件 (キューに入れられたメッセージ) の速度で配信されます。
デフォルトでは、キューに入れられたメッセージ保持は Persistent Session expiry period クォータに従います。ただし、インバウンド発行メッセージでメッセージの有効期限間隔 (MEI) が設定されている場合、MEI が優先されます。MEI が存在する場合は、永続セッションの有効期限に関係なく、MEI によってメッセージの保持期間が決定されます。
メッセージキューのレートは Queued messages per second per account クォータに応じて制限され、メッセージ数は Maximum number of queued messages per shared subscription group クォータによって制限されます。クォータを表示および管理するには、Service Quotas コンソール
AWS/Usage 名前空間で を検索してキュー CloudWatch ApproximateQueueDepthをモニタリングするか、次の CLI コマンドを使用して、各共有サブスクリプショングループのキュー深度に関連付けられたメトリクスを一覧表示できます。
aws cloudwatch list-metrics --namespace "AWS/Usage" --dimensions Name=Resource,Value='ApproximateQueueDepth'
これらの制限を超えると、制限に達する前にキューに入れられたメッセージのみが保持されます。制限を超える新しい受信メッセージは削除されます。システムは、キューに入れられ古いたメッセージを新しいメッセージに置き換えません。
メッセージのキューは、CloudWatch メトリクスと CloudWatch Logs に記録されます。CloudWatch と CloudWatch Logs に書き込まれるエントリについては、「メッセージブローカーのメトリクス」および「キューに保存されたログエントリ」を参照してください。キューに登録されたメッセージは、標準のメッセージング料金で請求されます。メッセージの料金の詳細については、「AWS IoT Core の料金
共有サブスクリプショングループのセッションライフサイクル
クリーンセッションがグループにサブスクライブすると、そのセッションはグループのオンラインメンバーになります。サブスクリプションを解除または切断すると、クリーンセッションはグループから離脱します。
永続セッションがグループにサブスクライブすると、そのセッションはグループのオンラインメンバーになります。切断しても、グループには残りますが、グループのオフラインメンバーになります。再接続すると、再びオンラインメンバーになります。永続セッションは、明示的にサブスクリプションを解除したとき、または切断後に期限切れになったときにグループから離脱ます。
クリーンスタートとセッションの有効期限
クリーンスタートとセッション有効期限を使用すると、永続セッションをより柔軟に処理できます。クリーンスタートフラグは、既存のセッションを使用せずにセッションを開始する必要があるかどうかを示します。セッションの有効期限間隔は、切断後にセッションを保持する期間を示します。セッションの有効期限間隔は、切断時に変更できます。詳細については、「MQTT 永続的セッション」を参照してください。
すべての ACK の理由コード
理由コードを使用すると、エラーメッセージをより簡単にデバッグまたは処理できます。理由コードは、ブローカーとのやり取りのタイプ (サブスクライブ、発行、確認) に基づいてメッセージブローカーから返されます。詳細については、「MQTT 理由コード」を参照してください。MQTT 理由コードの完全なリストについては、「MQTT v5 の仕様
トピックエイリアス
トピック名は、2 バイトの整数であるトピックエイリアスに置き換えることができます。トピックエイリアスを使用すると、トピック名の送信を最適化して、計測データサービスのデータコストを削減できます。 には、トピックエイリアスのデフォルト制限が 8 つ AWS IoT Core あります。詳細については、AWS 全般のリファレンスの「AWS IoT Core エンドポイントとクォータ」を参照してください。
メッセージの有効期限
発行されたメッセージには、メッセージの有効期限値を追加できます。これらの値は、メッセージの有効期限間隔 (MEI) を秒単位で表します。その間隔内にメッセージがサブスクライバーに送信されない場合、メッセージは期限切れになり、削除されます。メッセージの有効期限値を設定しない場合、メッセージは期限切れになりません。
アウトバウンドでは、サブスクライバーは有効期限の残り時間を含むメッセージを受信します。例えば、受信した発行メッセージの有効期限が 30 秒で、20 秒後にサブスクライバーにルーティングされた場合、メッセージの有効期限フィールドは 10 に更新されます。サブスクライバーが受信したメッセージの MEI が 0 に更新されている可能性があります。これは、残り時間が 999 ms 以下になるとすぐに 0 に更新されるためです。
