Security FAQ
AMS provides 24/7/365 follow-the-sun support through global operation centers. Dedicated AMS operations engineers actively monitor dashboards and incident queues. Usually, AMS manages your accounts through automation. In rare circumstances that require specific troubleshooting or deployment expertise, an AMS operations engineer might access your AWS accounts.
The following are common questions about the security best practices, controls, access models, and audit mechanisms that AMS Accelerate uses when an AMS operations engineer or automation accesses your accounts.
When do AMS operations engineers access my environments?
AMS operations engineers don't have persistent access to your accounts or instances. Access to customer accounts is granted to AMS operators only for justifiable business use cases, such as alerts, incidents, change requests, and so on. Access is documented in AWS CloudTrail logs.
For access justification, triggers, and trigger initiators, see AMS customer account access triggers.
What roles do AMS operations engineers assume when they access my accounts?
In the rare cases (~5%) that require human intervention in your environment, AMS operations engineers log in to your account with a default, read only access role. The default role doesn't have access to any content that's commonly stored in data stores, such as Amazon Simple Storage Service, Amazon Relational Database Service, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Redshift, and Amazon ElastiCache.
For a list of roles that AMS operations engineers and systems require to provide services in your account, see AMS customer account access IAM roles.
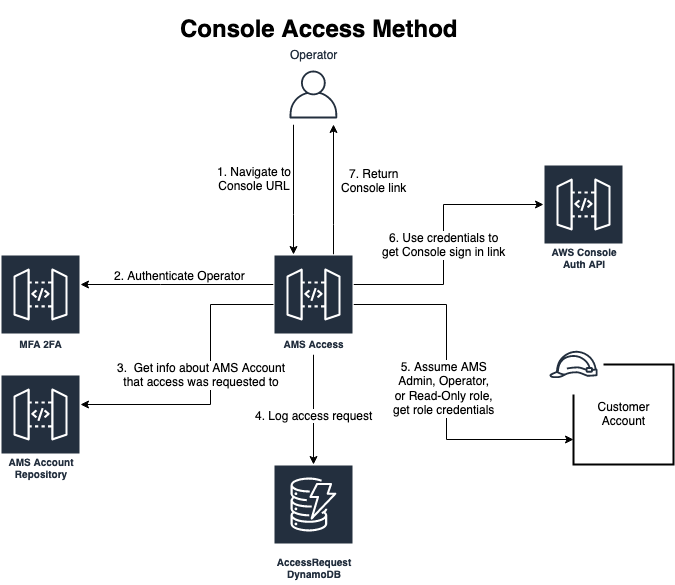
How does an AMS operations engineer access my account?
To access customer accounts, AMS operations engineers use an AWS internal AMS access service. This internal service is available only through a secure, private channel so that access to your accounts is secure and audited.
AMS operations engineers use the internal AMS access service authentication along with a two-factor authentication. And, operations engineer must provide a business justification (incident ticket or service request ID) that outlines the need to access your AWS account.
Based on the operation engineer’s authorization, the AMS access service provides the engineer with the appropriate role (Read-only/Operator/Admin) and login URL to your AWS console. Access to your account is short-lived and timebound.
To access Amazon EC2 instances, AMS operations engineers use the same internal AMS access service as the broker. After access is granted, AMS operations engineers use AWS Systems Manager Session Manager to access your instances with short-lived session credentials.
To provide RDP access for Windows instances, the operations engineer uses Amazon EC2 Systems Manager to create a local user on the instance and establish port forwarding to the instance. The operations engineer uses local user credentials for RDP access to the instance. The local user credentials are removed at the end of the session.
The following diagram outlines the process used by AMS operations engineers to access your account:
How do I track changes made by AMS in my AMS managed AWS accounts?
Account access
To help you track changes made by automation or by the AMS Accelerate operations team, AMS provides the Change record SQL interface in the Amazon Athena console and AMS Accelerate logs. These resources provide the following information:
Who accessed your account.
When the account was accessed.
What privileges were used to access your account.
What changes were made by AMS Accelerate in your account.
Why the changes were made in your account.
Resource configuration
View CloudTrail logs to track the configurations in your AWS resources for the past 90 days. If your configuration is older than 90 days, then access the logs in Amazon S3.
Instance logs
The Amazon CloudWatch Agent collects operating system logs. View the CloudWatch logs to see the login and other action logs that your operating system supports.
For more information, see Tracking changes in your AMS Accelerate accounts.
What are the process controls for AMS operations engineer access to my account?
Prior to joining AMS, operations engineers go through a criminal background check. Because AMS engineers manage customer infrastructure, they also have a mandatory annual background check. If an engineer fails the background check, then access is revoked.
All AMS operations engineers must complete mandatory security training, such as infrastructure security, data security, and incident response before they are granted access to resources.
How is privileged access managed?
A subset of users must complete additional training and maintain privileged access rights for elevated access. Access and usage is inspected and audited. AMS limits privileged access to exceptional circumstances or when least privilege access can't meet your request. Privileged access is also time bound.
Do AMS operations engineers use MFA?
Yes. All users must use MFA and Proof of Presence to provide services to you.
