Automatically rotate IAM user access keys at scale with AWS Organizations and AWS Secrets Manager
Tracy Hickey, Michael Davie, Arvind Patel, Laura Seletos, and Gaurav Verma, Amazon Web Services
Summary
Important: As a best practice, AWS recommends that you use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles instead of IAM users with long-term credentials such as access keys. The approach documented in this pattern is intended only for legacy implementations that require long-lived AWS API credentials. For these implementations, we still recommend that you consider options for using short-term credentials, such as using Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance profiles or IAM Roles Anywhere. The approach in this article is only for cases where you are unable to change to using short-term credentials immediately, and you require long-term credentials to be rotated on a schedule. With this approach, you are responsible for periodically updating your legacy application code or configuration to use the rotated API credentials. |
|---|
Access keys are long-term credentials for an IAM user. Regularly rotating your IAM credentials helps prevent a compromised set of IAM access keys from accessing components in your AWS account. Rotating IAM credentials is also an important part of security best practices in IAM.
This pattern helps you automatically rotate IAM access keys by using AWS CloudFormation templates, which are provided in the GitHub IAM key rotation
The pattern supports deployment in a single account or multiple accounts. If you’re using AWS Organizations, this solution identifies all AWS account IDs within your organization and dynamically scales as accounts are removed or new accounts are created. The centralized AWS Lambda function uses an assumed IAM role to locally run the rotation functions across multiple accounts that you select.
New IAM access keys are generated when existing access keys are 90 days old.
The new access keys are stored as a secret in AWS Secrets Manager. A resource-based policy allows only the specified IAM principal to access and retrieve the secret. If you choose to store keys in the management account, the keys for all accounts are stored in the management account.
The email address assigned to the owner of the AWS account where the new access keys were created receives a notification.
The previous access keys are deactivated at 100 days old, and then deleted at 110 days old.
A centralized email notification is sent to the AWS account owner.
Lambda functions and Amazon CloudWatch automatically perform these actions. You can then retrieve the new access key pair and replace them in your code or applications. The rotation, deletion, and deactivation periods can be customized.
Prerequisites and limitations
At least one active AWS account.
AWS Organizations, configured and set up (see tutorial).
Permissions to query AWS Organizations from your management account. For more information, see AWS Organizations and service-linked roles in the AWS Organizations documentation.
An IAM principal that has permissions to launch the AWS CloudFormation template and associated resources. For more information, see Grant self-managed permissions in the AWS CloudFormation documentation.
An existing Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket to deploy the resources.
Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) moved out of the sandbox. For more information, see Moving out of the Amazon SES sandbox in the Amazon SES documentation.
If you choose to run Lambda in a virtual private cloud (VPC), the following resources, which should be created before you run the main CloudFormation template:
A VPC.
A subnet.
Endpoints for Amazon SES, AWS Systems Manager, AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS), Amazon S3, and AWS Secrets Manager. (You can run the endpoint template that's provided in the GitHub IAM key rotation
repository to create these endpoints.)
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) user and password stored in AWS Systems Manager parameters (SSM parameters). Parameters must match the main CloudFormation template parameters.
Architecture
Technology stack
Amazon CloudWatch
Amazon EventBridge
IAM
AWS Lambda
AWS Organizations
Amazon S3
Architecture
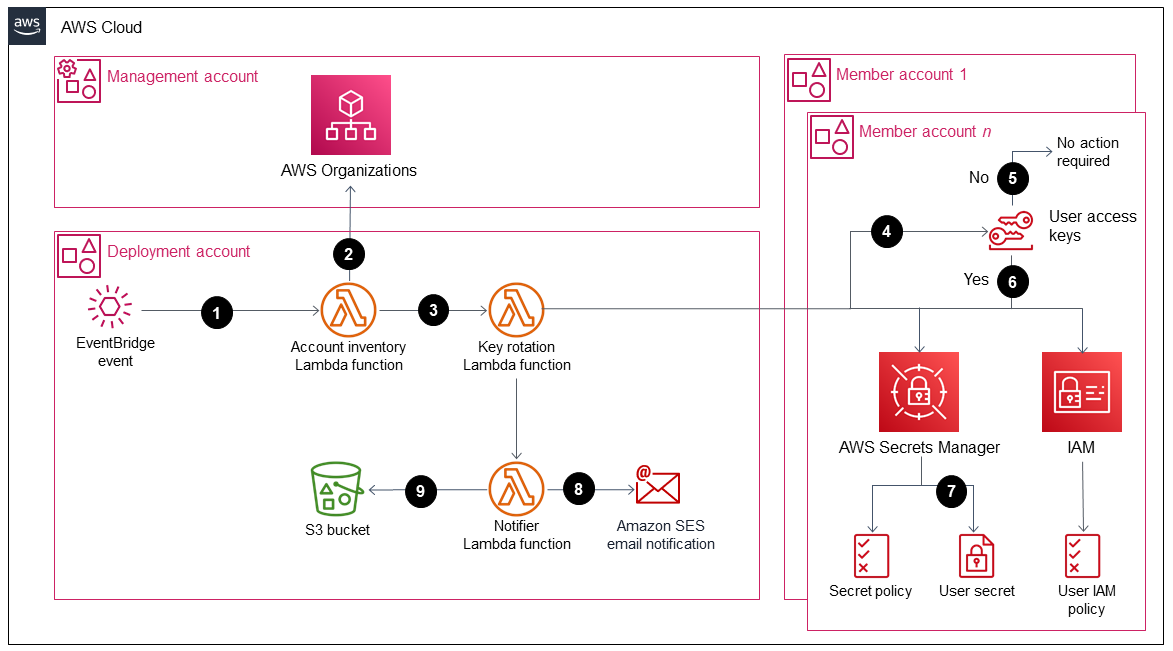
The following diagrams show the components and workflows for this pattern. The solution supports two scenarios for storing the credentials: in a member account and in the management account.
