Tag your Amazon EC2 resources
To help you manage your instances, images, and other Amazon EC2 resources, you can assign your own metadata to each resource in the form of tags. Tags enable you to categorize your AWS resources in different ways, for example, by purpose, owner, or environment. This is useful when you have many resources of the same type—you can quickly identify a specific resource based on the tags that you've assigned to it. This topic describes tags and shows you how to create them.
Warning
Tag keys and their values are returned by many different API calls. Denying access to
DescribeTags doesn’t automatically deny access to tags returned by
other APIs. As a best practice, we recommend that you do not include sensitive data in
your tags.
Contents
Tag basics
A tag is a label that you assign to an AWS resource. Each tag consists of a key and an optional value, both of which you define.
Tags enable you to categorize your AWS resources in different ways, for example, by purpose, owner, or environment. For example, you could define a set of tags for your account's Amazon EC2 instances that helps you track each instance's owner and stack level.
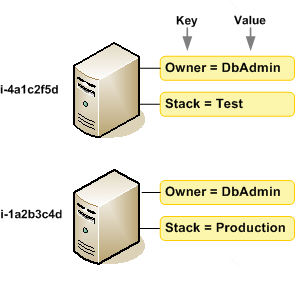
The following diagram illustrates how tagging works. In this example, you've assigned two
tags to each of your instances—one tag with the key Owner and
another with the key Stack. Each tag also has an associated value.
We recommend that you devise a set of tag keys that meets your needs for each resource type. Using a consistent set of tag keys makes it easier for you to manage your resources. You can search and filter the resources based on the tags you add. For more information about how to implement an effective resource tagging strategy, see the Tagging Best Practices AWS Whitepaper.
Tags don't have any semantic meaning to Amazon EC2 and are interpreted strictly as a string of characters. Also, tags are not automatically assigned to your resources. You can edit tag keys and values, and you can remove tags from a resource at any time. You can set the value of a tag to an empty string, but you can't set the value of a tag to null. If you add a tag that has the same key as an existing tag on that resource, the new value overwrites the old value. If you delete a resource, any tags for the resource are also deleted.
Note
After you delete a resource, its tags might remain visible in the console, API, and CLI output for a short period. These tags will be gradually disassociated from the resource and be permanently deleted.
Tag your resources
When you use the Amazon EC2 console, you can apply tags to resources by using the
Tags tab on the relevant resource screen, or you can use the
Tags Editor in the AWS Resource Groups console. Some resource screens
enable you to specify tags for a resource when you create the resource; for example, a
tag with a key of Name and a value that you specify. In most cases, the
console applies the tags immediately after the resource is created (rather than during
resource creation). The console might organize resources according to the
Name tag, but this tag doesn't have any semantic meaning to the Amazon EC2
service.
If you're using the Amazon EC2 API, the AWS CLI, or an AWS SDK, you can use the
CreateTags EC2 API action to apply tags to existing resources.
Additionally, some resource-creating actions enable you to specify tags for a resource
when the resource is created. If tags cannot be applied during resource creation, we
roll back the resource creation process. This ensures that resources are either created
with tags or not created at all, and that no resources are left untagged at any time. By
tagging resources at the time of creation, you can eliminate the need to run custom
tagging scripts after resource creation. For more information about enabling users to tag
resources on creation, see Grant permission to tag Amazon EC2 resources during creation.
You can apply tag-based resource-level permissions in your IAM policies to the Amazon EC2 API actions that support tagging on creation to implement granular control over the users and groups that can tag resources on creation. Your resources are properly secured from creation—tags are applied immediately to your resources, therefore any tag-based resource-level permissions controlling the use of resources are immediately effective. Your resources can be tracked and reported on more accurately. You can enforce the use of tagging on new resources, and control which tag keys and values are set on your resources.
You can also apply resource-level permissions to the CreateTags and
DeleteTags Amazon EC2 API actions in your IAM policies to control which
tag keys and values are set on your existing resources. For more information, see Example: Tag resources.
For more information about tagging your resources for billing, see Using cost allocation tags in the AWS Billing User Guide.
Tag restrictions
The following basic restrictions apply to tags:
-
Maximum number of tags per resource – 50
-
For each resource, each tag key must be unique, and each tag key can have only one value.
-
Maximum key length – 128 Unicode characters in UTF-8
-
Maximum value length – 256 Unicode characters in UTF-8
-
Allowed characters
-
Although EC2 allows for any character in its tags, other AWS services are more restrictive. The allowed characters across all AWS services are: letters (
a-z,A-Z), numbers (0-9), and spaces representable in UTF-8, and the following characters:+ - = . _ : / @. -
If you enable instance tags in instance metadata, instance tag keys can only use letters (
a-z,A-Z), numbers (0-9), and the following characters:+ - = . , _ : @. Instance tag keys can't contain spaces or/, and can't comprise only.(one period),..(two periods), or_index. For more information, see View tags for your EC2 instances using instance metadata.
-
-
Tag keys and values are case-sensitive.
-
The
aws:prefix is reserved for AWS use. If a tag has a tag key with this prefix, then you can't edit or delete the tag's key or value. Tags with theaws:prefix do not count against your tags per resource limit.
You can't terminate, stop, or delete a resource based solely on its tags; you must specify
the resource identifier. For example, to delete snapshots that you tagged with a tag key
called DeleteMe, you must use the DeleteSnapshots action with
the resource identifiers of the snapshots, such as snap-1234567890abcdef0.
When you tag public or shared resources, the tags you assign are available only to your AWS account; no other AWS account will have access to those tags. For tag-based access control to shared resources, each AWS account must assign its own set of tags to control access to the resource.
Tags and access management
If you're using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), you can control which users in your AWS account have permission to create, edit, or delete tags. For more information, see Grant permission to tag Amazon EC2 resources during creation.
You can also use resource tags to implement attribute-based control (ABAC). You can create IAM policies that allow operations based on the tags for the resource. For more information, see Control access using attribute-based access.
Tag your resources for billing
You can use tags to organize your AWS bill to reflect your own cost structure. To do this, sign up to get your AWS account bill with tag key values included. For more information about setting up a cost allocation report with tags, see Monthly cost allocation report in the AWS Billing User Guide. To see the cost of your combined resources, you can organize your billing information based on resources that have the same tag key values. For example, you can tag several resources with a specific application name, and then organize your billing information to see the total cost of that application across several services. For more information, see Using cost allocation tags in the AWS Billing User Guide.
Note
If you've just enabled reporting, data for the current month is available for viewing after 24 hours.
Cost allocation tags can indicate which resources are contributing to costs, but deleting or deactivating resources doesn't always reduce costs. For example, snapshot data that is referenced by another snapshot is preserved, even if the snapshot that contains the original data is deleted. For more information, see Amazon Elastic Block Store volumes and snapshots in the AWS Billing User Guide.
Note
Elastic IP addresses that are tagged do not appear on your cost allocation report.