では AWS IoT Core、最小 MEI は 1 です。クライアント側から間隔を 0 に設定すると、1 に調整されます。メッセージの最大有効期間は 604800 (7 日) です。これより大きい値はすべて最大値に調整されます。
クロスバージョン通信では、メッセージの有効期限切れの動作は、インバウンド発行メッセージの MQTT バージョンによって決定されます。例えば、MQTT5 経由で接続されたセッションから送信されたメッセージの有効期限付きのメッセージは、MQTT3 セッションでサブスクライブされているデバイスでは期限切れになる可能性があります。次の表は、メッセージ有効期限が次のタイプの発行メッセージをどのようにサポートするかを示しています。
| メッセージの種類を発行する | メッセージの有効期限間隔 |
|---|---|
| 通常発行 | サーバーが指定された時間内にメッセージの配信に失敗すると、期限切れのメッセージは削除され、サブスクライバーはそのメッセージを受信できなくなります。これには、デバイスが QoS 1 メッセージを発行していない場合などが含まれます。 |
| Retain | 保持されたメッセージの有効期限が切れて新しいクライアントがそのトピックをサブスクライブした場合、クライアントはサブスクライブ時にメッセージを受信しません。 |
| ラストウィル | ラストウィルメッセージの間隔は、クライアントが接続を切断し、サーバーがラストウィルメッセージをサブスクライバーに配信しようとした後に始まります。 |
| キューに追加済みのメッセージ | クライアントがオフラインのときにメッセージ有効期限間隔が設定されたアウトバウンド QoS 1 の有効期限が切れた場合、永続セッションが再開されても、クライアントは期限切れメッセージを受信しません。 |
その他の MQTT 5 の機能
サーバー切断
接続が切断されると、サーバーは事前にクライアントに DISCONNECT を送信して、切断の理由コードを添えて接続の終了を通知できます。
リクエスト/レスポンス
発行者は、受信時に発行者が指定したトピックへの返信を受信者に送信するようリクエストできます。
最大パケットサイズ
クライアントとサーバーは、サポートする最大パケットサイズを個別に指定できます。
ペイロード形式とコンテンツタイプ
メッセージを発行するときのペイロード形式 (バイナリ、テキスト) とコンテンツタイプを指定できます。これらはメッセージの受信者に転送されます。
MQTT 5 プロパティ
MQTT 5 プロパティは、セッションの有効期限やリクエスト/レスポンスパターンなどの MQTT 5 の新機能をサポートするために、MQTT 標準に追加された重要な機能です。では AWS IoT Core、アウトバウンドメッセージのプロパティを転送するルールを作成するか、HTTP Publish を使用して新しいプロパティの一部を含む MQTT メッセージを発行できます。
次の表に、 が AWS IoT Core サポートするすべての MQTT 5 プロパティを示します。
| プロパティ | 説明 | 入力タイプ | パケット |
|---|---|---|---|
| ペイロード形式インジケータ | ペイロードが UTF-8 としてフォーマットされているかどうかを示すブール値。 | バイト | PUBLISH、CONNECT |
| コンテンツタイプ | ペイロードの内容を説明する UTF-8 文字列。 | UTF-8 文字列 | PUBLISH、CONNECT |
| レスポンストピック | 受信者がリクエスト/レスポンスフローの一部として公開すべきトピックを説明する UTF-8 文字列。トピックにはワイルドカード文字を含めないでください。 | UTF-8 文字列 | PUBLISH、CONNECT |
| 相関データ | リクエストメッセージの送信者が、レスポンスメッセージの対象となるリクエストを識別するために使用するバイナリデータ。 | バイナリ | PUBLISH、CONNECT |
| ユーザーのプロパティ | UTF-8 文字列。このプロパティは、1 つのパケットに複数回表示されることがあります。受信者は、送信されたのと同じ順序でキーと値のペアを受け取ります。 | UTF-8 文字列ペア | 接続、発行、ウィルのプロパティ、サブスクライブ、切断、サブスクライブ解除 |
| メッセージの有効期限間隔 | メッセージの有効期限間隔を秒単位で表す 4 バイトの整数。存在しない場合、メッセージの有効期限はありません。 | 4 バイト整数 | PUBLISH、CONNECT |
| セッションの有効期限間隔 |
セッションの有効期限を秒単位で表す 4 バイトの整数。 は最大 7 日間 AWS IoT Core をサポートし、デフォルトの最大は 1 時間です。設定した値がアカウントの最大値を超える場合、 AWS IoT Core は CONNACK で調整された値を返します。 |