What happens to their access when an AMS employee leaves the organization or changes job roles?
Access to customer accounts and resources is provisioned through internal group membership. Membership is based on strict criteria including the specific job role, reporting manager, and employment status in AMS. If an operations engineer’s job family changes or their user ID is disabled, then access is revoked.
What access controls govern AMS operation engineer access to my accounts?
There are multiple layers of technical controls to enforce the “need to know” and “least privilege” principles for access to your environment. The following is a list of the access controls:
All operations engineers must be part of a specific internal AWS group to access customer accounts and resources. Group membership is strictly based on a need to know basis and automated with predefined criteria.
AMS practices “non-persistence” access to your environment. This means that access to your AWS accounts by AMS operations is "just-in-time" with short-lived credentials. Access to your accounts is provided only after an internal business case justification (service request, incident, change management request, and so on) is submitted and reviewed.
AMS follows the least privilege principle. So, authorized operations engineers assume Read-Only access by default. Write access is only used by engineers when changes to your environment are required due to an incident or a change request.
AMS uses standard, easily identifiable AWS Identity and Access Management roles that use the “ams” prefix to monitor and manage your accounts. All access is logged in AWS CloudTrail for you to audit.
AMS uses automated backend tooling to detect unauthorized changes to your account during the customer information validation phase of change executions.
How does AMS monitor root user access?
Root access always triggers the incident response process. AMS uses Amazon GuardDuty detection to monitor root user activity. If GuardDuty generates an alert, then AMS creates an event for further investigation. AMS notifies you if unexpected root account activity is detected, and the AMS Security team initiates an investigation.
How does AMS respond to security incidents?
AMS investigates security events that are generated from detection services such as Amazon GuardDuty, Amazon Macie, and from customer-reported security issues. AMS collaborates with your security response team to run the Security Incident Response (SIR) process. The AMS SIR process is based on the NIST SP 800-61 Rev. 2, Computer Security Incident Handling Guide
What industry standard certifications and frameworks does AMS adhere to?
Like other AWS services, AWS Managed Services is certified for OSPAR, HIPAA, HITRUST, GDPR, SOC*, ISO*, FedRAMP (Medium/High), IRAP, and PCI. For more information about the customer compliance certifications, regulations, and frameworks that AWS aligns with, see AWS Compliance
Security guardrails
AWS Managed Services uses multiple controls to protect your information assets and to help you keep your AWS infrastructure secure. AMS Accelerate maintains a library of AWS Config rules and remediation actions to help you make sure that your accounts comply with industry standards for security and operational integrity. AWS Config rules continuously track configuration changes on your recorded resources. If a change violates a rule's conditions, then AMS reports its findings to you. You can remediate violations automatically or by request, according to the severity of the violation.
AMS uses AWS Config rules to help meet the requirements of the following standards:
Center for Internet Security (CIS)
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cloud Security Framework (CSF)
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard (DSS)
For more information, see Security management in AMS Accelerate
How can I get access to the latest reports on security certification, frameworks, and compliance on AWS?
You can find current security and compliance reports for AWS services using the following methods:
You can use AWS Artifact
to download the latest report on an AWS service's security, availability, and confidentiality. For a list of most AWS services, including AWS Managed Services, that are compliant with global compliance frameworks, see https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/services-in-scope/
. For example, select PCI and search for AWS Managed Services. You can search for "AMS" to find AMS specific security artifacts from an AMS managed AWS account. AWS Managed Services is in scope for SOC 3
. The AWS SOC 2 (System and Organizations Controls) report is published to the AWS Artifact repository. This report evaluates the AWS controls that meet the criteria for security, availability, and confidentiality in the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) TSP section 100, Trust Services Criteria.
Does AMS share reference architecture diagrams of different aspects of AMS features?
To view AMS reference architecture, download the AWS Managed Services for Proactive Monitoring PDF.
How does AMS track who access my accounts and what the business need is for access?
To support service continuity and the security of your accounts, AMS accesses your account or instances only in response to proactive health or maintenance, health or security events, planned activity, or customer requests. Access to your accounts is authorized through AMS processes as outlined in the access model for AMS Accelerate. These authorization flows contain guardrails to prevent inadvertent or inappropriate access. As part of the access flow, AMS supplies the authorization system with a business need. This business need might be a work item associated with your account, such as a case that you opened with AMS. Or, the business need might be an authorized workflow, such as the Patching solution. All access requires a justification that is validated, verified, and authorized in real time by internal AMS systems based on business rules to align access requests with a business need.
AMS operations engineers aren't given a path to access your accounts without valid business needs. All account access and the associated business need are emitted to AWS CloudTrail entries inside your AWS accounts. This provides full transparency and the opportunity for you to perform your own audit and inspection. In addition to your inspection, AMS has automated inspections, and performs manual inspection as required, of access requests and performs audits of tooling and human access to review anomalous access.
Do AMS engineers have access to my data stored in an AWS data storage services, such as Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, and Amazon Redshift?