Option 1: Store the credentials in a member account
Option 2: Store the credentials in the management account

The diagrams show the following workflow:
An EventBridge event initiates an
account_inventoryLambda function every 24 hours.This Lambda function queries AWS Organizations for a list of all AWS account IDs, account names, and account emails.
The
account_inventoryLambda function initiates anaccess_key_auto_rotationLambda function for each AWS account ID and passes the metadata to it for additional processing.The
access_key_auto_rotationLambda function uses an assumed IAM role to access the AWS account ID. The Lambda script runs an audit against all users and their IAM access keys in the account.If the IAM access key's age hasn’t exceeded the best practice threshold, the Lambda function takes no further action.
If the IAM access key's age has exceeded the best practice threshold, the
access_key_auto_rotationLambda function determines which rotation action to perform.When action is required, the
access_key_auto_rotationLambda function creates and updates a secret in AWS Secrets Manager if a new key is generated. A resource-based policy is also created that allows only the specified IAM principal to access and retrieve the secret. In the case of option 1, the credentials are stored in Secrets Manager in the respective account. In the case of option 2 (if theStoreSecretsInCentralAccountflag is set to True), the credentials are stored in Secrets Manager in the management account.A
notifierLambda function is initiated to notify the account's owner of the rotation activity. This function receives the AWS account ID, account name, account email, and the rotation actions that were performed.The
notifierLambda function queries the deployment S3 bucket for an email template and dynamically updates it with the relevant activity metadata. The email is then sent to the account owner's email address.
Notes:
This solution supports resiliency in multiple Availability Zones. However, it doesn’t support resiliency in multiple AWS Regions. For support in multiple Regions, you can deploy the solution in the second Region and keep the key rotation EventBridge rule disabled. You can then enable the rule when you want to run the solution in the second Region.
You can run this solution in audit mode. In audit mode, IAM access keys aren’t modified, but an email is sent to notify users. To run the solution in audit mode, set the
DryRunFlagflag to True when you run the key rotation template or in the environment variable for theaccess_key_auto_rotationLambda function.
Automation and scale
The CloudFormation templates that automate this solution are provided in the GitHub IAM key rotationASA-iam-key-auto-rotation-iam-assumed-roles.yaml CloudFormation template in multiple accounts instead of deploying the solution individually to each member account.
Tools
AWS services
Amazon CloudWatch helps you monitor the metrics of your AWS resources and the applications you run on AWS in real time.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) helps you securely manage access to your AWS resources by controlling who is authenticated and authorized to use them.
AWS Lambda is a compute service that helps you run code without needing to provision or manage servers. It runs your code only when needed and scales automatically, so you pay only for the compute time that you use.
AWS Organizations is an account management service that helps you consolidate multiple AWS accounts into an organization that you create and centrally manage.
AWS Secrets Manager helps you replace hardcoded credentials in your code, including passwords, with an API call to Secrets Manager to retrieve the secret programmatically.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is a cloud-based object storage service that helps you store, protect, and retrieve any amount of data.
Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) helps you send and receive emails by using your own email addresses and domains.
Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) helps you coordinate and manage the exchange of messages between publishers and clients, including web servers and email addresses.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) helps you launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you’ve defined. This virtual network resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS.
Amazon VPC endpoints provide an interface to connect to services powered by AWS PrivateLink, including many AWS services. For each subnet that you specify from your VPC, an endpoint network interface is created in the subnet and assigned a private IP address from the subnet address range.
Code
The required AWS CloudFormation templates, Python scripts, and runbook documentation are available in the GitHub IAM key rotation
Template | Deploy in | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment account | This is the main template for the solution. |
| Single or multiple member accounts where you want to rotate the credentials | You can use CloudFormation stack sets to deploy this template in multiple accounts. |
| Central/management account | Use this template to keep an inventory of accounts in AWS Organizations. |
| Deployment account | Use this template to automate the creation of endpoints only if you want to run the Lambda functions in a VPC (set the |
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Choose your deployment S3 bucket. | Sign in to the AWS Management Console for your account, open the Amazon S3 console | Cloud architect |
Clone the repository. | Clone the GitHub IAM key rotation | Cloud architect |
Upload the files to the S3 bucket. | Upload the cloned files to your S3 bucket. Use the following default folder structure to copy and paste all cloned files and directories: NoteYou can customize this folder structure in the CloudFormation templates. | Cloud architect |
Modify the email template. | Modify the | Cloud architect |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Launch the CloudFormation template for key rotation. |
| Cloud architect |
Launch the CloudFormation template for assumed roles. |
| Cloud architect |
Launch the CloudFormation template for account inventory. |
| Cloud architect |
Launch the CloudFormation template for VPC endpoints. | This task is optional.
| Cloud architect |
Related resources
Security best practices in IAM (IAM documentation)
AWS Organizations and service-linked roles (AWS Organizations documentation)
Selecting a stack template (CloudFormation documentation)
Working with AWS CloudFormation StackSets (CloudFormation documentation)