4 バイト整数 | CONNECT、CONNACK、DISCONNECT |
| 割り当てられたクライアント識別子 | クライアント ID がデバイスによって指定されていない場合 AWS IoT Core に によって生成されるランダムなクライアント ID。ランダムクライアント ID は、現在ブローカーによって管理されている他のセッションでは使用されていない新しいクライアント ID でなければなりません。 | UTF-8 文字列 | CONNACK |
| サーバーキープアライブ | サーバーによって割り当てられたキープアライブ時間を表す 2 バイトの整数。クライアントがキープアライブ時間を超えて非アクティブになると、サーバーはクライアントを切断します。 | 2 バイト整数 | CONNACK |
| 問題情報をリクエストする | 失敗した場合に理由文字列とユーザープロパティのどちらが送信されるかを示すブール値。 | バイト | CONNECT |
| 最大受信 | PUBACK を受信せずに送信できる PUBLISH QOS > 0 パケットの最大数を表す 2 バイトの整数。 | 2 バイト整数 | CONNECT、CONNACK |
| トピックエイリアスの最大数 | この値は、トピックエイリアスとして受け入れられる最大値を示します。デフォルトは 0 です。 | 2 バイト整数 | CONNECT、CONNACK |
| 最大の QoS | が AWS IoT Core サポートする QoS の最大値。デフォルトは 1 です。 AWS IoT Core では、QoS 2 はサポートされていません。 | バイト | CONNACK |
| 保持可能 |
AWS IoT Core メッセージブローカーが保持されたメッセージをサポートしているかどうかを示すブール値。デフォルトは 1 です。 |
バイト | CONNACK |
| 最大パケットサイズ | が AWS IoT Core 受け入れて送信する最大パケットサイズ。128 KB を超えることはできません。 | 4 バイト整数 | CONNECT、CONNACK |
| ワイルドカードによるサブスクリプションが利用可能 |
AWS IoT Core メッセージブローカーがワイルドカードサブスクリプション利用可能をサポートしているかどうかを示すブール値。デフォルトは 1 です。 |
バイト | CONNACK |
| サブスクリプション ID が利用可能 |
AWS IoT Core メッセージブローカーが Subscription Identifier Available をサポートしているかどうかを示すブール値。デフォルトは 0 です。 |
バイト | CONNACK |
MQTT 理由コード
MQTT 5 では、理由コードレスポンスによるエラーレポートが改善されました。 は、パケット別にグループ化された以下を含む理由コードを返す AWS IoT Core ことができます。MQTT 5 でサポートされている理由コードの完全なリストについては、「MQTT 5 specifications
| 値 | 16 進数 | 理由コード名 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0x00 | Success | 接続を受け入れます。 |
| 128 | 0x80 | 未指定のエラー | サーバーは障害の理由を明らかにしたくないか、他の理由コードのいずれにも当てはまりません。 |
| 133 | 0x85 | クライアント ID が無効です | クライアント ID は有効な文字列ですが、サーバーでは許可されていません。 |
| 134 | 0x86 | ユーザー名またはパスワードが間違っています | サーバーは、クライアントによって指定されたユーザー名またはパスワードを受け入れません。 |
| 135 | 0x87 | 権限がありません | クライアントは接続する権限がありません。 |
| 144 | 0x90 | トピック名が無効です | ウィルトピック名は正しい形式になっていますが、サーバーでは受け入れられません。 |
| 151 | 0x97 | リソースクォータ | 実装または管理で指定されている制限を超過しました。 |
| 155 | 0x9B | QoS はサポートされていません | サーバーは Will QoS で設定された QoS をサポートしていません。 |
| 値 | 16 進数 | 理由コード名 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0x00 | Success | メッセージは受け入れられます。QoS 1 メッセージの発行が続行されます。 |
| 128 | 0x80 | 未指定のエラー | 受信者は発行を承認しませんが、理由を明らかにしたくないか、他の値のいずれとも一致しません。 |