AMS engineers don't have access to customer content stored in AWS services that are commonly used for data storage. Access to AWS APIs used to read, write, modify, or delete data in these services is restricted by an explicit IAM deny policy associated with IAM roles used for AMS engineer access. In addition, internal AMS guardrails and automations prevent AMS operations engineers from removing or modifying the deny conditions.
Do AMS engineers have access to customer data that's stored in Amazon EBS, Amazon EFS and Amazon FSx?
AMS engineers can log into Amazon EC2 instances as an administrator. Administrator access is required for remediation in certain scenarios that include, but are not limited to, operating system (OS) issues and patch failures. AMS engineers typically access the system volume to remediate detected issues. However, access for AMS engineers isn't limited or restricted to the system volume.
How is access restricted or controlled for automation roles that have high privileges to my environments?
The ams-access-admin role is used exclusively by AMS automation. These automations deploy, manage, and maintain the required resources used by AMS to deploy into your environments for telemetry, health, and security data collection to perform operational functions. AMS engineers can't assume automation roles and are restricted by role mapping in internal systems. At runtime, AMS dynamically applies a scoped down least privilege session policy to every automation. This session policy limits the capability and permissions of the automation.
How does AMS implement the principle of least privilege as advocated in the AWS Well-Architected Framework for automation roles?
At runtime, AMS applies a scoped down, least privilege session policy to every automation. This scoped down session policy limits the capability and permissions of the automation. Session policies that have permissions to create IAM resources also have a requirement to attach a permission boundary. This permission boundary reduces privilege escalation risk. Every team onboards a session policy that's used only by that team.
What logging and monitoring systems are used to detect unauthorized access attempts or suspicious activities involving automation roles?
AWS maintains centralized repositories that provide core log archival functionality for internal use by AWS service teams. These logs are stored in Amazon S3 for high scalability, durability, and availability. AWS service teams can then collect, archive, and view service logs in a central log service.
Production hosts at AWS are deployed using master baseline images. The baseline images are equipped with a standard set of configurations and functions that include logging and monitoring for security purposes. These logs are stored and accessible by AWS security teams for root cause analysis in the event of a suspected security incident.
Logs for a given host are available to the team that owns that host. Teams can search their logs for operational and security analysis.
How are security incidents or breaches concerning the automation infrastructure handled, and what protocols help with swift response and mitigation?
AWS contingency plans and incident response playbooks have defined and tested tools and processes to detect, mitigate, investigate, and assess security incidents. These plans and playbooks include guidelines for responding to potential data breaches in accordance with contractual and regulatory requirements.
Are regular security assessments, vulnerability scans, and penetration tests conducted on the automation infrastructure?
AWS Security performs regular vulnerability scans on the host operating systems, web applications, and databases in the AWS environment using a variety of tools. AWS Security teams also subscribe to news feeds for applicable vendor flaws and proactively monitor vendors’ websites and other relevant outlets for new patches.
How is access to the automation infrastructure restricted to authorized personnel only?
Access to AWS systems are allocated based on least privilege and approved by an authorized individual. Duties and areas of responsibility (for example, access request and approval, change management request and approval, change development, testing and deployment, and so on) are segregated across different individuals to reduce unauthorized or unintentional modification or misuse of AWS systems. Group or shared accounts aren't permitted within the system boundary.
What measures are implemented to uphold security standards and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches in the automation pipeline?
Access to resources, including services, hosts, network devices, and Windows and UNIX groups, is approved in the AWS proprietary permission management system by the appropriate owner or manager. The permissions management tool log captures requests for access changes. Job function changes automatically revoke the employee's access to resources. Continued access for that employee must be requested and approved.
AWS requires two-factor authentication over an approved cryptographic channel for authentication to the internal AWS network from remote locations. Firewall devices restrict access to the computing environment, enforce computing clusters' boundaries, and restrict access to production networks.
Processes are implemented to protect audit information and audit tools from unauthorized access, modification, and deletion. Audit records contain a set of data elements in order to support necessary analysis requirements. In addition, audit records are available to authorized users for inspection or analysis on demand, and in response to security-related or business-impacting events.
User access rights to AWS systems (for example, network, applications, tools, etc.) is revoked within 24 hours of termination or deactivation. Inactive user accounts are disabled and/or removed at least every 90 days.
Is anomaly detection or monitoring turned on for access or audit logging to detect privilege escalation or access misuse to proactively alert the AMS team?
Production hosts at AWS are equipped with logging for security purposes. This service logs human actions on hosts, including log ons, failed log on attempts, and log offs. These logs are stored and accessible by AWS security teams for root cause analysis in the event of a suspected security incident. Logs for a given host are also available to the team that owns that host. A front end log analysis tool is available to service teams to search their logs for operational and security analysis. Processes are implemented to help protect logs and audit tools from unauthorized access, modification, and deletion. The AWS Security team performs log analysis to identify events based on defined risk management parameters.
What types of customer data is extracted from AMS managed accounts, and how is this utilized and stored?
AMS does not access or use your content for any purpose. AMS defines customer content as software (including machine images), data, text, audio, video, or images that a customer or any end user transfers to AWS for processing, storage, or hosting by AWS services in connection with a customer's account, and any computational results that a customer or their end user derives from the foregoing through their use of AWS services.