How Amazon QuickSight works
Using Amazon QuickSight, you can access data and prepare it for use in reporting. It saves your prepared data either in SPICE memory or as a direct query. You can use a variety of data sources for analysis. When you create an analysis, the typical workflow looks the following illustration:
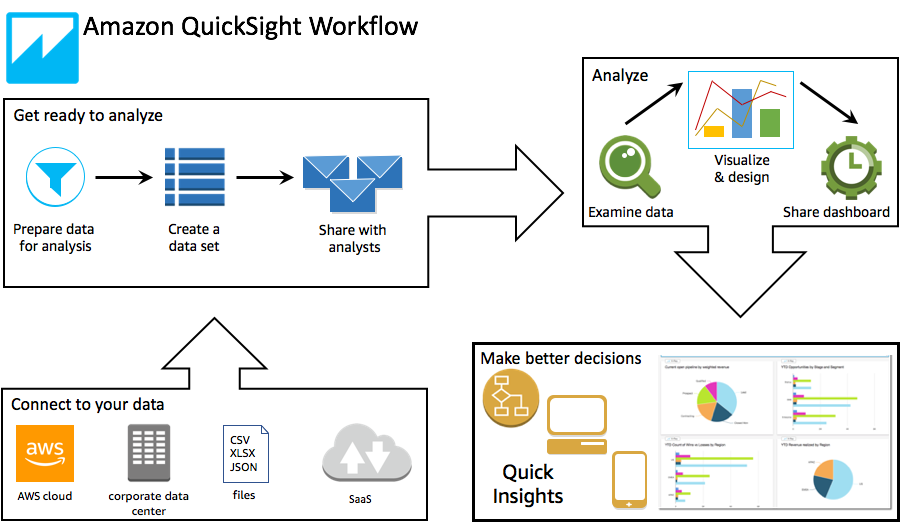
-
Create a new analysis.
-
Add new or existing datasets.
-
Choose fields to create the first chart. QuickSight automatically suggests the best visualization.
-
Add more charts, tables, or insights to the analysis. Resize and rearrange them on one or more sheets. Use extended features to add variables, custom controls, colors, additional pages (called sheets), and more.
-
Publish the analysis as a dashboard to share it with other people.
Topics
Sample data
To get a first look at how QuickSight works, you can explore Amazon QuickSight using the following sample data:
-
Business overview data (revenue)
-
People overview data (human resources)
-
Web and social media analytics data (marketing)
Also, a variety of datasets are available free online that you can use with Amazon QuickSight, for
example the AWS public
datasets