| 135 | 0x87 | 権限がありません | PUBLISH は許可されていません。 |
| 144 | 0x90 | トピック名が無効です | トピック名の形式は正しくありませんが、クライアントまたはサーバーでは受け入れられません。 |
| 145 | 0x91 | 使用中のパケット識別子 | パケット ID は既に使用されています。これは、クライアントとサーバー間のセッション状態が一致していないことを示している可能性があります。 |
| 151 | 0x97 | リソースクォータ | 実装または管理で指定されている制限を超過しました。 |
| 値 | 16 進数 | 理由コード名 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 129 | 0x81 | 正しい形式でないパケット | 受信したパケットはこの仕様に準拠していません。 |
| 130 | 0x82 | プロトコルエラー | 予期しないパケットまたは順不同のパケットが受信されました。 |
| 135 | 0x87 | 権限がありません | リクエストは承認されていません。 |
| 139 | 0x8B | サーバーのシャットダウン | サーバーはシャットダウン中です。 |
| 141 | 0x8D | キープアライブタイムアウト | キープアライブ時間の 1.5 倍の間、パケットが受信されなかったため、接続は閉じられます。 |
| 142 | 0x8E | セッションの引き継ぎ | 同じ ClientID を使用する別の接続が接続されたため、この接続は閉じられました。 |
| 143 | 0x8F | トピックフィルターが無効です | トピックフィルターは正しく構成されていますが、サーバーでは受け入れられません。 |
| 144 | 0x90 | トピック名が無効です | トピック名は正しい形式ですが、このクライアントまたはサーバーでは受け入れられません。 |
| 147 | 0x93 | 受信上限を超えました | クライアントまたはサーバーが、PUBACK または PUBCOMP を送信していない発行の受信数が最大受信数を超えています。 |
| 148 | 0x94 | トピックのエイリアスが無効です | クライアントまたはサーバーが、CONNECT または CONNACK パケットで送信した最大トピックエイリアスを超えるトピックエイリアスを含む PUBLISH パケットを受信しました。 |
| 151 | 0x97 | リソースクォータ | 実装または管理で指定されている制限を超過しました。 |
| 152 | 0x98 | 管理アクション | 管理アクションにより接続が切断されました。 |
| 155 | 0x9B | QoS はサポートされていません | クライアントが CONNACK の最大 QoS で指定した QoS よりも大きい QoS を指定しました。 |
| 161 | 0xA1 | サブスクリプション ID はサポートされていません | サーバーはサブスクリプション ID をサポートしていません。サブスクリプションは受け付けられません。 |
| 値 | 16 進数 | 理由コード名 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0x00 | 付与された QoS 0 | サブスクリプションが承認され、送信される最大 QoS は QoS 0 になります。これはリクエストされた QoS よりも低い可能性があります。 |
| 1 | 0x01 | 付与された QoS 1 | サブスクリプションが承認され、送信される最大 QoS は QoS 1 になります。これはリクエストされた QoS よりも低い可能性があります。 |
| 128 | 0x80 | 未指定のエラー | サブスクリプションは受け付けられず、サーバーは理由を明らかにしたくないか、他の理由コードのいずれも適用されません。 |
| 135 | 0x87 | 権限がありません | クライアントには、このサブスクライブを行う権限がありません。 |
| 143 | 0x8F | トピックフィルターが無効です | トピックフィルターは正しく構成されていますが、このクライアントでは使用できません。 |
| 145 | 0x91 | 使用中のパケット識別子 | 指定されたパケット識別子は既に使用されています。 |
| 151 | 0x97 | リソースクォータ | 実装または管理で指定されている制限を超過しました。 |
| 値 | 16 進数 | 理由コード名 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0x00 | Success | サブスクリプションが削除されます。 |
| 128 | 0x80 | 未指定のエラー | サブスクリプション解除を完了できませんでした。サーバーは理由を明らかにしたくないか、他の理由コードのいずれも適用されません。 |
| 143 | 0x8F | トピックフィルターが無効です | トピックフィルターは正しく構成されていますが、このクライアントでは使用できません。 |
| 145 | 0x91 | 使用中のパケット識別子 | 指定されたパケット識別子は既に使用されています。 |
AWS IoT MQTT 仕様との違い
メッセージブローカーの実装は MQTT v3.1.1 仕様
-
AWS IoT は MQTT 3 の次のパケットをサポートしていません: PUBREC、PUBREL、PUBCOMP。
-
AWS IoT は MQTT 5 の次のパケットをサポートしていません: PUBREC、PUBREL、PUBCOMP、AUTH。
-
AWS IoT は MQTT 5 サーバーリダイレクトをサポートしていません。
-
AWS IoT は、MQTT サービス品質 (QoS) レベル 0 および 1 のみをサポートします。 AWS IoT は、QoS レベル 2 での発行またはサブスクライブをサポートしていません。QoS 2 レベル 2 がリクエストされると、メッセージブローカーは PUBACK または SUBACK を送信しません。
-
では AWS IoT、QoS レベル 0 のトピックにサブスクライブすると、メッセージが 0 回以上配信されます。メッセージは複数回配信される場合があります。複数回配信されるメッセージは、異なるパケット ID を使用して送信される場合があります。これらの場合、DUP フラグは設定されません。
-
接続リクエストに応答するとき、メッセージブローカーは CONNACK メッセージを送信します。このメッセージには、接続で前のセッションを再開するかどうかを示すフラグが含まれます。
-
追加の制御パケットまたは切断リクエストを送信する前に、クライアントは、 AWS IoT メッセージブローカーから CONNACK メッセージがデバイスで受信されるのを待機する必要があります。
-
クライアントがトピックをサブスクライブすると、メッセージブローカーは SUBACK を送信してから、クライアントが新しい一致するメッセージの受信を開始するまでに、遅延が生じる場合があります。
-
クライアントが、トピックをサブスクライブするために、
#トピックフィルターでワイルドカード文字を使用する場合、トピック階層において、そのレベルとそれ以下の文字列はすべて一致します。ただし、親トピックは照合されません。例えば、トピックへのサブスクリプションsensor/#は、トピックsensor/sensor/temperaturesensor/temperature/room1に発行されたメッセージを受信しますが、sensorに発行されたメッセージは受信しません。 ワイルドカードの使用の詳細については、「トピック名フィルター」を参照してください。 -
メッセージブローカーは、クライアント ID を使用して、各クライアントを識別します。クライアント ID は MQTT ペイロードの一部としてクライアントからメッセージブローカーに渡されます。クライアント ID が同じ 2 つのクライアントがメッセージブローカーに同時に接続することはできません。あるクライアントが別のクライアントのクライアント ID を使用してメッセージブローカーに接続すると、新しいクライアント接続が受け入れられ、以前に接続されたクライアントは切断されます。API を使用してクライアントを手動で切断することもできます。詳細については、「MQTT 接続の管理」を参照してください。
-
まれに、メッセージブローカーは、パケット ID が異なる同じ論理 PUBLISH メッセージを再送信する場合があります。
-
ワイルドカード文字を含むトピックフィルターへのサブスクリプションでは、保持されたメッセージの受信ができません。保持されたメッセージを受信するには、サブスクライブリクエストに、保持されたメッセージのトピックと完全に一致するトピックフィルターが含まれている必要があります。
-
メッセージブローカーはメッセージと ACK の正しい受信順序を確保するわけではありません。
-
AWS IoT は、仕様とは異なる制限を持つことができます。詳細については、AWS IoT リファレンスガイドの「AWS IoT Core メッセージブローカーとプロトコルの制限とクォータ」を参照してください。
-
MQTT DUP フラグはサポートされていません。
MQTT 接続の管理
AWS IoT Core にはAPIs が用意されています。これらの機能により、 AWS IoT クライアントフリートをより詳細に制御でき、接続の問題のトラブルシューティングに役立ちます。
DeleteConnection API
DeleteConnection API を使用して、クライアント ID を指定 AWS IoT Core して MQTT デバイスを から切断します。 IDs クライアントを切断すると、 はクライアントを AWS IoT Core メッセージブローカーから AWS IoT Core 切断し、オプションでセッション状態をクリーンアップして Last Will and Testament (LWT) メッセージを抑制できます。
DeleteConnection API を呼び出すと、 AWS IoT Core はクリーンな切断を確保するためにいくつかのアクションを実行します。 AWS IoT Core まず、 は MQTT 切断メッセージをクライアントに送信して MQTT セッションを終了します。その後、サービスは基盤となる TCP/TLS ソケットを閉じます。
メッセージブローカーはデバイスに DISCONNECT パケットを送信し、切断理由 API_INITIATED_DISCONNECT でライフサイクルイベントを発行します。これにより、切断が開始されたのが、クライアントやネットワークの問題ではなく、API を介したものである場合を特定することができます。これらのイベントは、可視性、トラブルシューティング、監査の目的でモニタリングできます。たとえば、 AWS IoT ルールを使用してこれらのイベントを処理し、クライアントが切断された日時と理由を追跡できます。
cleanSession パラメータを に設定するとtrue、 はすべてのサブスクリプションとキューに入れられたメッセージを含むクライアントのセッション状態 AWS IoT Core を削除します。セッションをクリーンアップすると、永続セッションは終了します。クライアントが永続セッションで、かつ preventWillMessage パラメータが false に設定されている場合、サービスは、使用可能な場合、LWT メッセージをディスパッチします。これは、計画的なメンテナンス実施時に役立ちます。
DeleteConnection API を呼び出すと、切断プロセスはすぐに開始されますが、クライアントが切断を認識する正確なタイミングは、ネットワーク条件とクライアントの実装によって異なります。ほとんどのクライアントは数秒以内に切断を検出しますが、ネットワーク接続が不十分な場合、クライアントが切断されていることを認識するまでに時間がかかることがあります。
注記
切断を強制的に行うと、クライアントは新しいセッション状態で再認証および再認可する必要があります。API コール自体は、クライアントの再接続を妨げません。そのため、必要に応じて、DeleteConnection API コールを発行する前に、クライアントの認証情報またはポリシーをさらに変更する必要があります。
料金については、「AWS IoT Core の料金
ユースケース
DeleteConnection API は、問題のある動作を示したり、リソースを過剰に消費したりするクライアントの誤った動作を管理するのに役立ちます。切断を強制することで、クライアントが適切な認証と認可を使用して接続を再確立することができ、リソース消費の問題の解消につながります。
クライアントリダイレクトのシナリオでも、この API は役立ちます。クライアントを別のエンドポイントまたは にリダイレクトする必要がある場合は AWS リージョン、それらをプログラムで切断し、DNS 設定を変更して別の AWS IoT Core エンドポイントに再接続できます。この API は、渋滞した接続を解決したり、通常のオペレーションを妨げている可能性のある問題のあるセッション状態をクリアしたりするのに役立ちます。
API パラメータ
DeleteConnection API は、次のパラメータを受け入れます。
- clientId (必須)
-
切断する MQTT クライアントの一意の識別子。これは URL パスで指定されます。クライアント ID はドル記号 ($) で始めることはできません。
注記
MQTT クライアント ID には、HTTP リクエストで無効な文字を含めることができます。
DeleteConnectionAPI を使用する場合は、MQTT では有効でも、HTTP では無効なクライアント ID の文字をすべて URL エンコード (パーセントエンコード) する必要があります。これには、スペース、スラッシュ (/)、UTF-8 の文字などの特殊文字が含まれます。たとえば、スペースは %20、スラッシュは %2F、UTF-8 の文字の ü は %C3%BC になります。適切なエンコーディングにより、HTTP ベースの API コールで MQTT クライアント ID が正しく送信されます。 - cleanSession (オプション)
-
切断時にクライアントのセッション状態を削除するかどうかを指定します。サブスクリプションやキューに入れられたメッセージを含むすべてのセッション情報を削除するには、
trueに設定します。セッション状態を保持するには、falseに設定します。デフォルトでは、これはfalseに設定されます (セッション状態を保持します)。クリーンセッションの場合、このパラメータは無視されます。 - preventWillMessage (オプション)
-
切断時に利用可能な場合、 が Last Will and Testament (LWT) メッセージを AWS IoT Core ディスパッチするかどうかを制御します。LWT メッセージをディスパッチしないようにする場合は、
trueに設定します。ディスパッチを許可するには、falseに設定します。デフォルトでは、これはfalseに設定されます (使用可能な場合は LWT をディスパッチします)。
API 構文
DeleteConnection API は次の HTTP リクエスト形式を使用します。
DELETE /connections/<clientId>?cleanSession=<cleanSession>&preventWillMessage=<preventWillMessage> HTTP/1.1
リクエストの例:
// Basic disconnect (preserves session, allows LWT message) DELETE /connections/myDevice123 HTTP/1.1 // Disconnect and clear session DELETE /connections/myDevice123?cleanSession=TRUE HTTP/1.1 // Disconnect, clear session, and prevent LWT message DELETE /connections/myDevice123?cleanSession=TRUE&preventWillMessage=TRUE HTTP/1.1
リクエストが成功すると、レスポンス本文なしで「HTTP 200 OK」が返されます。
注記
AWS 署名バージョン 4 がリクエストに署名するために使用するサービス名は、iotdevicegateway です。aws iot describe-endpoint --endpoint-type iot:Data-ATS コマンドを使用すると、エンドポイントを見つけることができます。
必要なアクセス許可
DeleteConnection API を使用するには、次の IAM アクセス許可が必要です。
iot:DeleteConnection
リソースベースのポリシーを使用して、特定のクライアント ID にこのアクセス許可の適用範囲を指定できます。例えば、次のようになります。
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "iot:DeleteConnection", "Resource": "arn:aws:iot:region:account:client/myDevice*" } ] }
重要な考慮事項
切断されたクライアントは、再接続を防ぐために追加のロジックが実装されていない限り、すぐに再接続を試みることができます。切断オペレーションは現在の接続のみを終了し、再接続することをを妨げるものではありません。再接続を防ぐ必要がある場合は、クライアント側のロジックを実装するか、デバイスの認証情報を無効にすることを検討してください。
レート制限は、標準の API レート制限の一部として AWS IoT Core API に適用されます。一括切断オペレーションを計画するときは、これらの制限を考慮し、スロットリングを避けるために適切な再試行ロジックとバッチ処理戦略を実装してください。詳細については、「AWS IoT Core エンドポイントとクォータ」を参照してください。
エラーレスポンス
DeleteConnection API は次のエラーレスポンスを返すことができます。
- InvalidRequestException
-
リクエストが無効である。これは、クライアント ID 形式が無効である場合、ドル記号 ($) がプレフィックスとして含まれている場合、または必須パラメータが欠落している場合に発生する可能性があります。
- ResourceNotFoundException
-
指定されたクライアント ID が存在しないか、現在接続されておらず、永続セッションがありません。
- UnauthorizedException
-
この操作を実行する権限がありません。必要な
iot:DeleteConnection権限があることを確認してください。 - ForbiddenException
-
発信者にはリクエストを行う権限がありません。これは、IAM アクセス許可が不十分であるか、リソースベースのポリシー制限が原因で発生する可能性があります。
- ThrottlingException
-
レートが制限を超えています。API コールの頻度を減らし、エクスポネンシャルバックオフを使用して適切な再試行ロジックを実装してください。
- InternalFailureException
-
予期しないエラーが発生しました。しばらくしてからリクエストを再試行してください。
- ServiceUnavailableException
-
サービスが一時的に使用できません しばらくしてからリクエストを再試行してください。